Embed presentation
Download to read offline


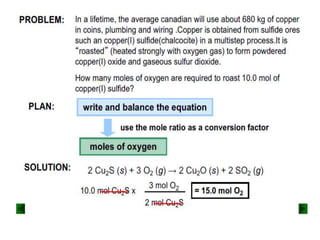







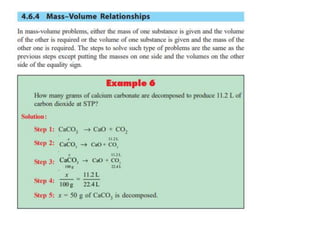






Gases are usually expressed in terms of volume, but to compare volumes measured under different conditions, they must be converted to normal temperature and pressure using gas laws. The volume of a gas can also be converted to its weight and vice versa using the relation that the mass of a gas is directly proportional to its density and volume. For example, 2 grams of sulfur burned to form SO2 can be used to calculate the volume of oxygen consumed at standard temperature and pressure.















