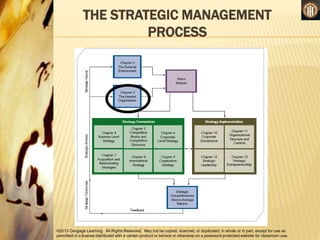
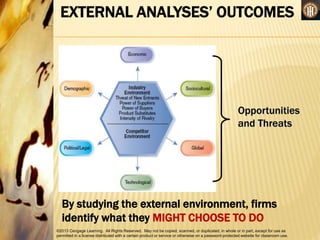
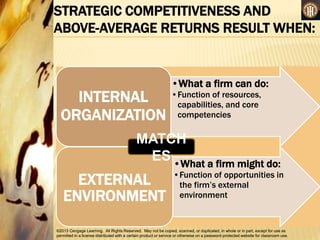
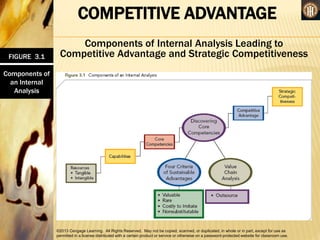
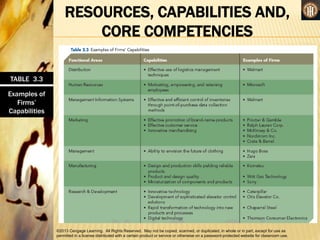
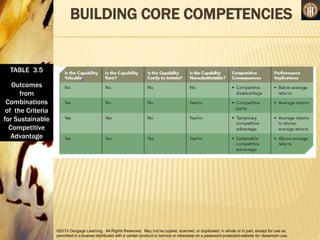
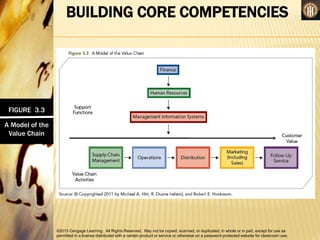
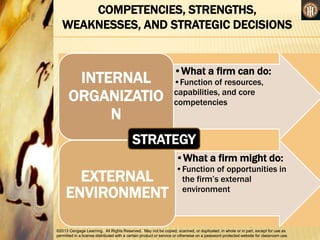
This document discusses analyzing a company's internal environment to understand its resources, capabilities, and core competencies. It defines key terms like resources, capabilities, core competencies, and value chain. The document emphasizes that understanding internal strengths and weaknesses is important for identifying what a company can do well. It also provides examples of how companies like Subway have leveraged their core competencies for competitive advantage. Overall, the document outlines frameworks and considerations for analyzing a company's internal environment to help it identify current and future competitive advantages.