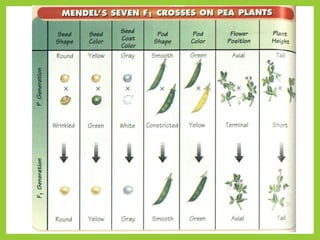
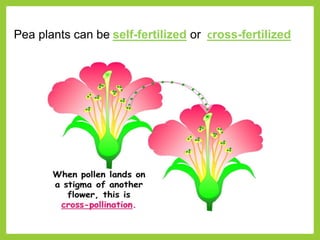
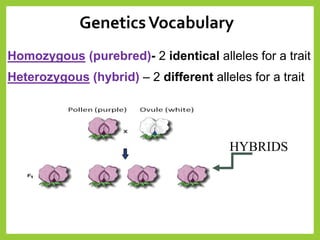
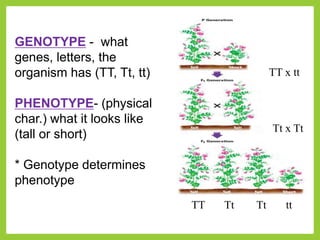
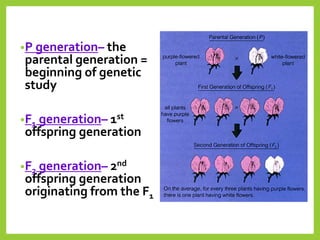
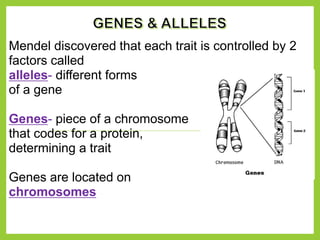
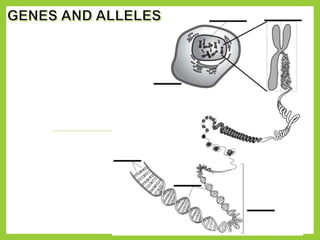
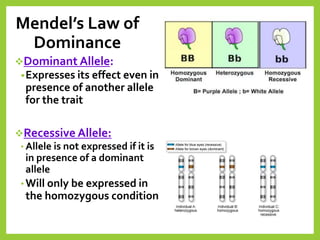
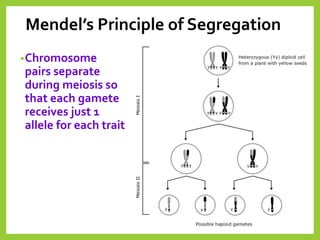
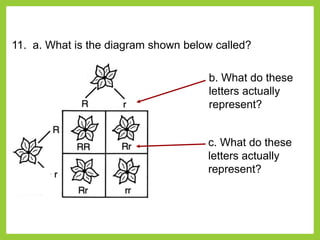
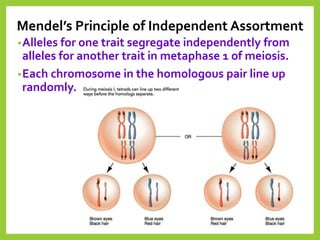
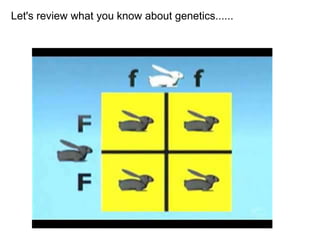
Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk in the 1800s who is considered the father of modern genetics. He studied inheritance of traits in pea plants by cross-breeding them. Peas were useful for his experiments because they have a short life cycle, are self-pollinating, and have simple traits that occur in only two variations. Through his experiments, Mendel discovered that traits are passed from parents to offspring through discrete units called alleles located on chromosomes. He established that some alleles are dominant and others recessive through his Law of Dominance. Mendel also discovered the principle of segregation, where each gamete receives one of the two alleles for each trait from the parental generation.