This document describes different types of graphs:
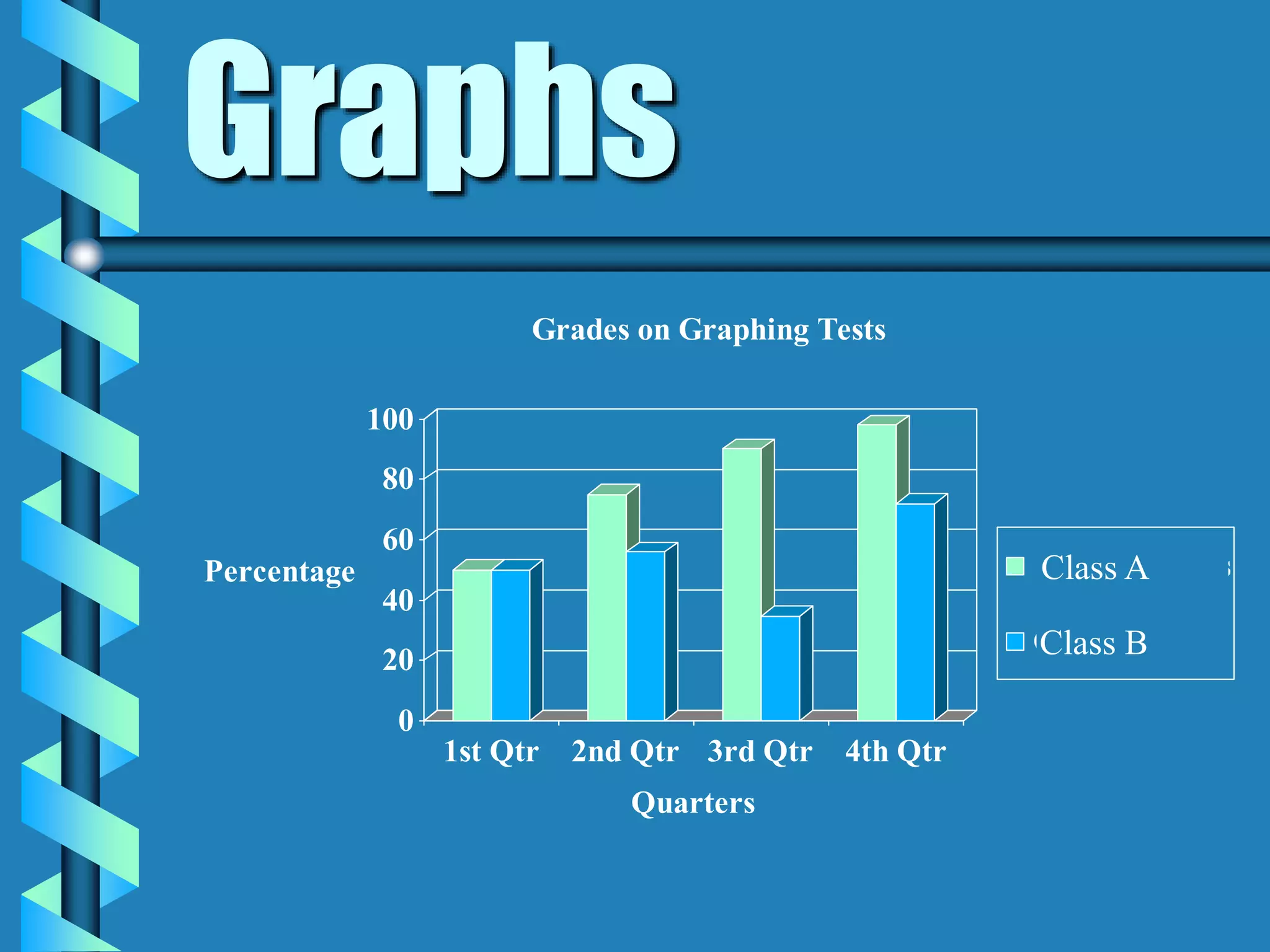
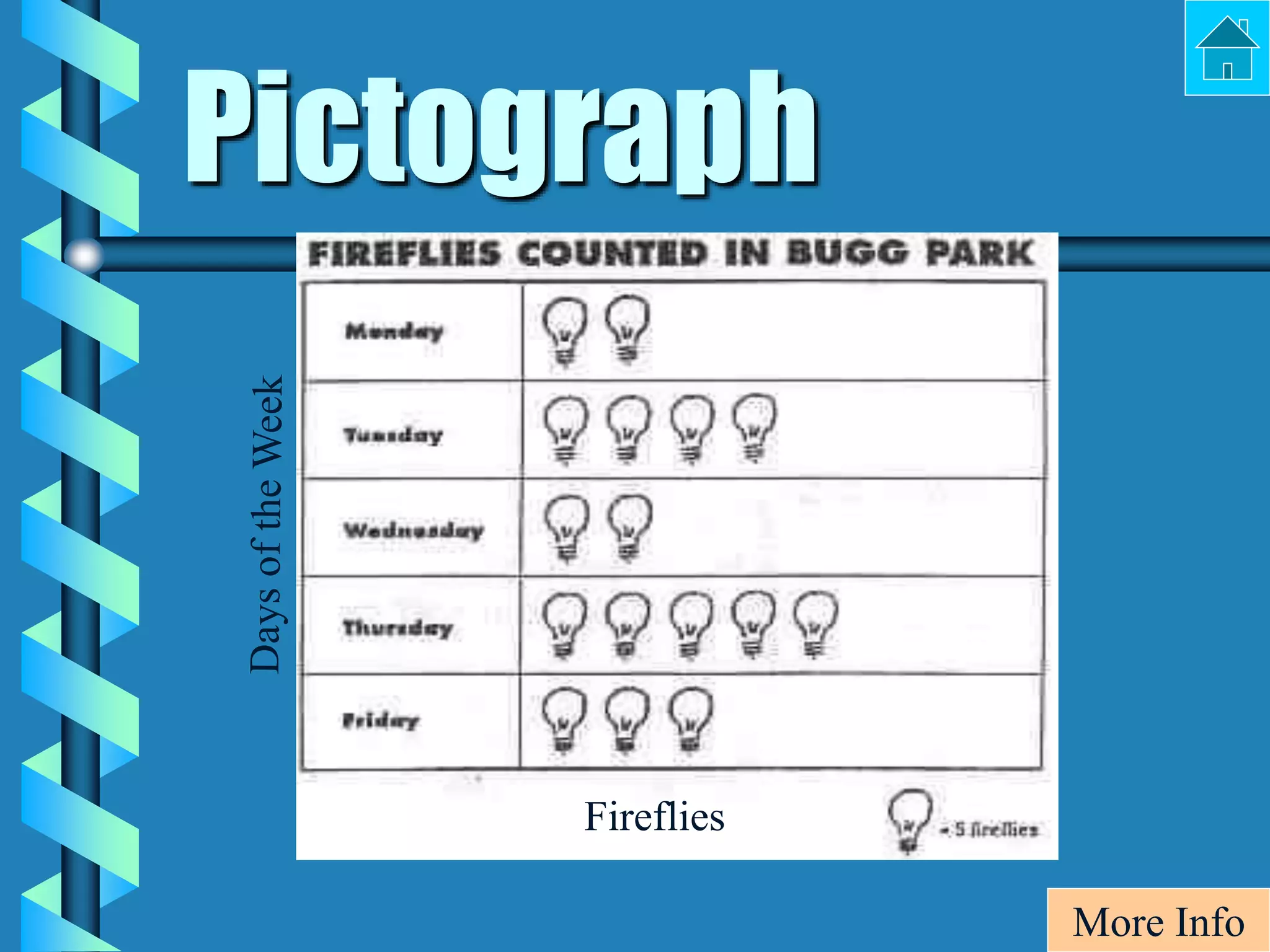
