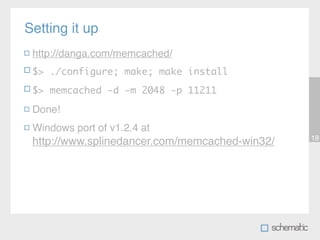
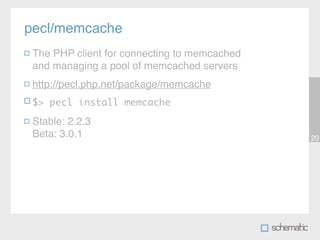
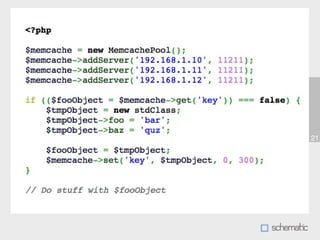
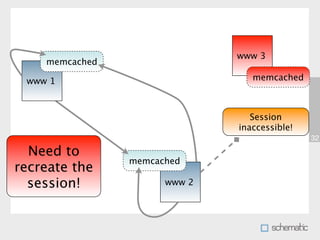
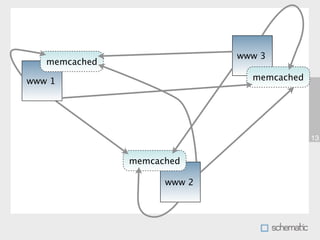
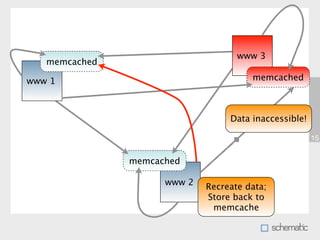
This document discusses using Memcache to cache data and speed up websites. Memcache stores data in RAM for fast access and can reduce database queries and page load times. It acts as a simple key-value store. The document outlines how to set up Memcache, use the PHP Memcache client to store and retrieve data, and techniques for caching database queries and sessions to improve performance. Memcache is fast but does not provide data redundancy or failover, so caching strategies must account for potential data loss.







![$> telnet localhost 11211
Trying ::1...
Connected to localhost.
Escape character is '^]'.
set foobar 0 0 15
This is a test.
STORED
get foobar
VALUE foobar 0 15
This is a test. 17
END
quit
Connection closed by foreign host.
$>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bramsey-codeworks2009-memcache-091130182335-phpapp01/85/Give-Your-Site-a-Boost-with-Memcache-17-320.jpg)