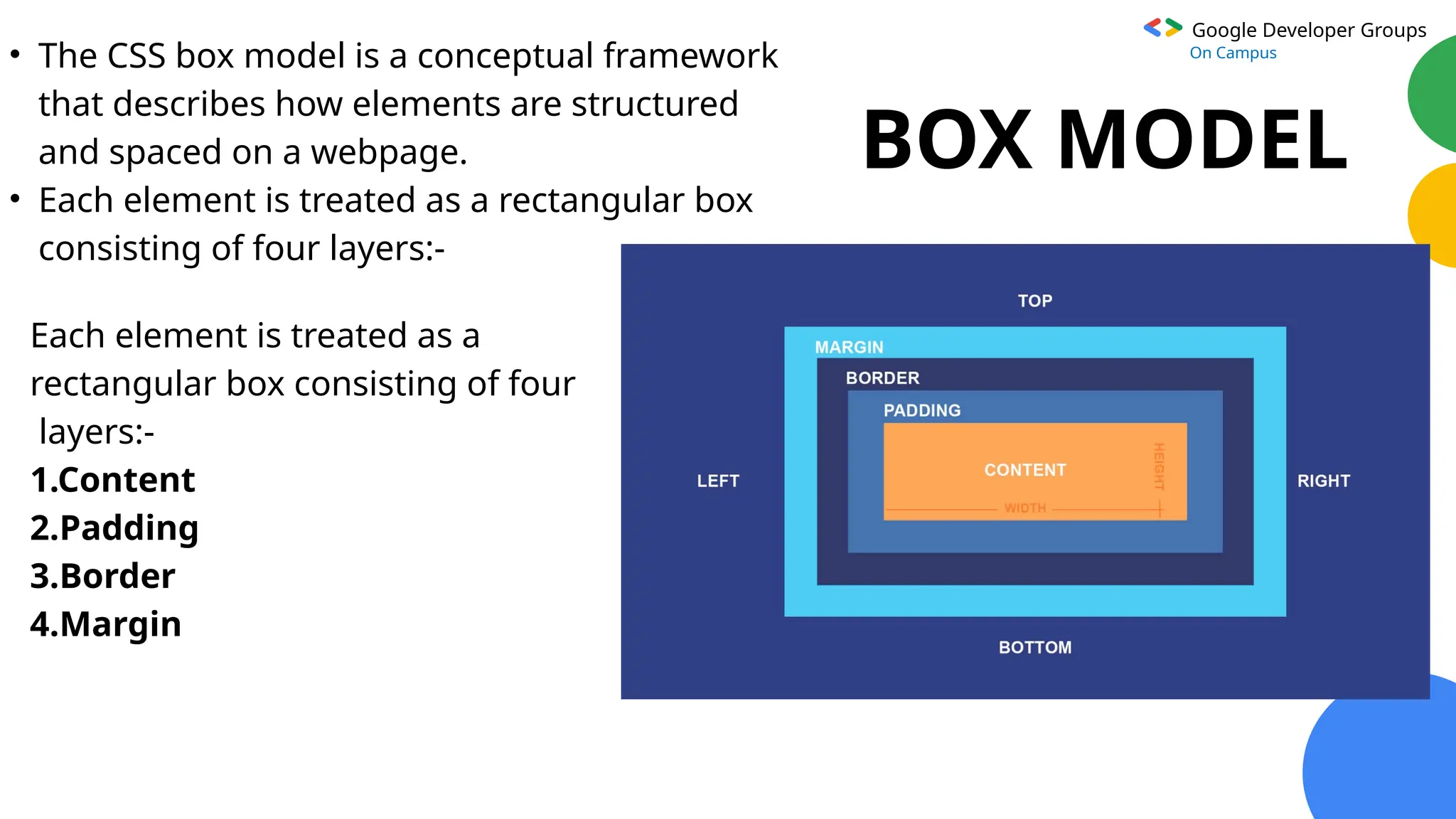
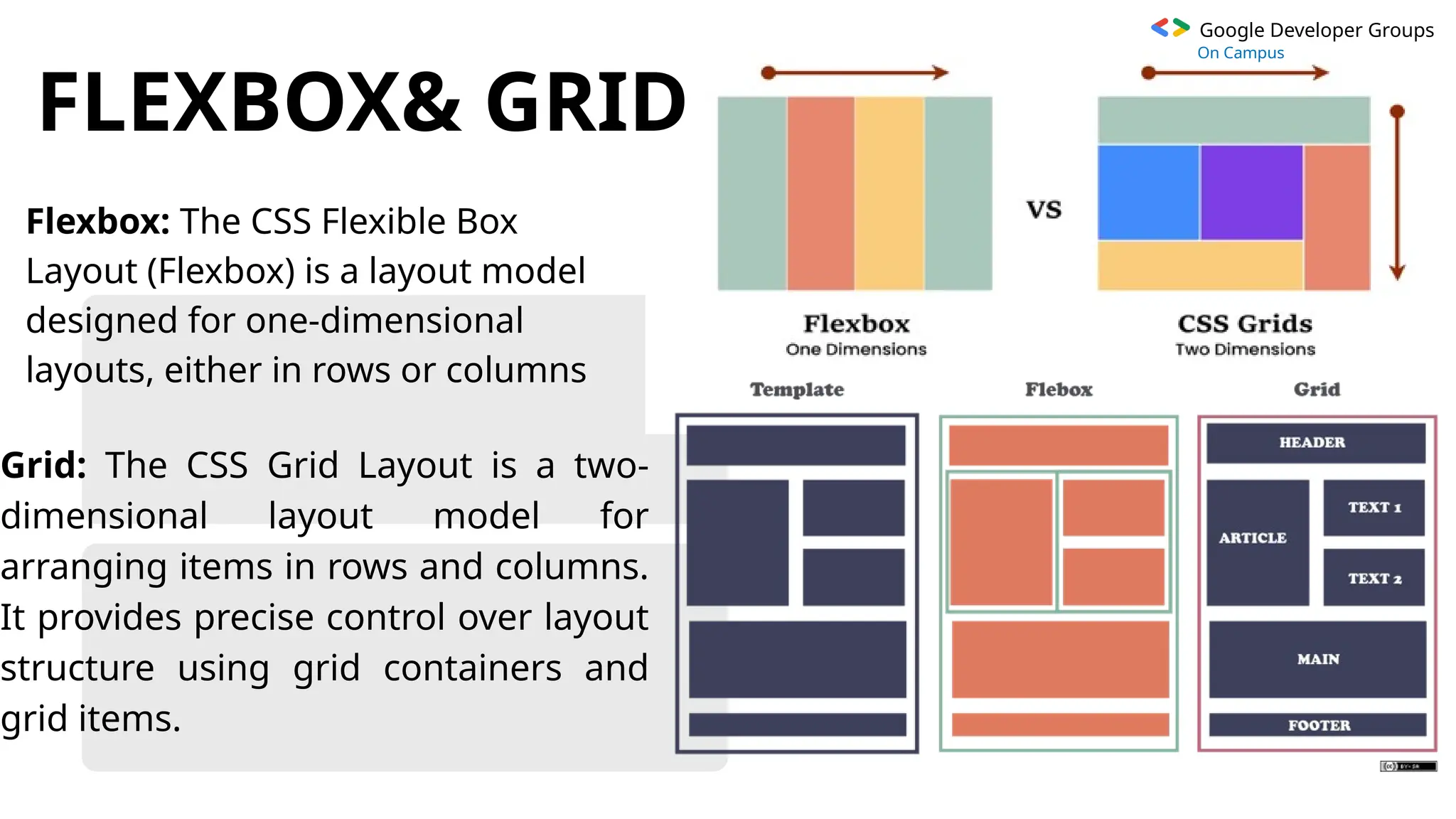
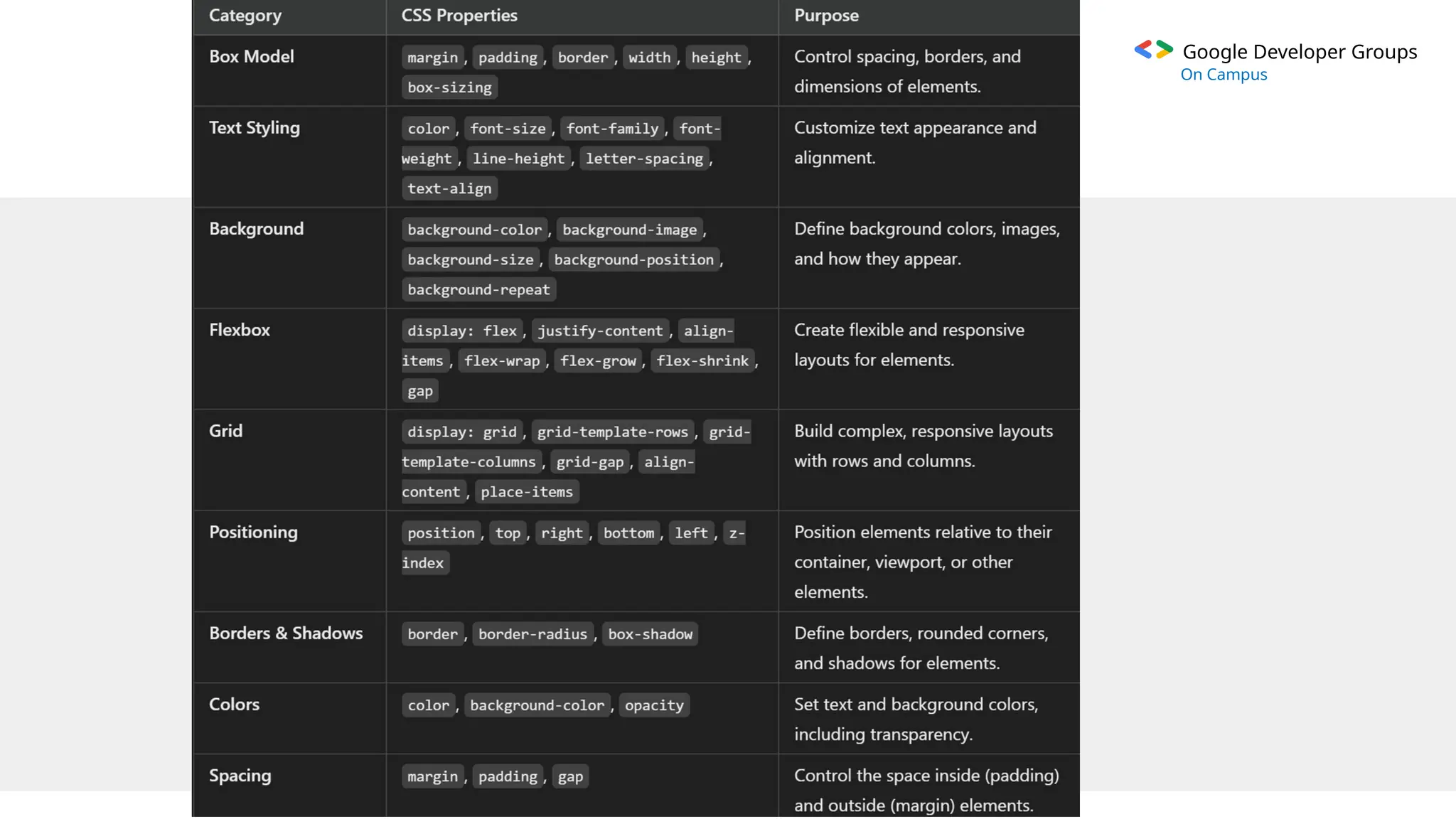
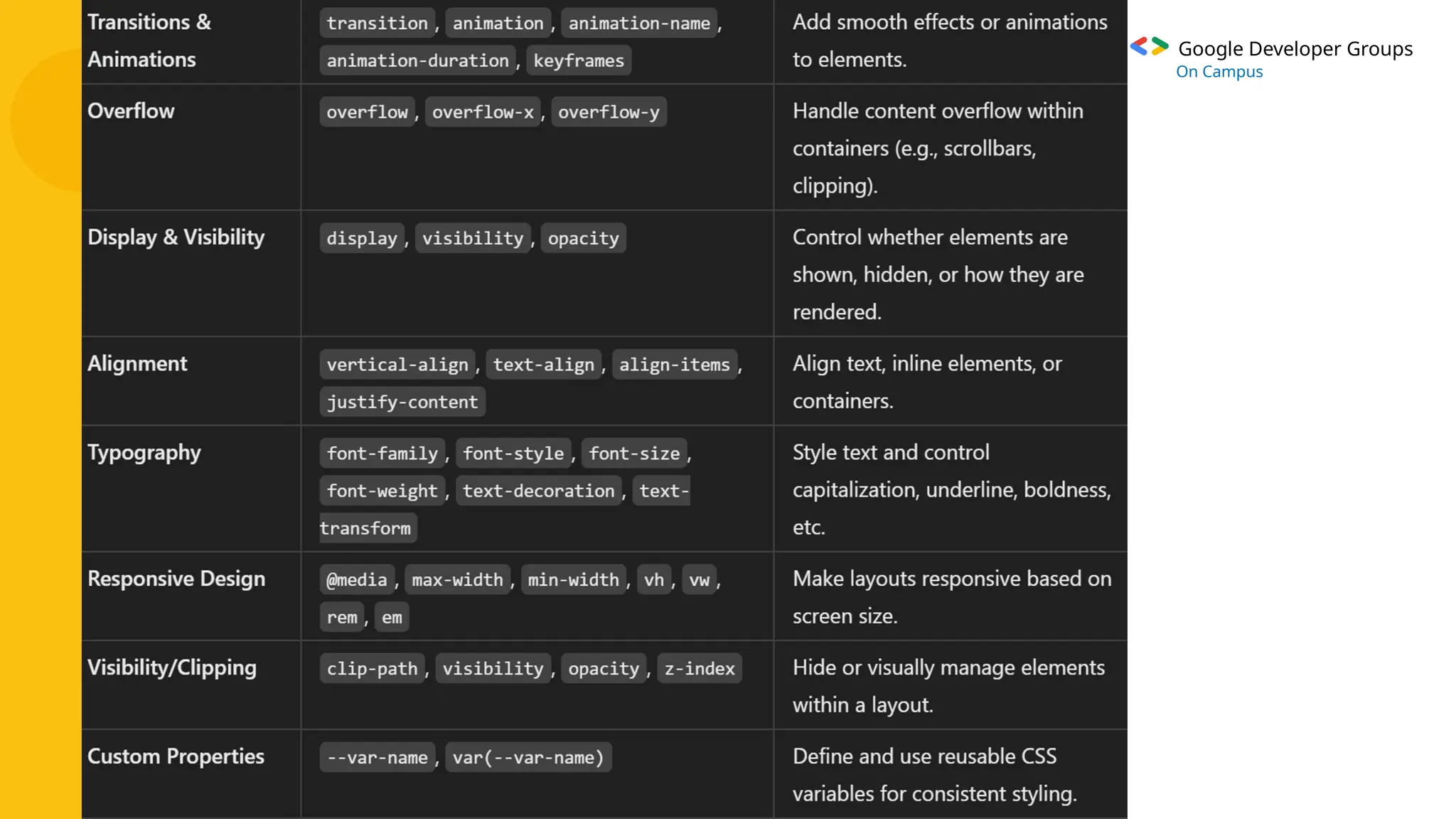
The document provides an overview of Cascading Style Sheets (CSS), including its definition, purpose, and key features, such as selectors and the box model. It explains the types of CSS (inline, internal, external) and how CSS is used to enhance website design, usability, and responsiveness. Additionally, it covers advanced techniques like flexbox and grid layouts, as well as the advantages of using CSS for efficient web development.