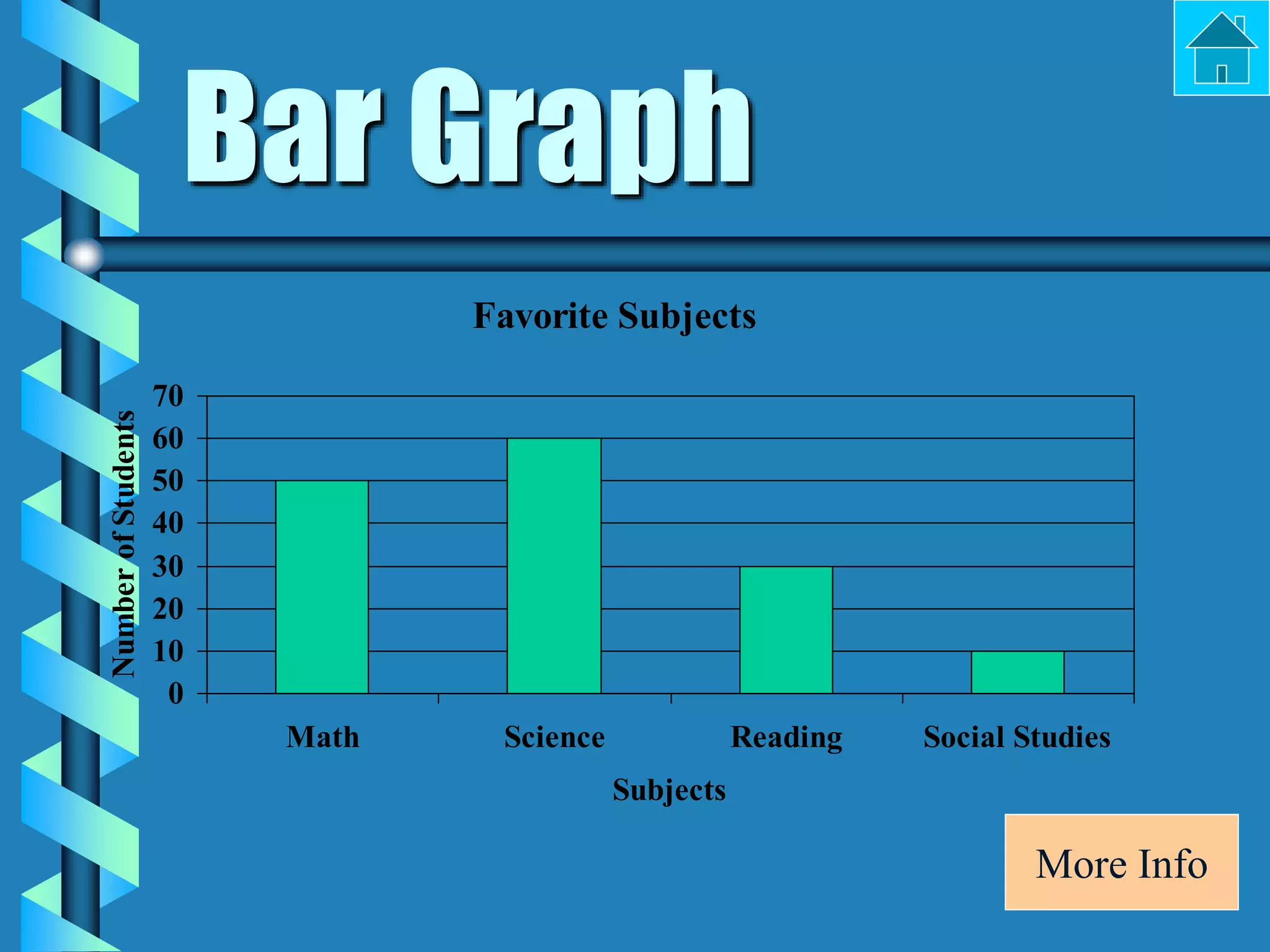
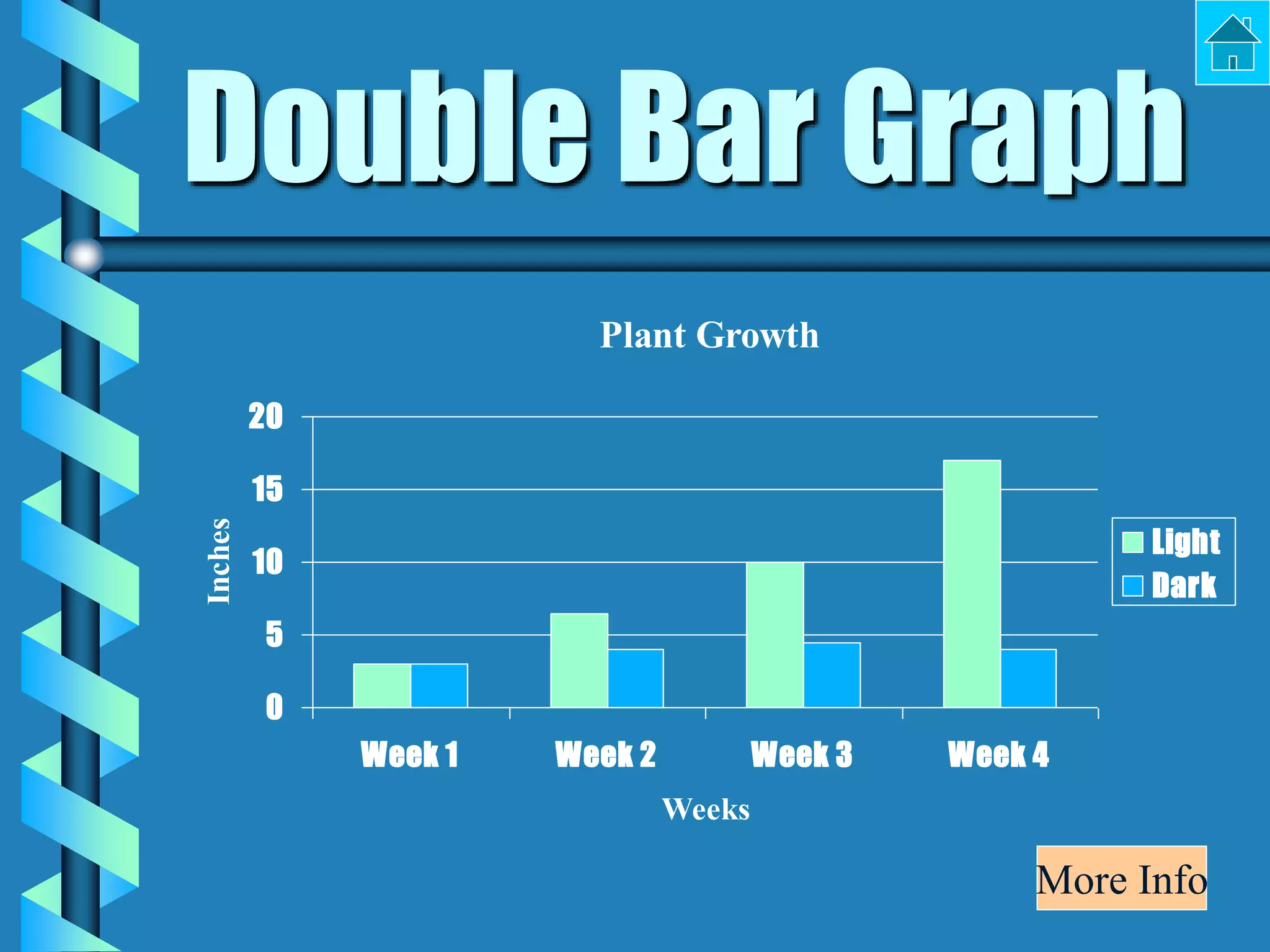
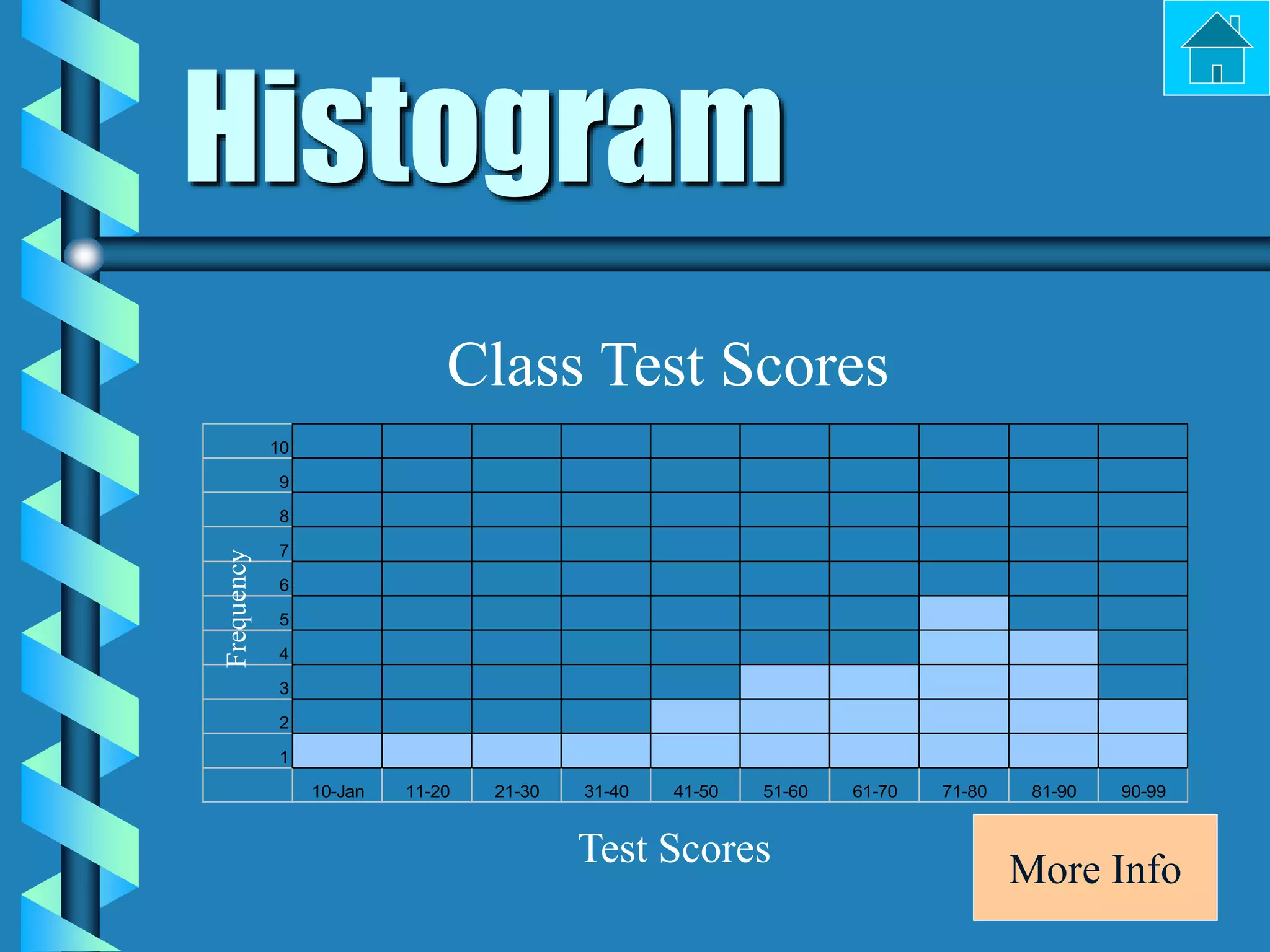
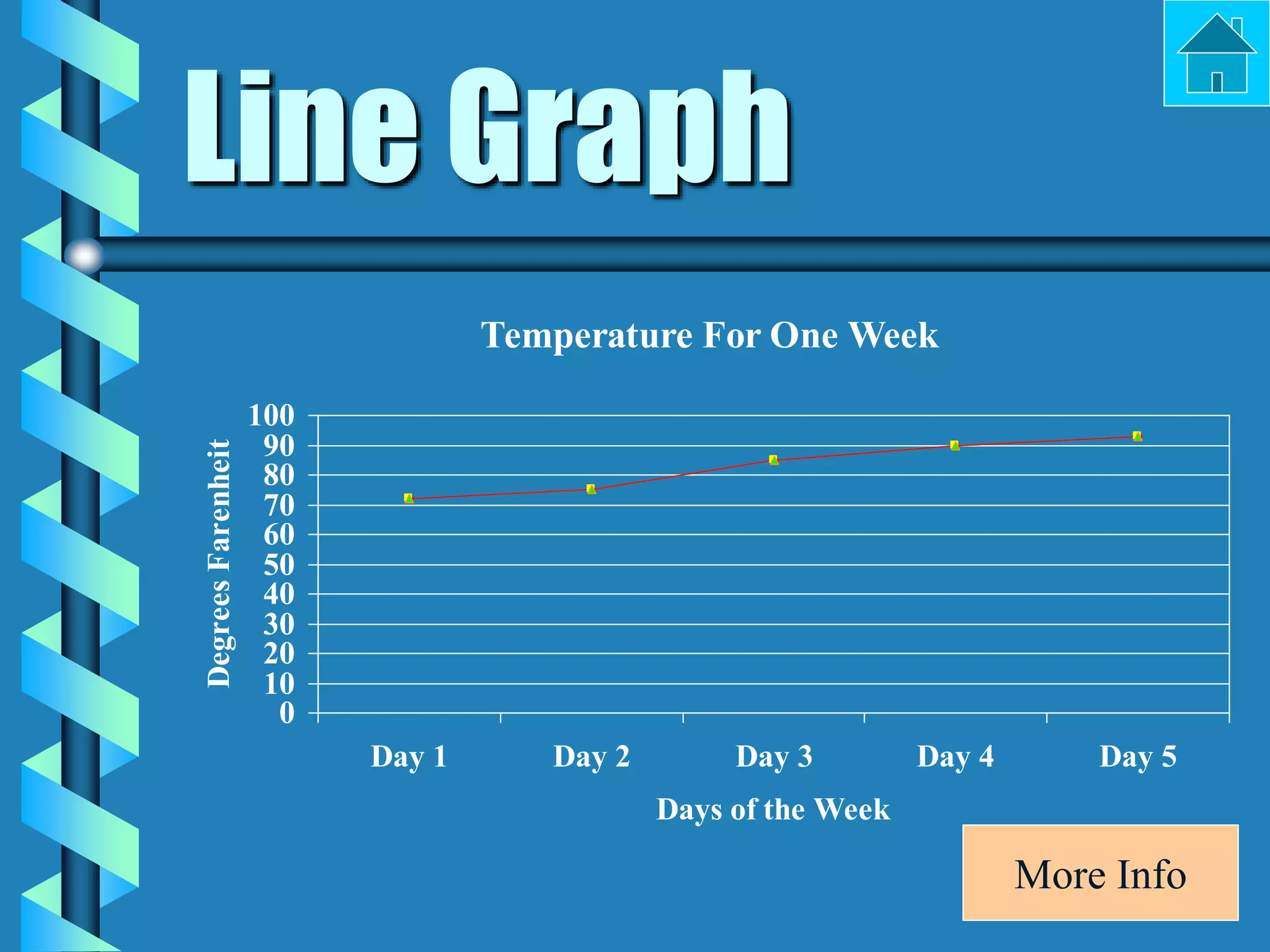
