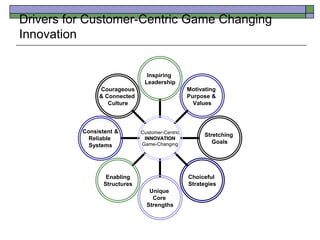
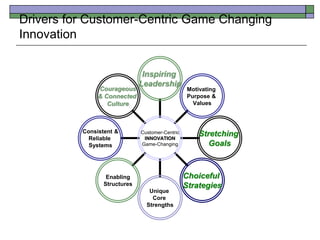
This document discusses how P&G transformed its culture and processes to focus on innovation and put the consumer at the center of everything. Some key points:
- P&G shifted from a technology-push model to a customer-pull model of innovation where consumer insights drove new products and services.
- Innovation was organized as a core business strategy with goals, metrics, reviews, and leader development. Resources were allocated to outstanding innovations.
- An open culture of collaboration, both internally and externally, was fostered to generate more connections and ideas. Innovation risks were systematically managed.
- Building innovative teams required intellectual diversity, interdisciplinary skills, and a focus on consumer immersion to generate breakthrough insights.