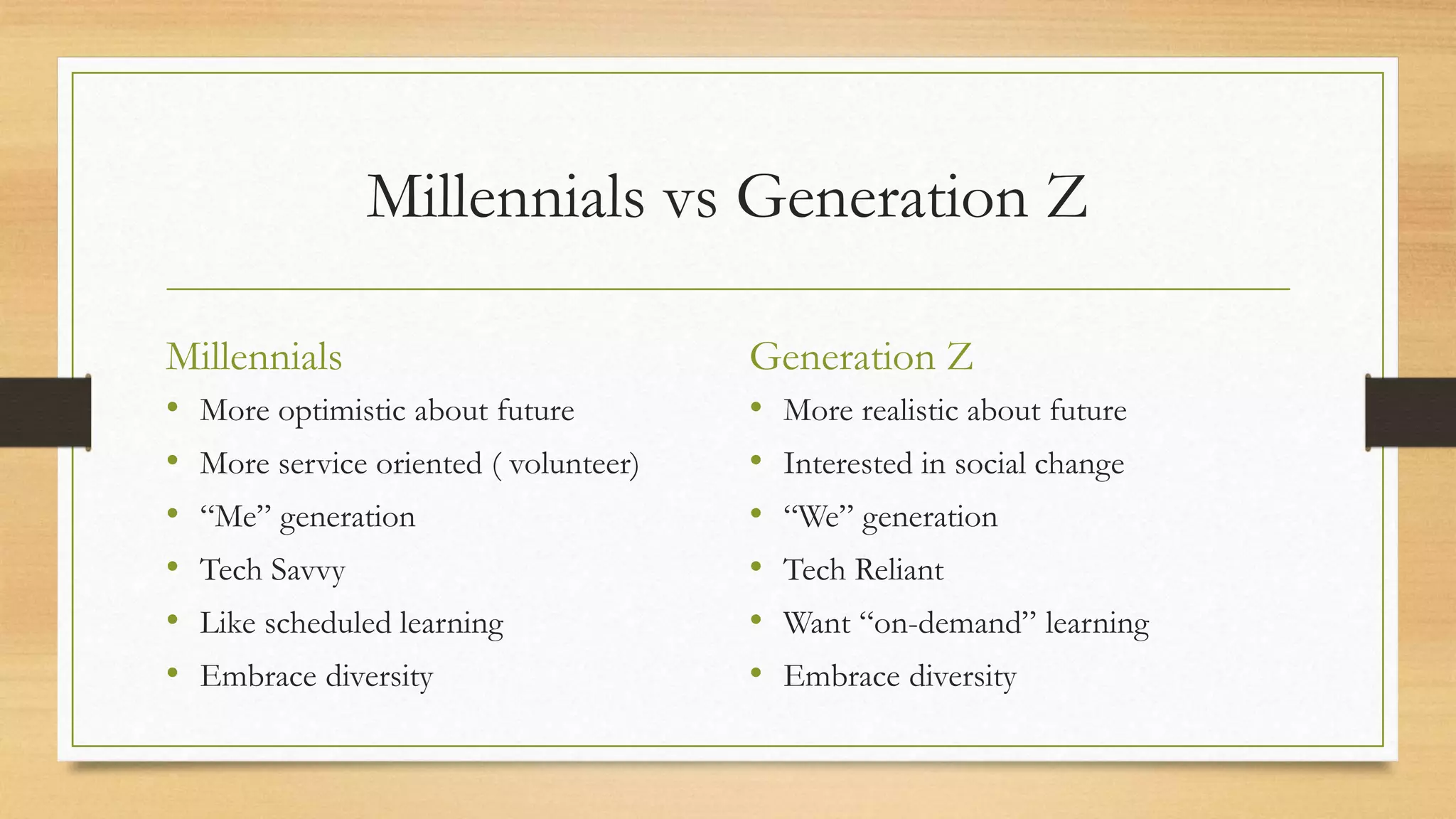
Generation Z, born between 1995-2014, has different expectations for higher education than previous generations. They are more technology dependent and rely on online learning. Generation Z sees college as a means to a good job and are cost conscious. They prefer mobile communication and "on demand" learning. Academic advisors will need to engage Generation Z using technology, provide critical information redundantly, and consider peer opinions to effectively serve this pragmatic and self-reliant generation.