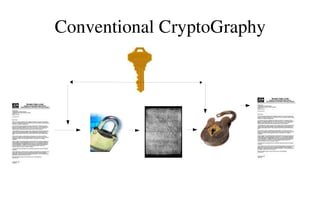
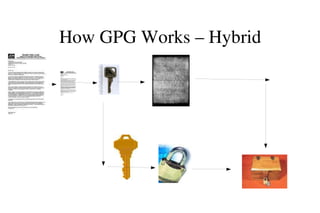
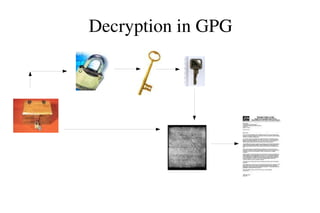
The document provides an overview of Gnu Privacy Guard (GPG), a free software replacement for PGP. It discusses generating and exchanging keys, encrypting and decrypting documents, and making and verifying signatures with GPG. The document also covers cryptographic concepts like symmetric and asymmetric ciphers, digital signatures, and how GPG implements a hybrid cryptosystem. Key management topics like validating keys, distributing keys, and managing trust are also outlined.