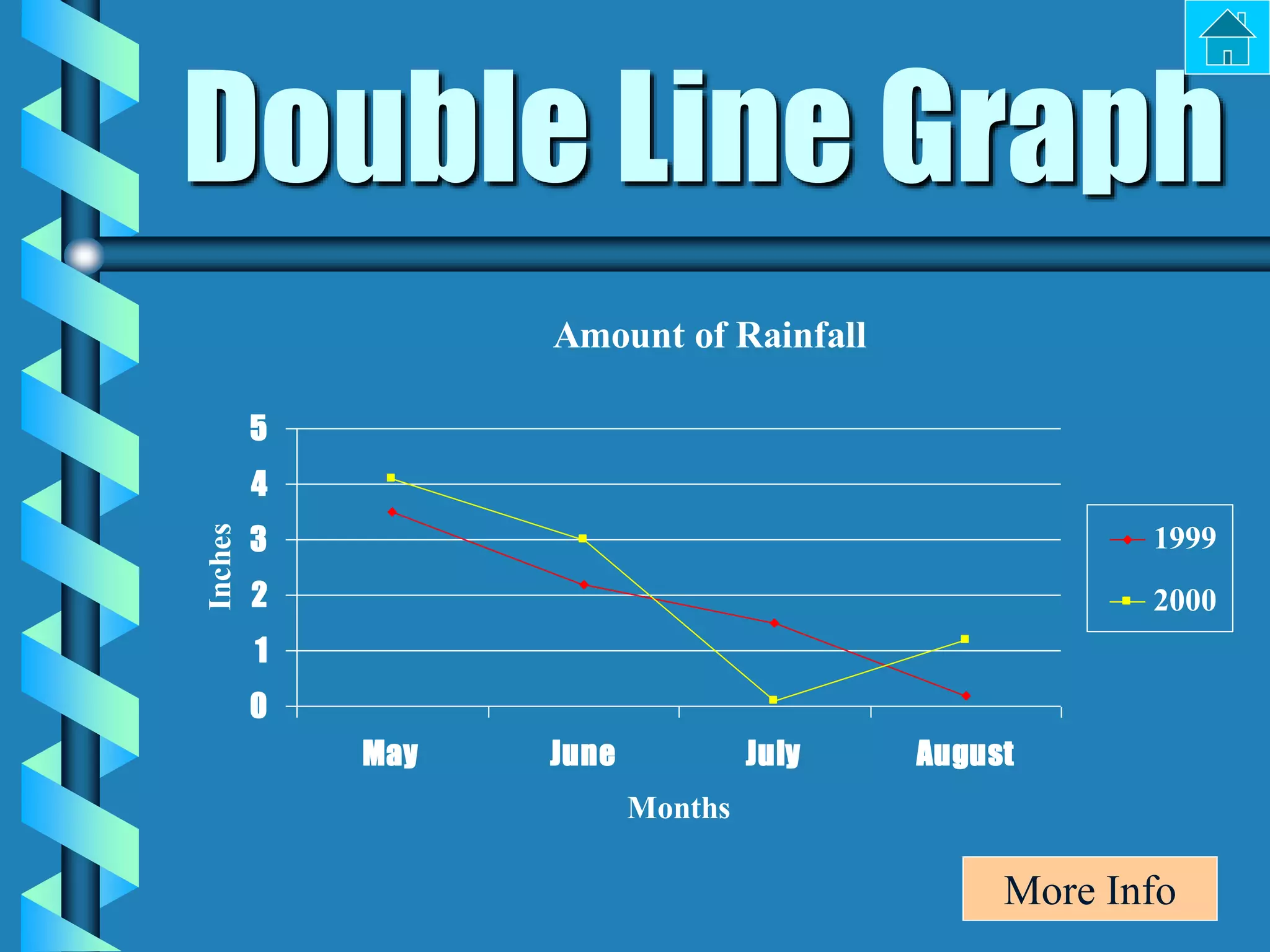
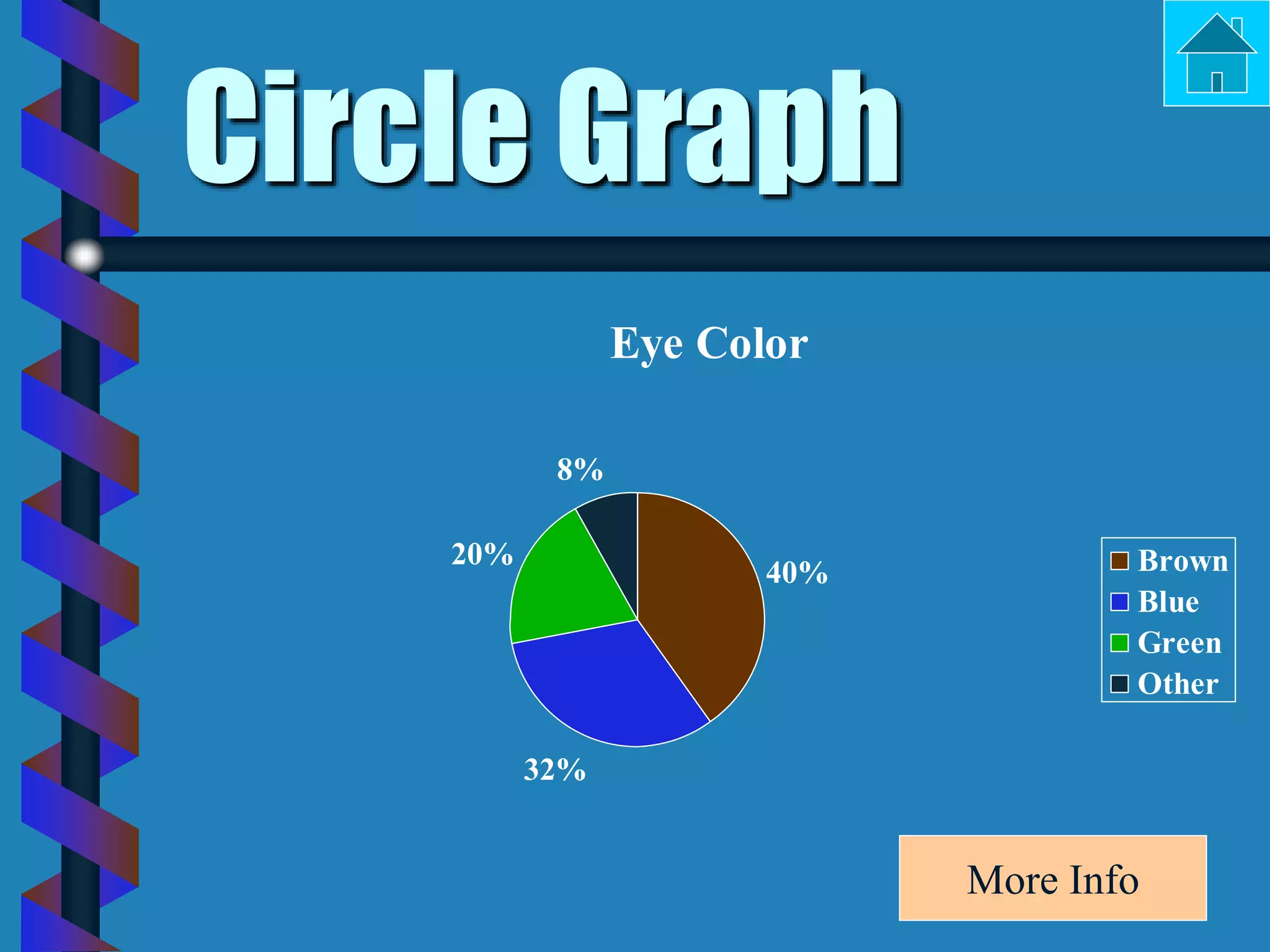
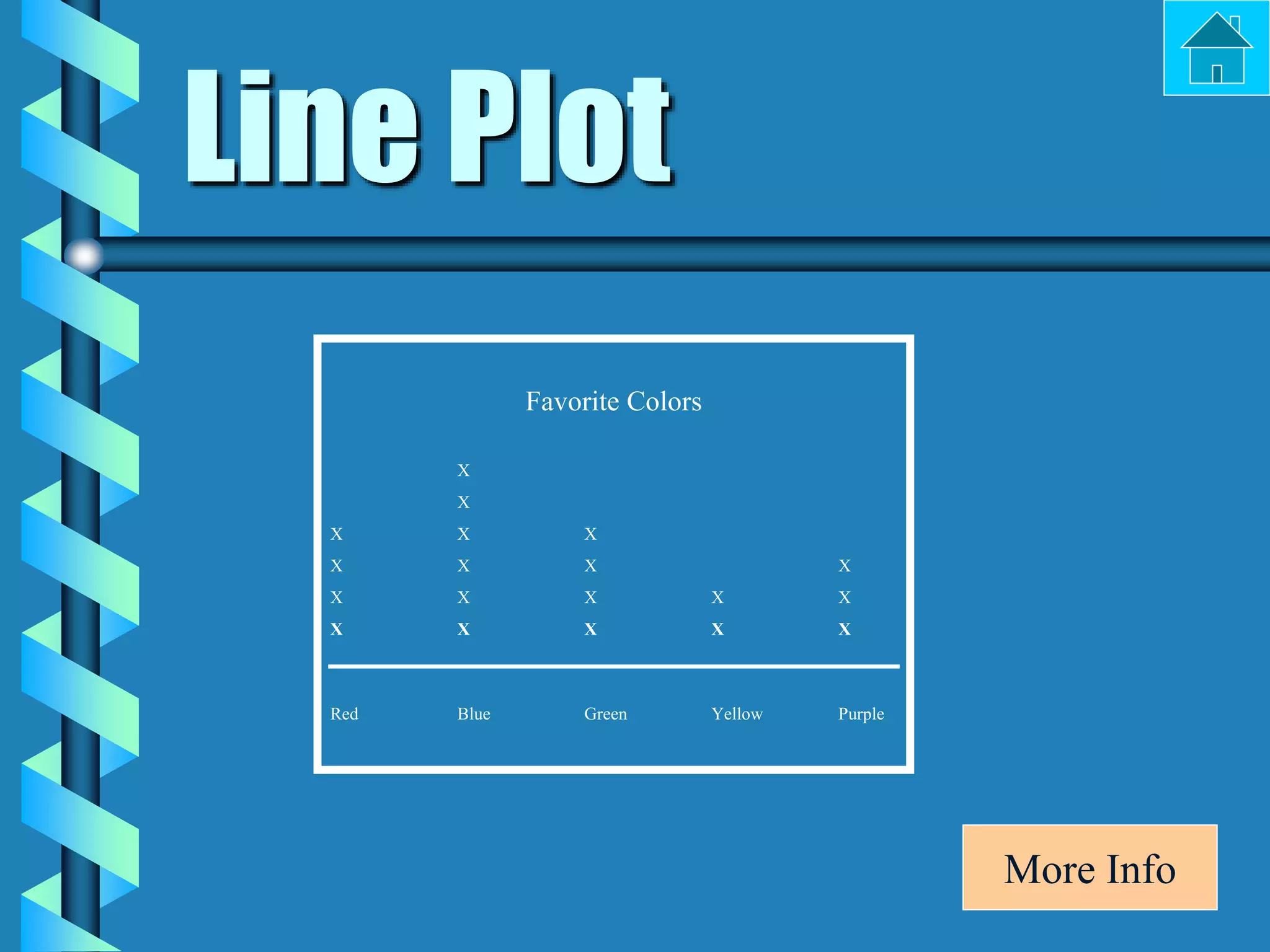
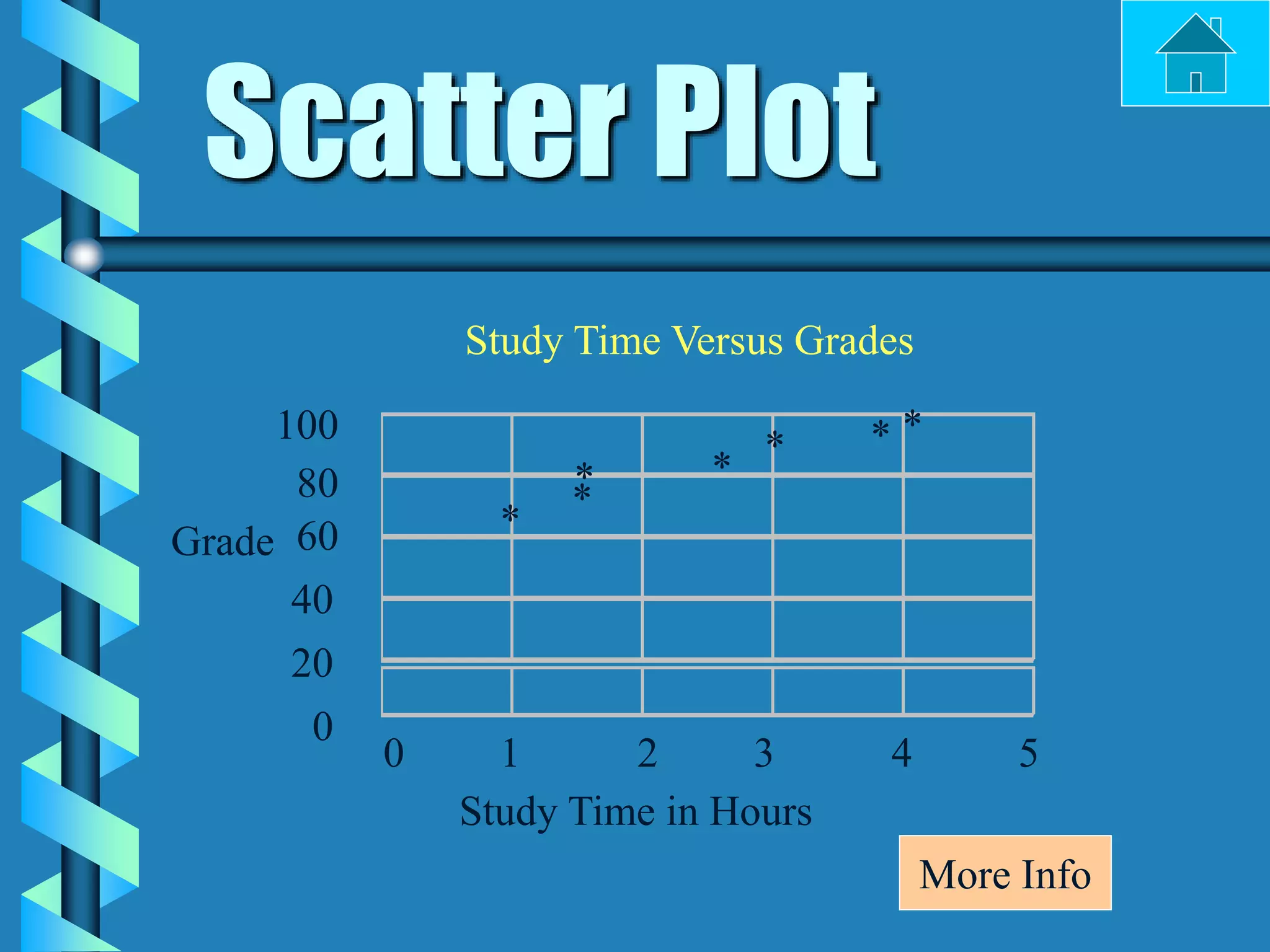
