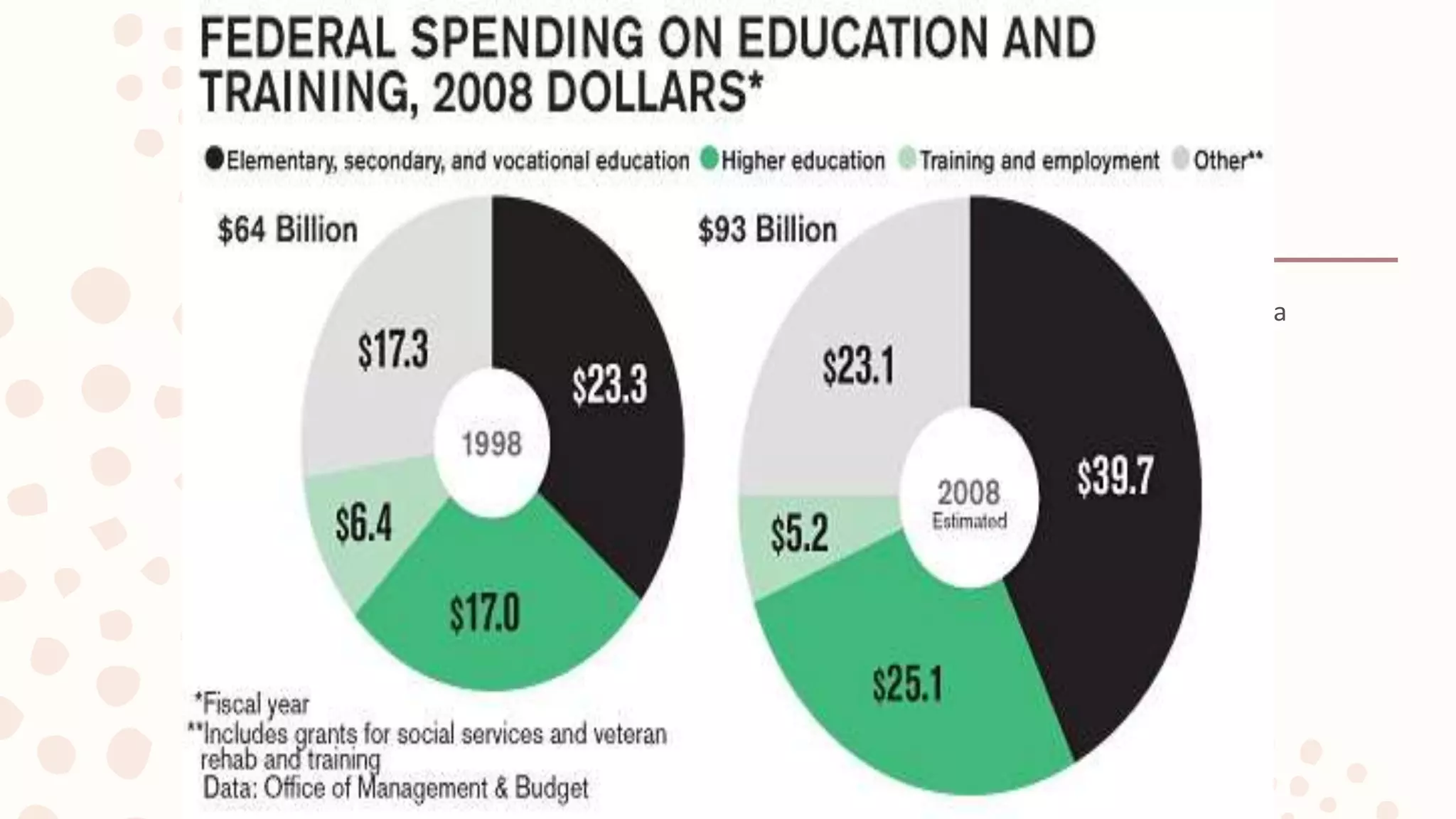
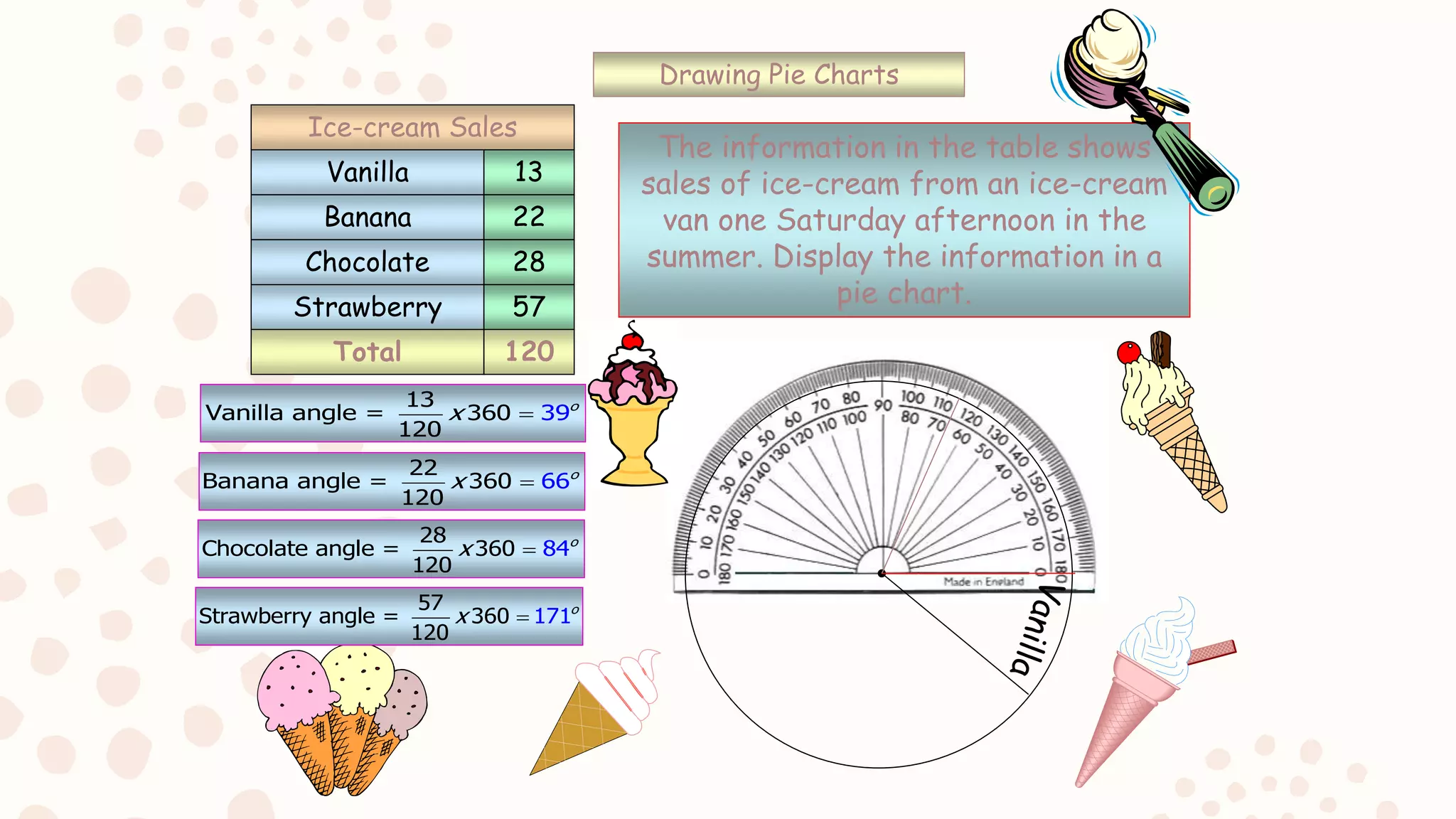
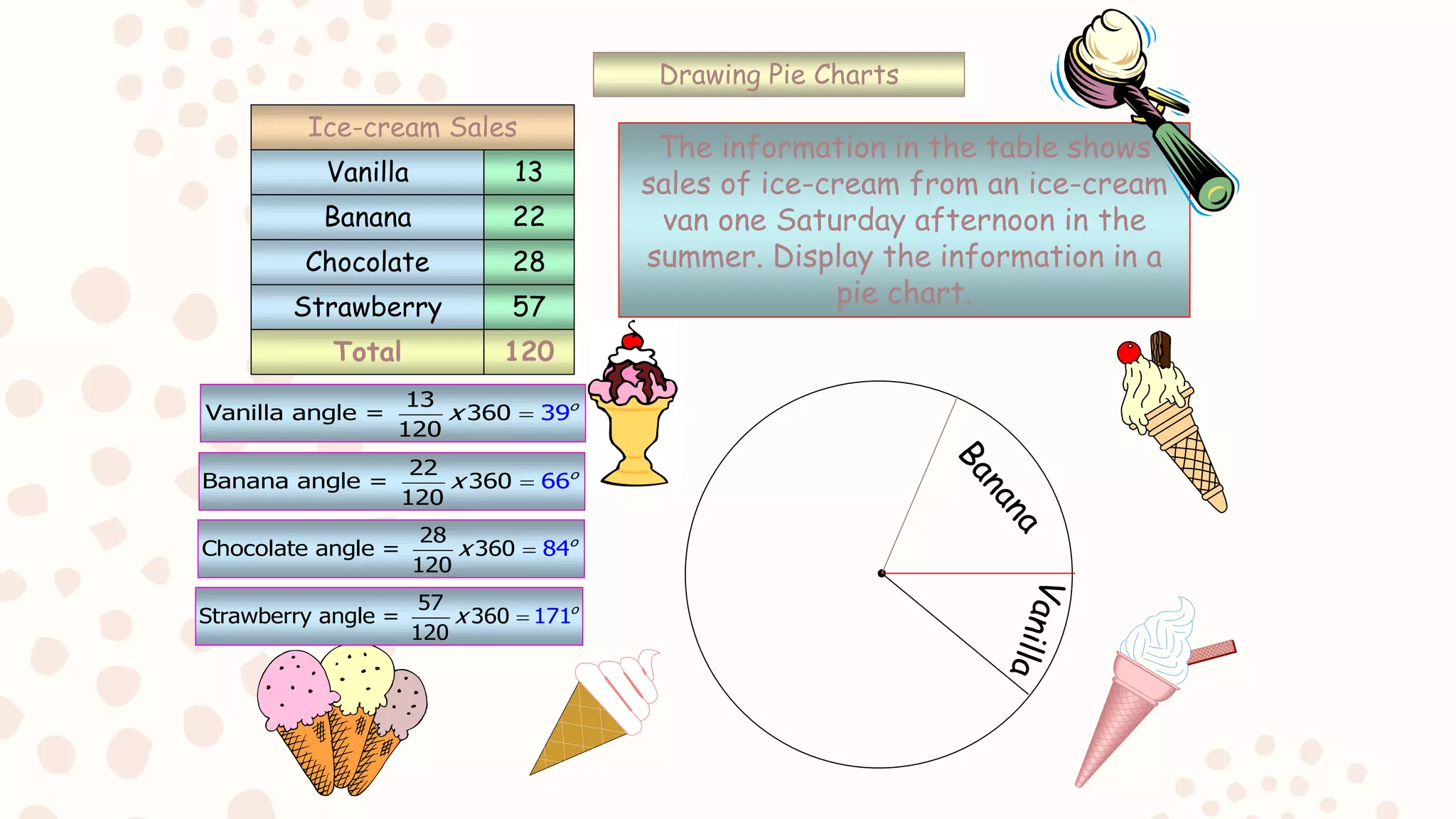
