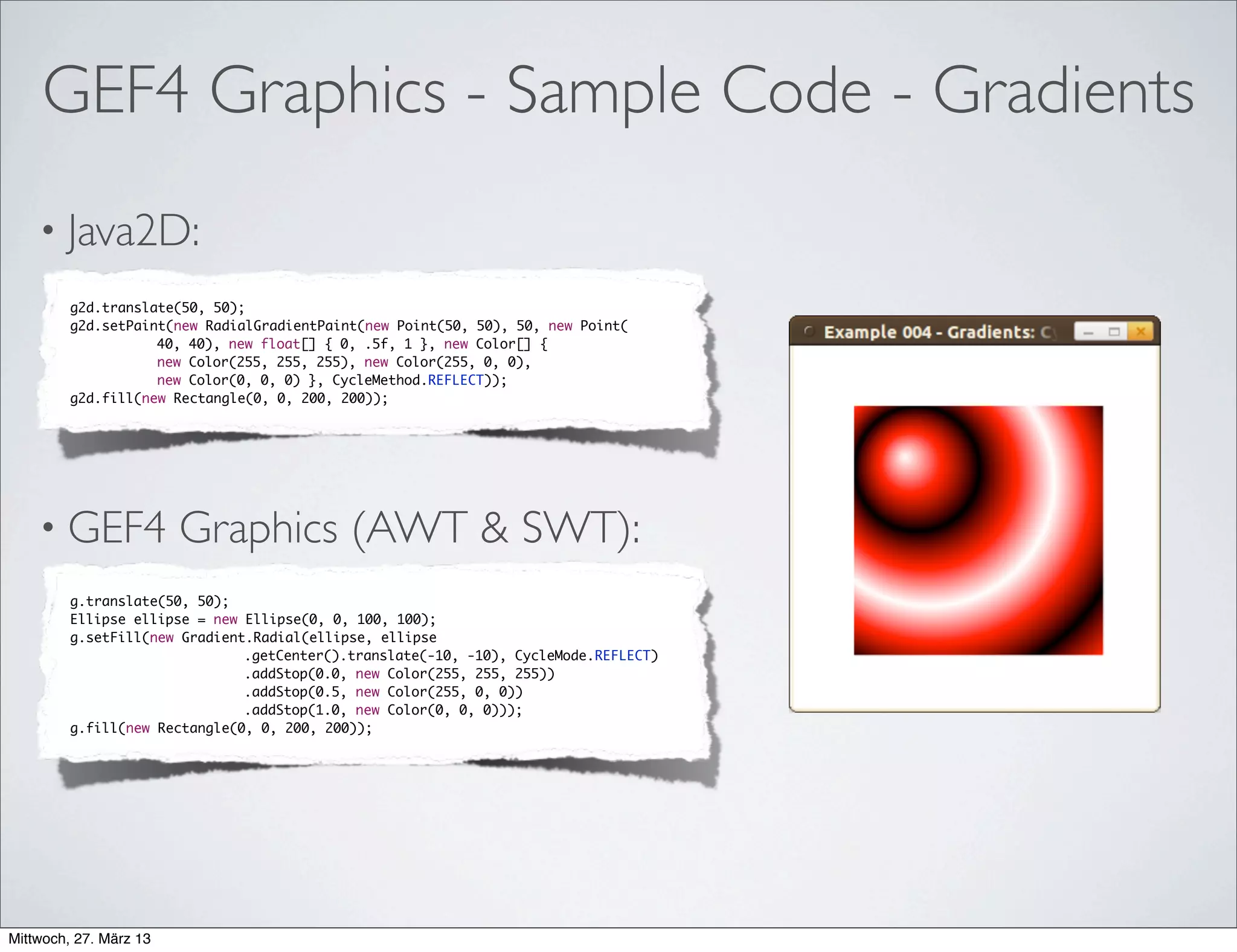
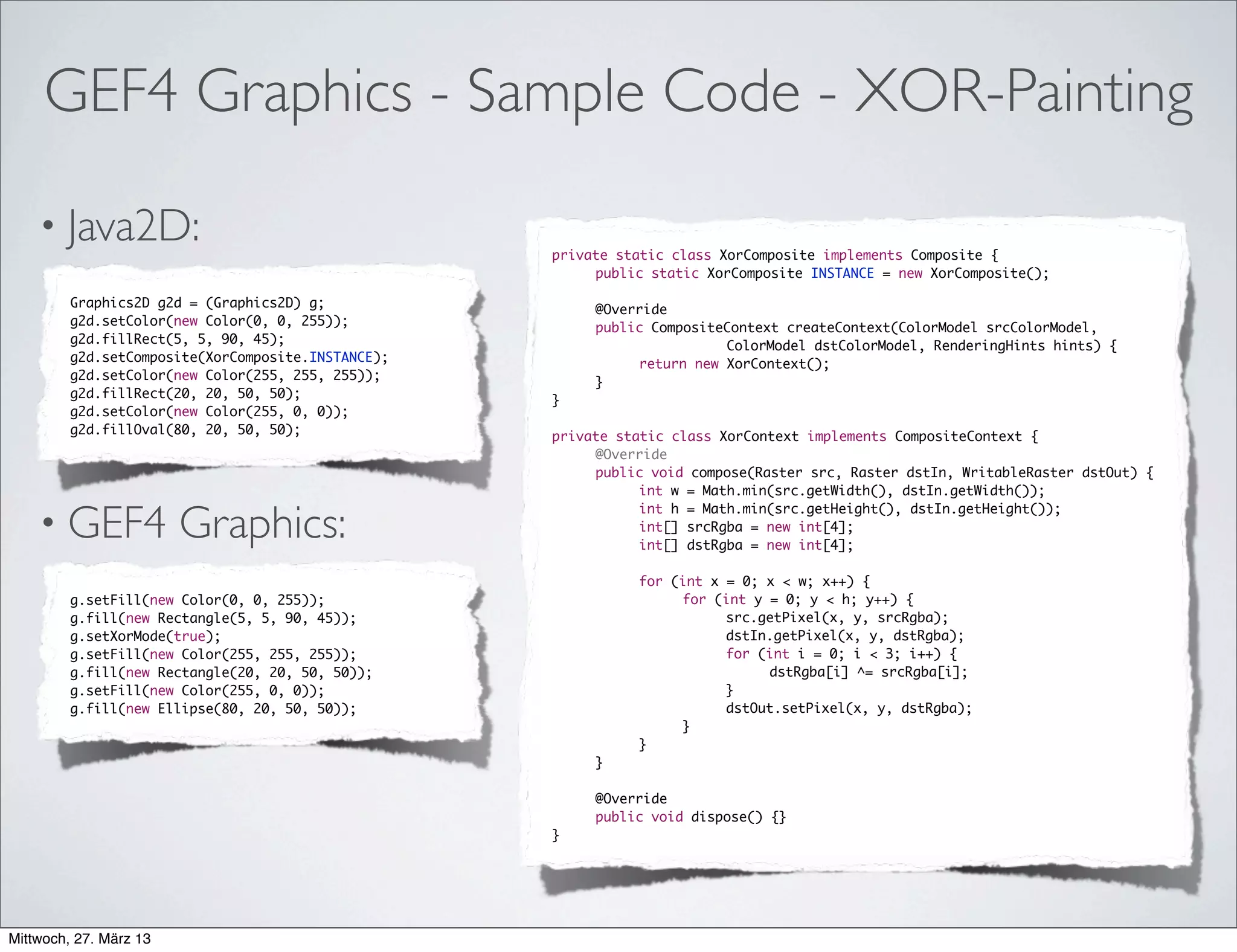
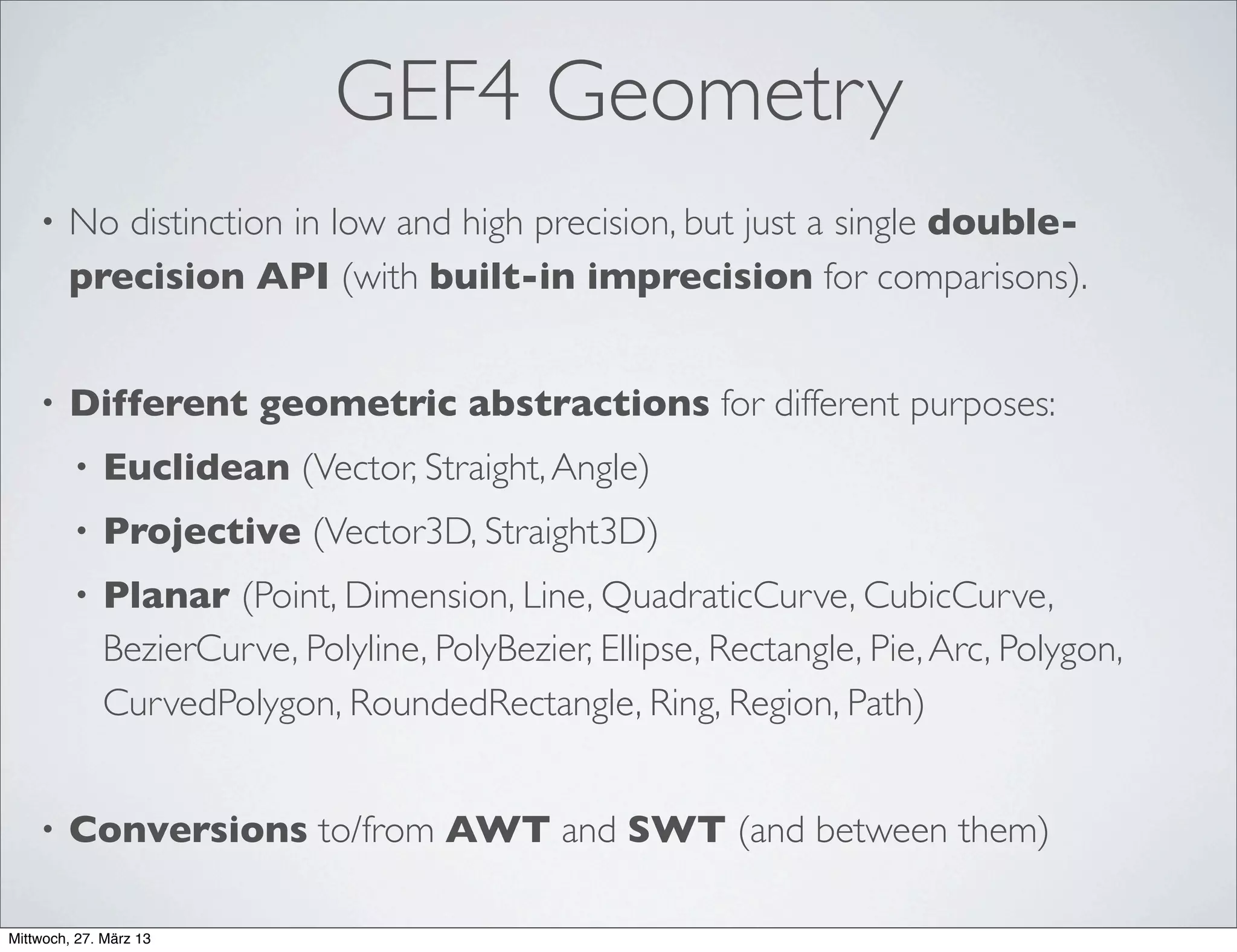
This document discusses GEF4, a project to develop a next generation version of the Graphical Editing Framework (GEF) and Zest projects. It provides an overview of the status and goals of the GEF4 Geometry and Graphics components, which aim to modernize the underlying technologies while maintaining a stable API. The document invites the reader to get involved by providing feedback, trying early versions, and contributing code or other assistance to help guide the future development of GEF4.











![GEF4 Geometry - Sample Code
// Bezier approximation of curves
BezierCurve[] fromCurve = curve.toBezier();
BezierCurve[] fromShape = shape.getOutline().toBezier();