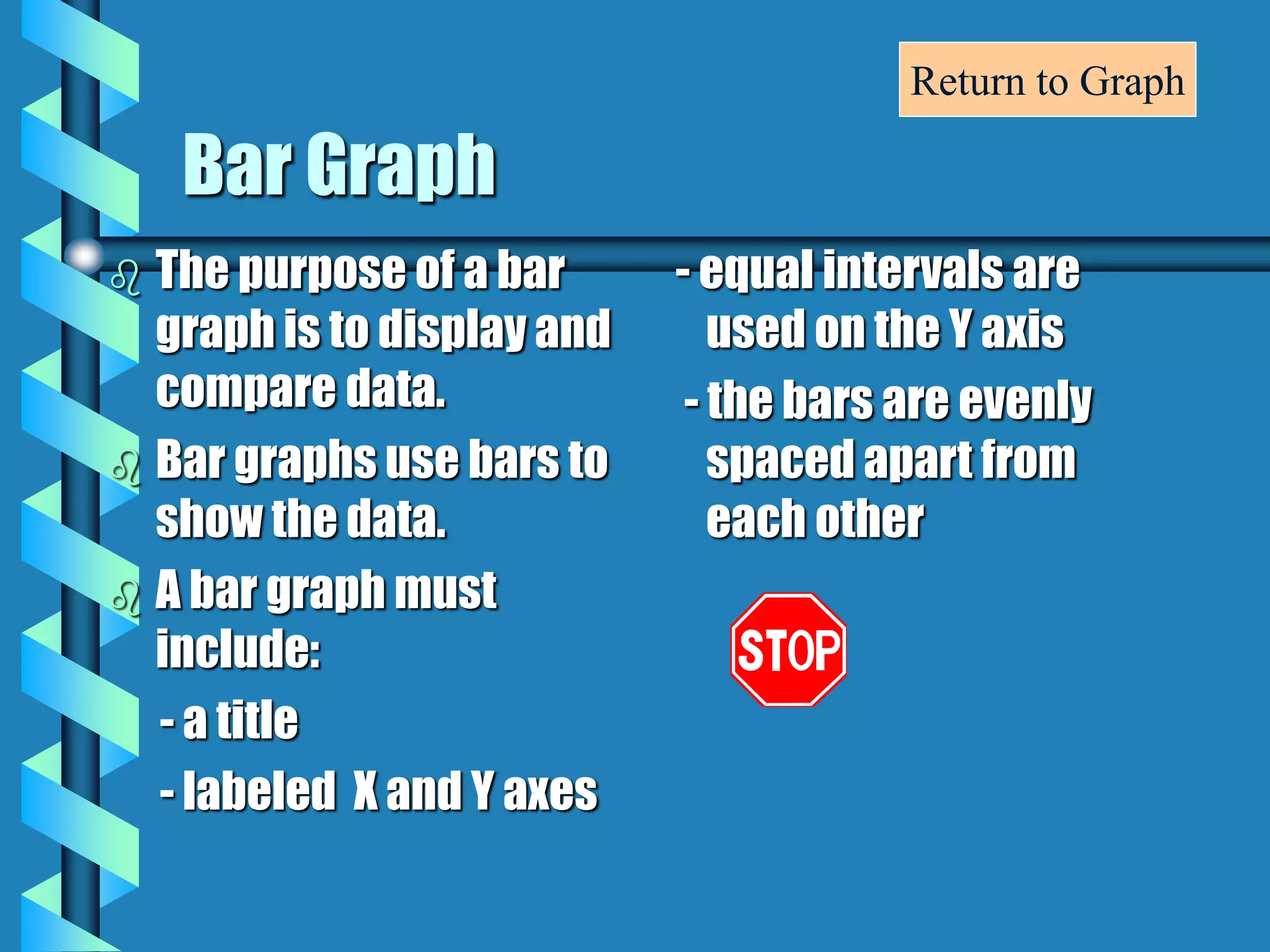
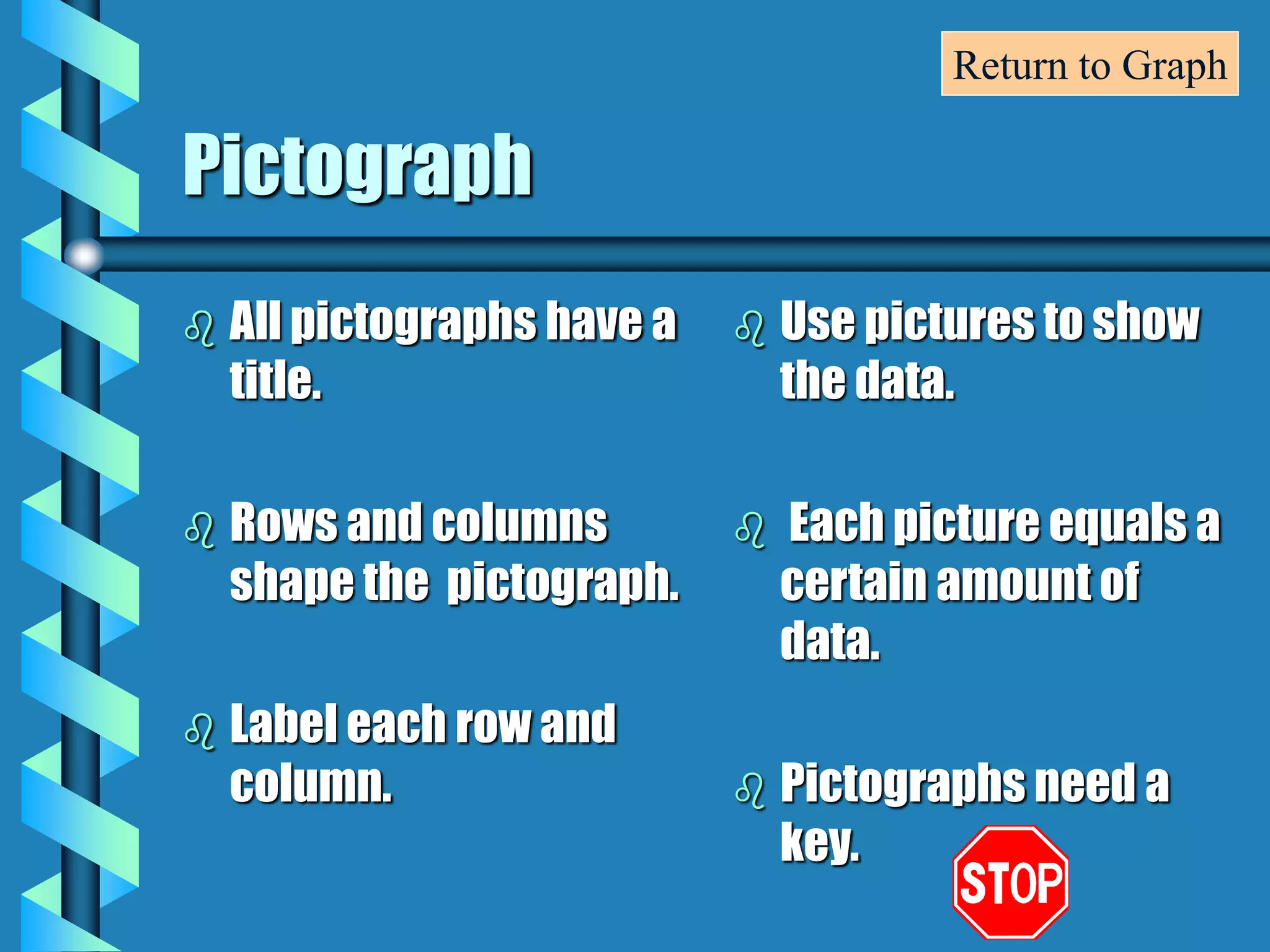
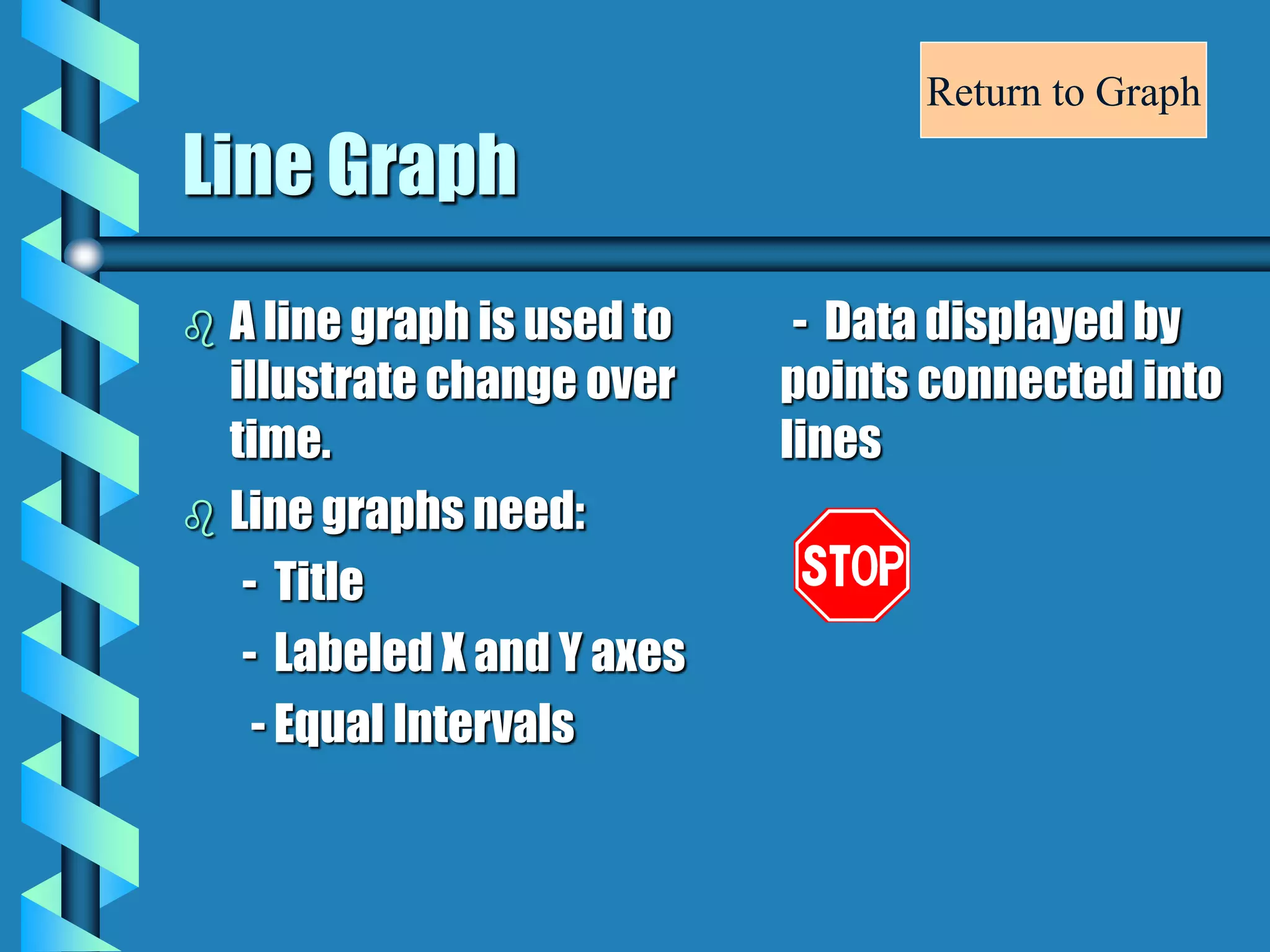
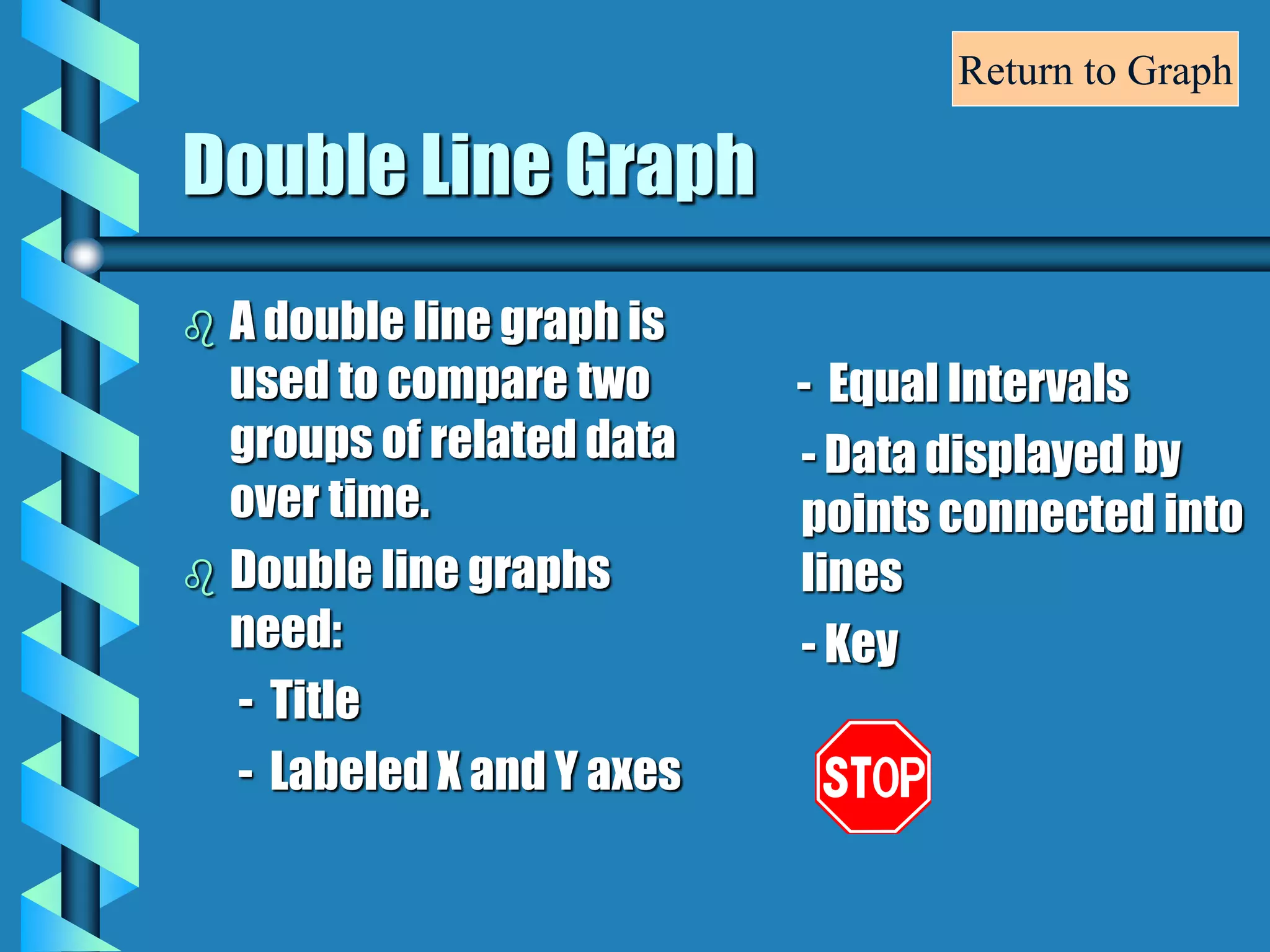
