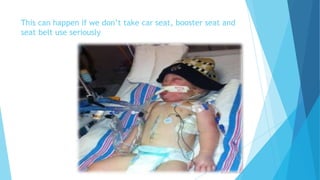
The document outlines a child safety seminar hosted by Taylor Gosson, focusing on topics such as household and car seat safety and SIDS awareness for new parents and grandparents. It highlights essential safety tips, including proper sleeping positions for infants to reduce SIDS risk and car seat regulations according to New Jersey law. Additionally, the seminar covers the functionalities of the 9-1-1 system and the importance of knowing how to utilize emergency services effectively.