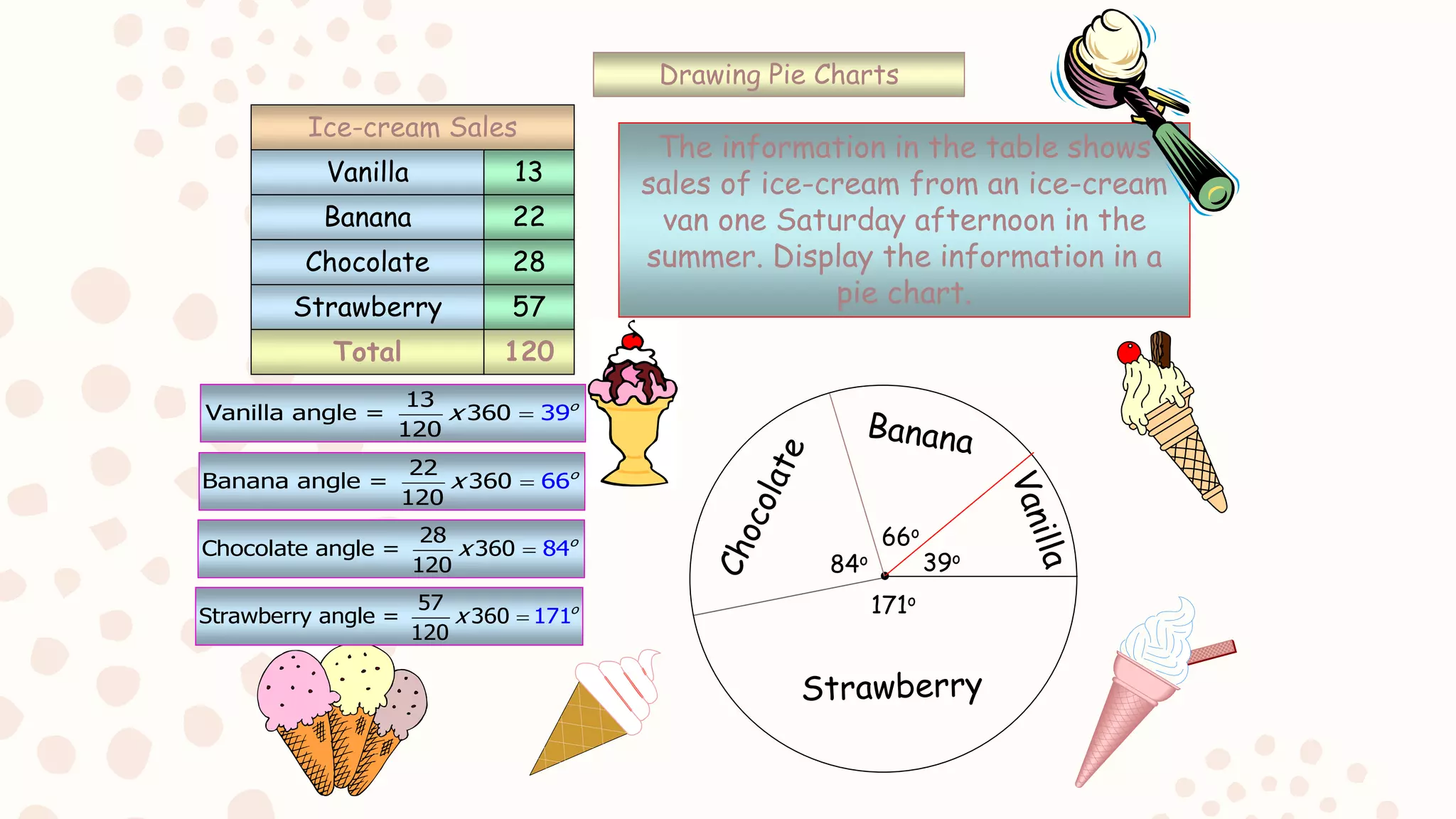
The document discusses various graphical representations of data including bar diagrams, histograms, line graphs, pictographs, and pie charts. It provides examples of how each type of graph can be used to visualize different types of data as well as rules for properly constructing each graph. Specific applications of histograms, line graphs, and pie charts in everyday life are also described.