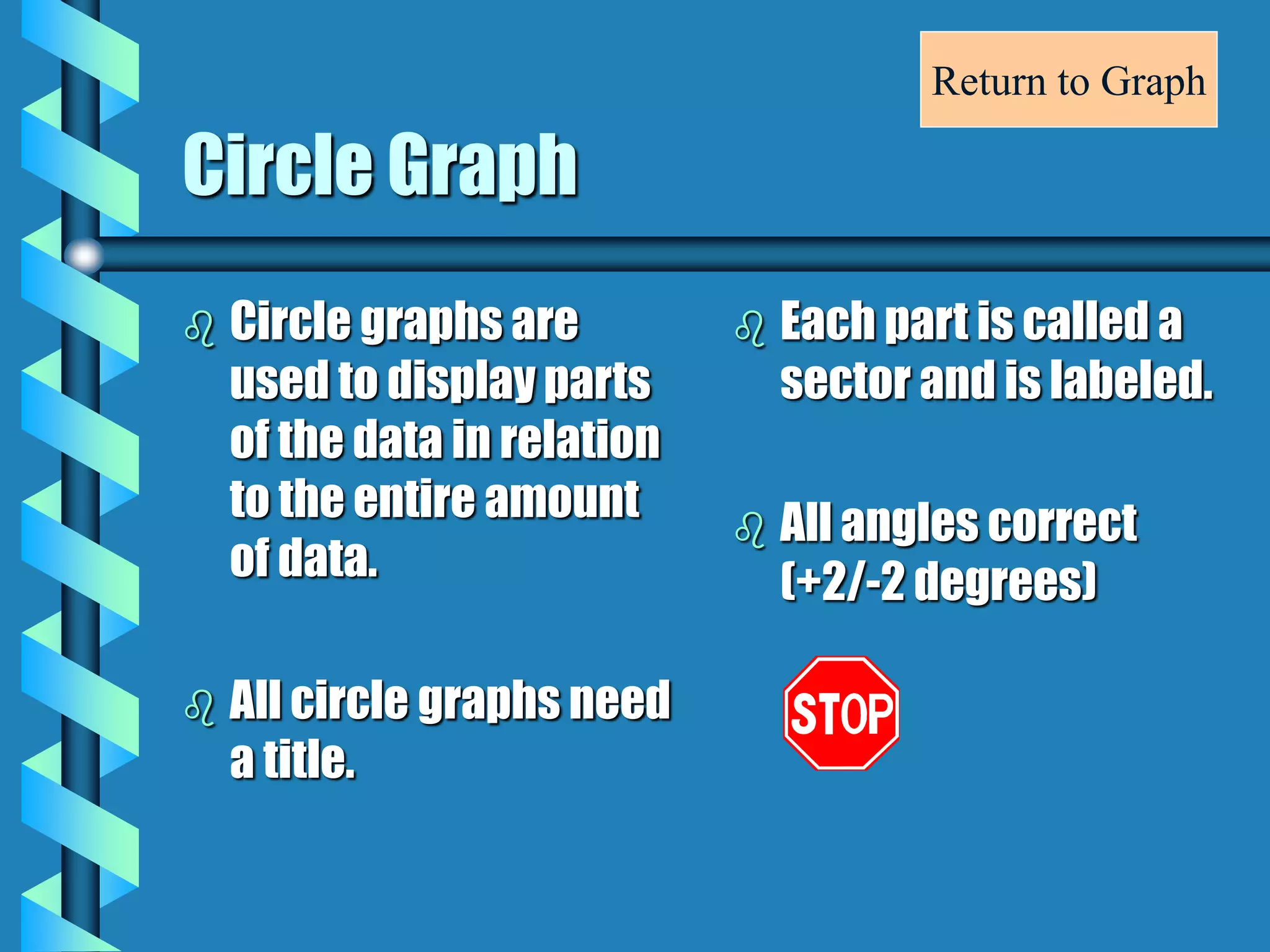
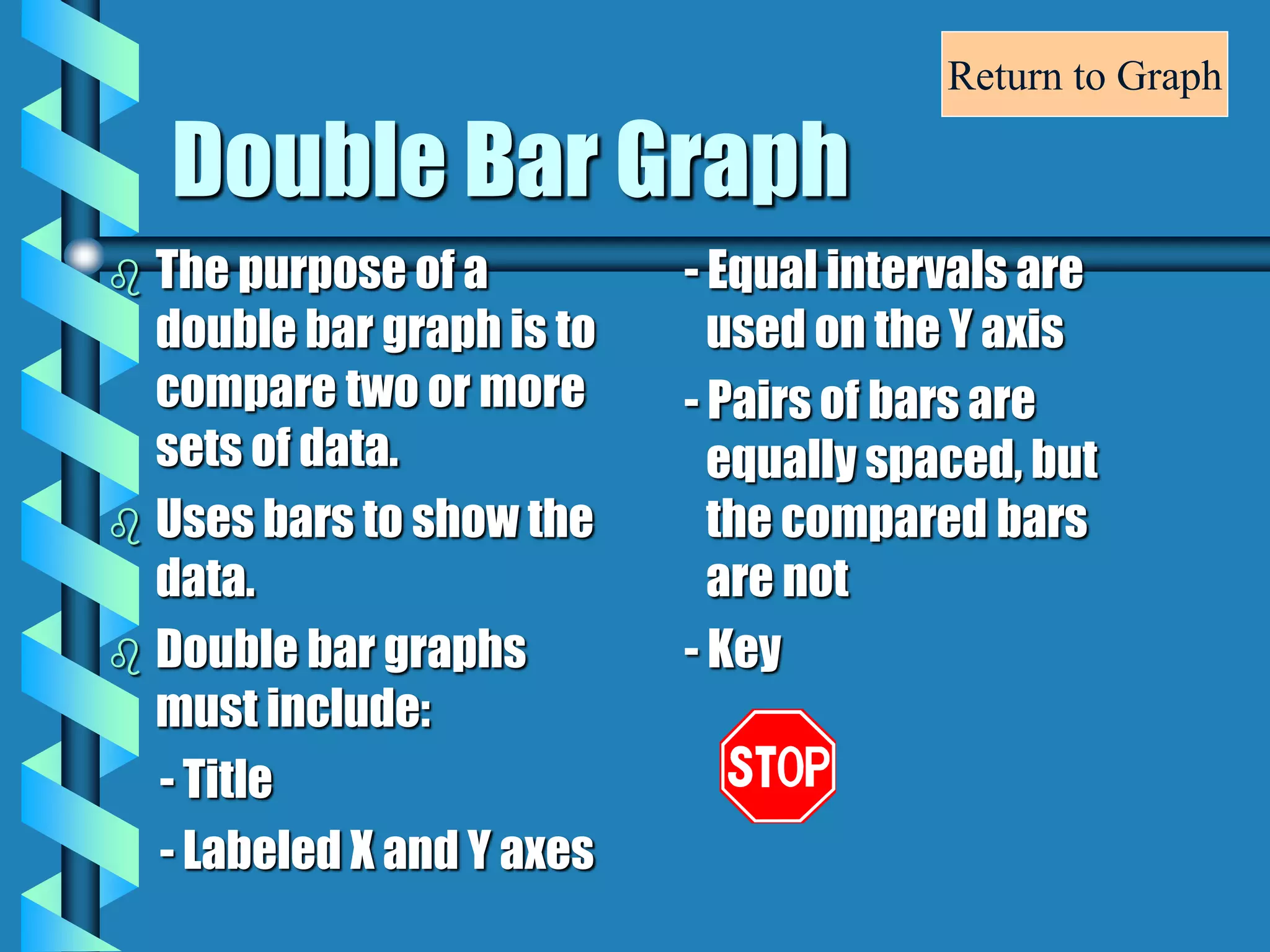
- Bar graphs, pictographs, line graphs, double line graphs, circle graphs, double bar graphs, line plots, histograms, and scatter plots.
- Each graph type has a specific purpose and structure. For example, bar graphs compare data using bars, line graphs show change over time with connected points, and scatter plots show the relationship between two variables.
- Key elements are described for each graph, such as titles, labeled axes, equal intervals, data points, and keys for additional information.