Embed presentation
Download to read offline
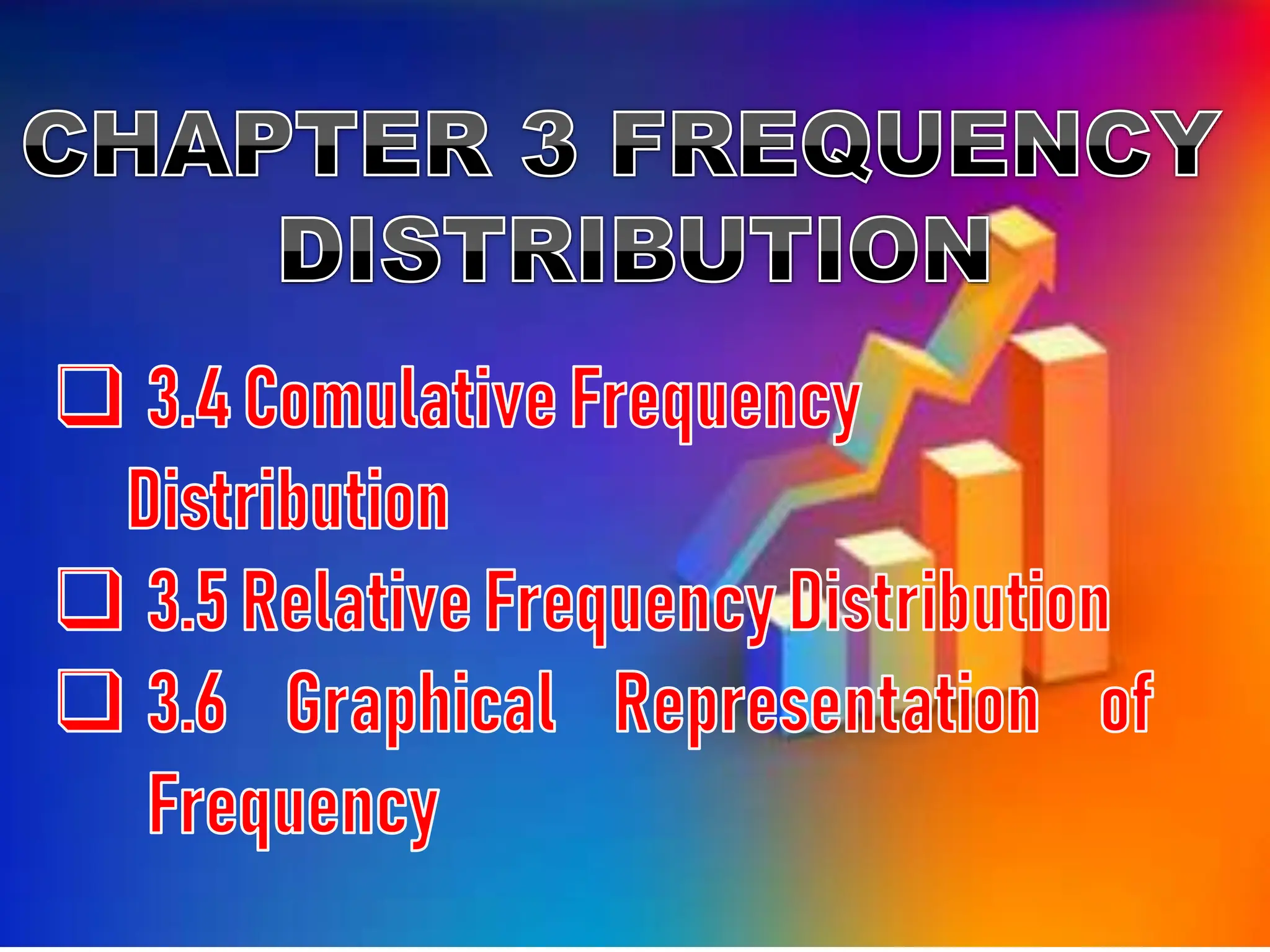

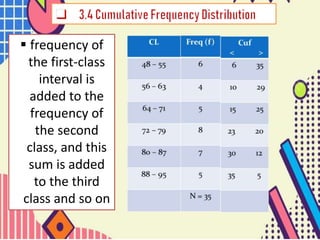
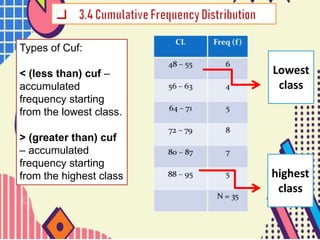
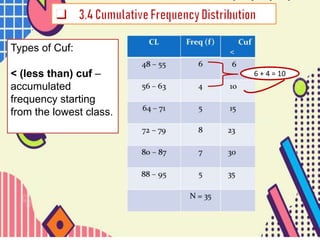
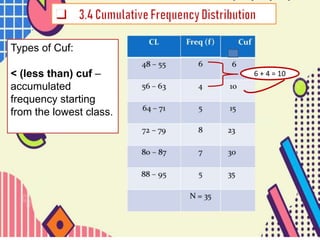

This document discusses types of cumulative frequency (cuf) in data classification. It explains that less than (<) cuf is the accumulated frequency starting from the lowest data class, where the frequency of each subsequent class is added to the previous classes. Greater than (>) cuf is the accumulated frequency starting from the highest data class, where the frequency of each preceding class is added. An example shows how the < cuf is calculated by adding the frequencies of the first two lowest classes.






