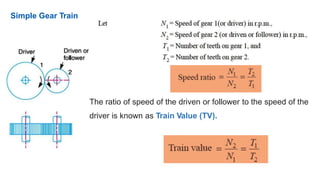
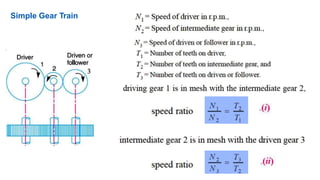
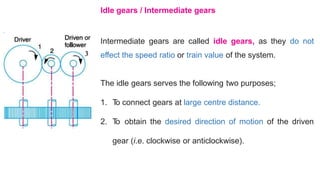
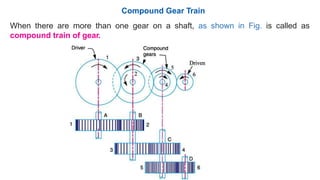
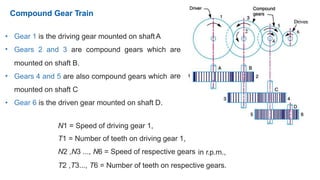
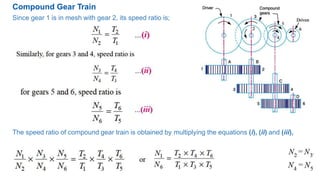
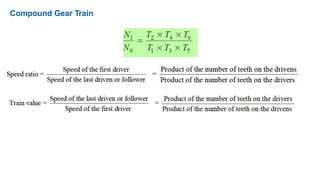
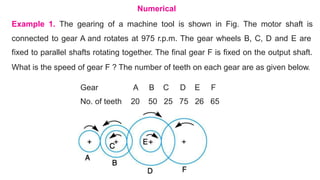
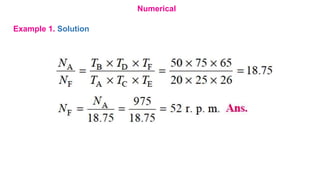
Gear trains can be either simple or compound. A simple gear train uses only one gear on each shaft to transmit motion from one shaft to another. A compound gear train uses more than one gear on a shaft. The speed ratio of a simple gear train is the ratio of the speeds of the driven gear to the driver gear. For a compound gear train, the overall speed ratio is calculated by multiplying the individual speed ratios of each stage. An example calculates the speed of the final gear in a compound gear train given the number of teeth on each gear and the input speed.