ICurve[] fromPolyShape = polyShape.getOutlineSegments();
List<BezierCurve> beziers = new ArrayList<BezierCurve>();
for (ICurve c : fromPolyShape)
beziers.addAll(Arrays.asList(c.toBezier()));
// PolyBezier interpolation
PolyBezier interpolation = PolyBezier.interpolateCubic(p0, p1, p2, p3, ...);
// support for affine transformations
Polygon rhomb = new Rectangle(10, 10, 10, 10).getRotatedCCW(Angle.fromDeg(45));
PolyBezier slanted = new Ellipse(100, 100, 100, 50).getRotatedCCW(Angle.fromDeg(30));
Ring rotatedClippingArea = region.getRotatedCCW(Angle.fromDeg(300));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gef4continuetoshareandenjoy-150121054522-conversion-gate01/75/GEF4-Continue-to-Share-and-Enjoy-16-2048.jpg)




![GEF4 Graphics - More Sample Code
• Java2D:
• GEF4 Graphics (Java2D & SWT):
g2d.translate(50, 50);
g2d.setPaint(new RadialGradientPaint(new Point(50, 50), 50, new Point(
40, 40), new float[] { 0, .5f, 1 }, new Color[] {
new Color(255, 255, 255), new Color(255, 0, 0),
new Color(0, 0, 0) }, CycleMethod.REFLECT));
g2d.fill(new Rectangle(0, 0, 200, 200));
g.translate(50, 50);
Ellipse ellipse = new Ellipse(0, 0, 100, 100);
g.setFill(new Gradient.Radial(ellipse, ellipse
.getCenter().translate(-10, -10), CycleMode.REFLECT)
.addStop(0.0, new Color(255, 255, 255))
.addStop(0.5, new Color(255, 0, 0))
.addStop(1.0, new Color(0, 0, 0)));
g.fill(new Rectangle(0, 0, 200, 200));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gef4continuetoshareandenjoy-150121054522-conversion-gate01/75/GEF4-Continue-to-Share-and-Enjoy-22-2048.jpg)