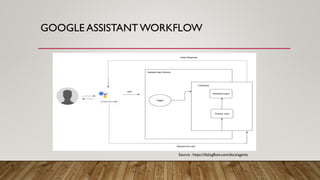
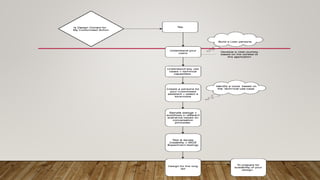
This document discusses building customized apps for Google Assistant using Dialogflow. It provides an overview of the Google Assistant workflow and how Dialogflow is used to build agents with intents, contexts and fulfillment. It also covers basics of conversation design, building blocks for conversations and considerations for real-life user conditions. The document includes an agenda, background on Google Assistant, statistics, diagrams of the workflow and integrations available through Dialogflow. It demonstrates an example using Dialogflow and references additional resources.