![Google Developer Groups
On Campus
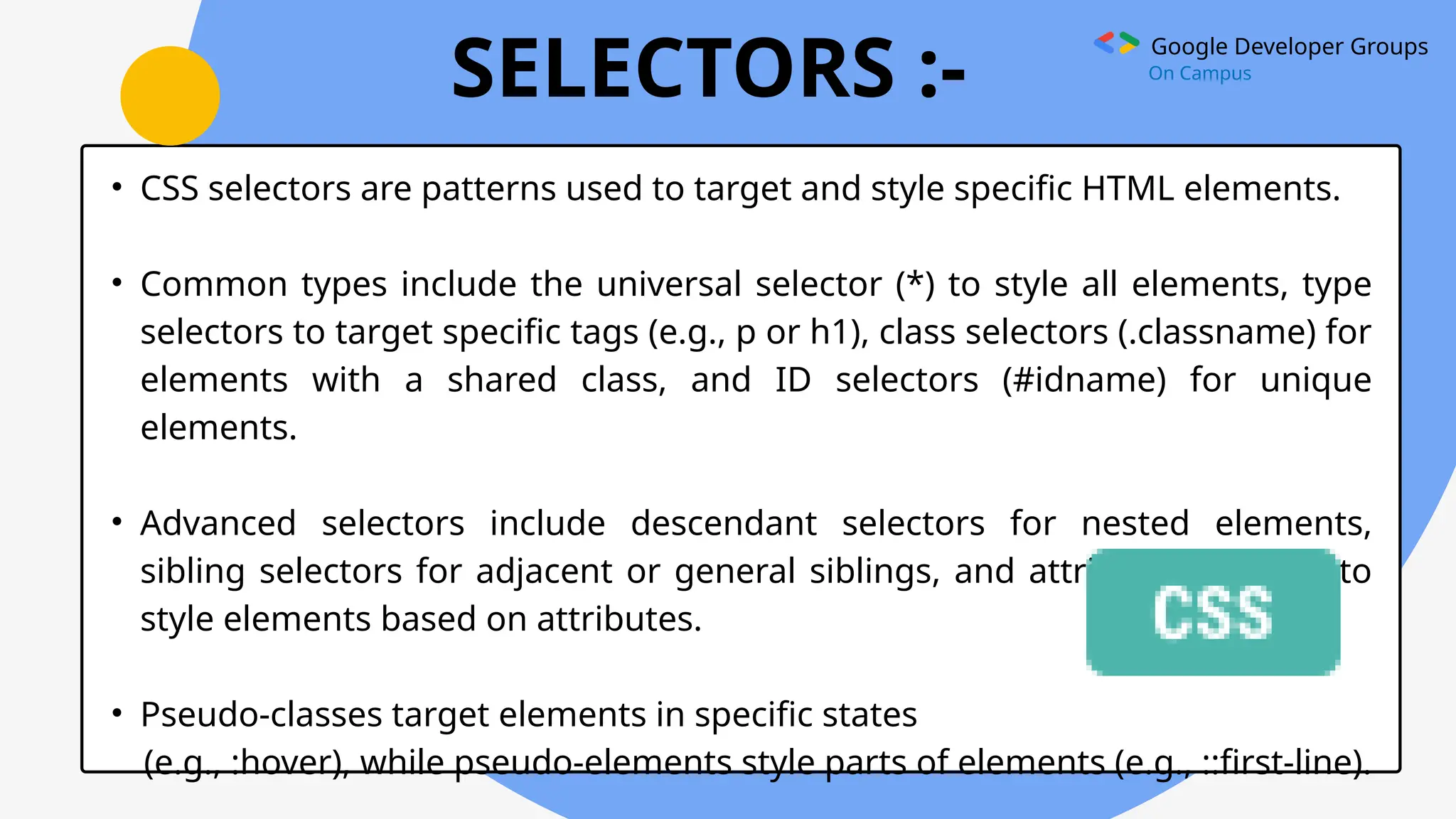
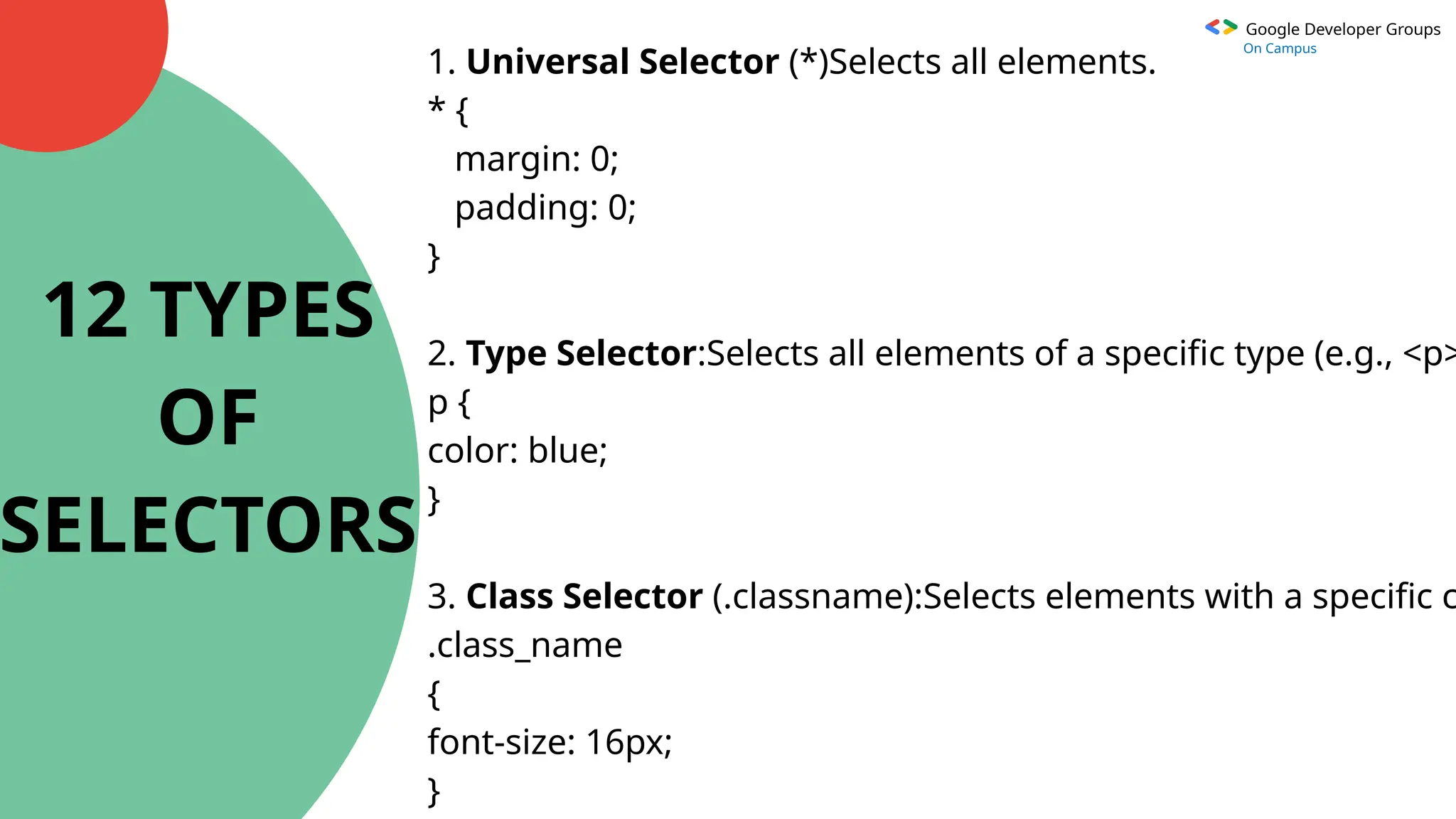
10. Attribute Selector ([attribute]): Selects elements with a specific
attribute.
input[type="text"] {
border: 1px solid black;
}
11. Pseudo-class Selector (:pseudo-class): Selects elements in a specific
state.
a:hover {
color: purple;
}
12. Pseudo-element Selector (::pseudo-element):Selects and styles
specific parts of an element.
p::first-line {](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gdgcssppt-241224181623-13fb38fd/75/GDG-CSS-TECH-WINTER-BREAK-VIEW-PPT-pptxx-12-2048.jpg)