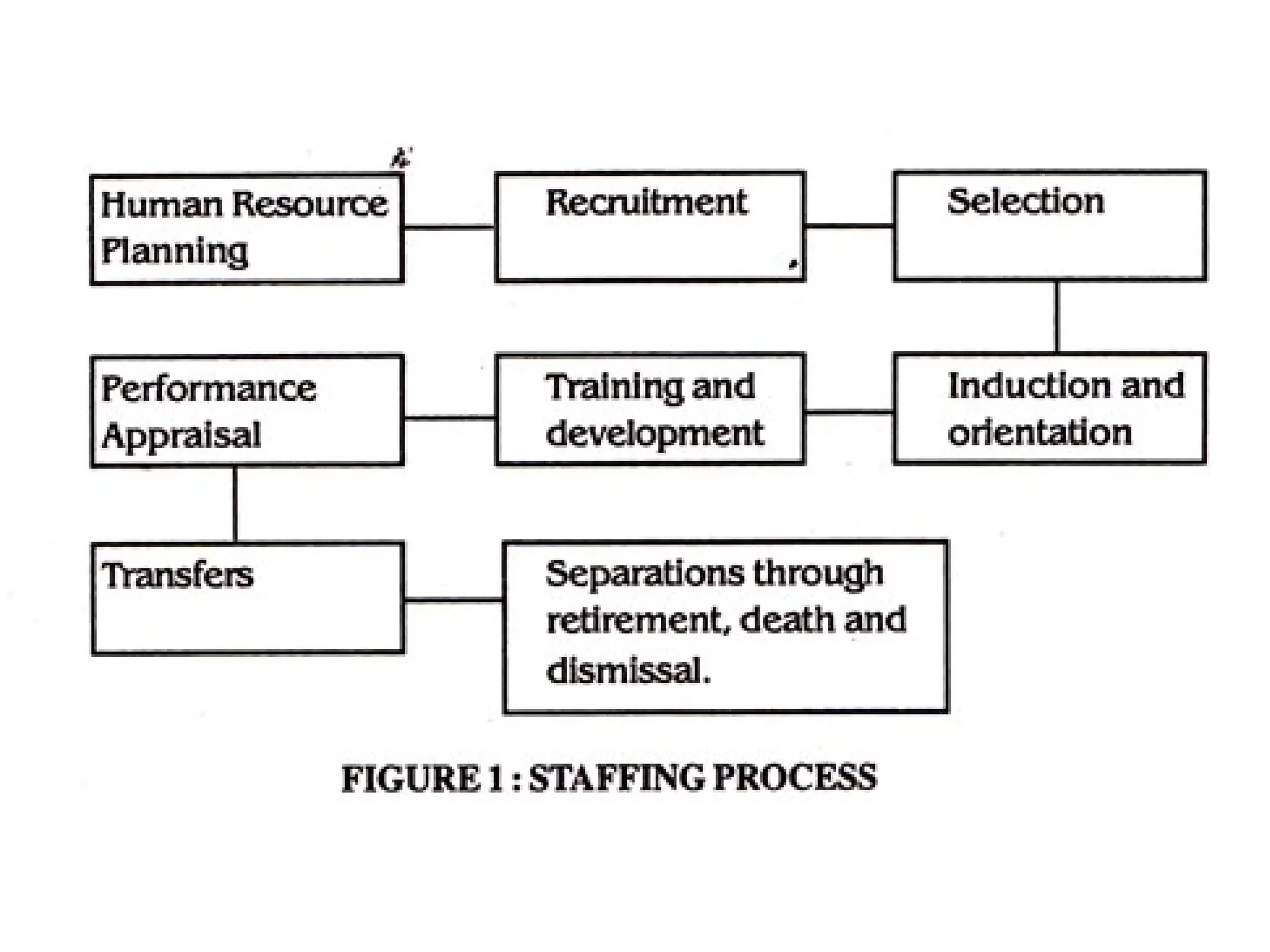
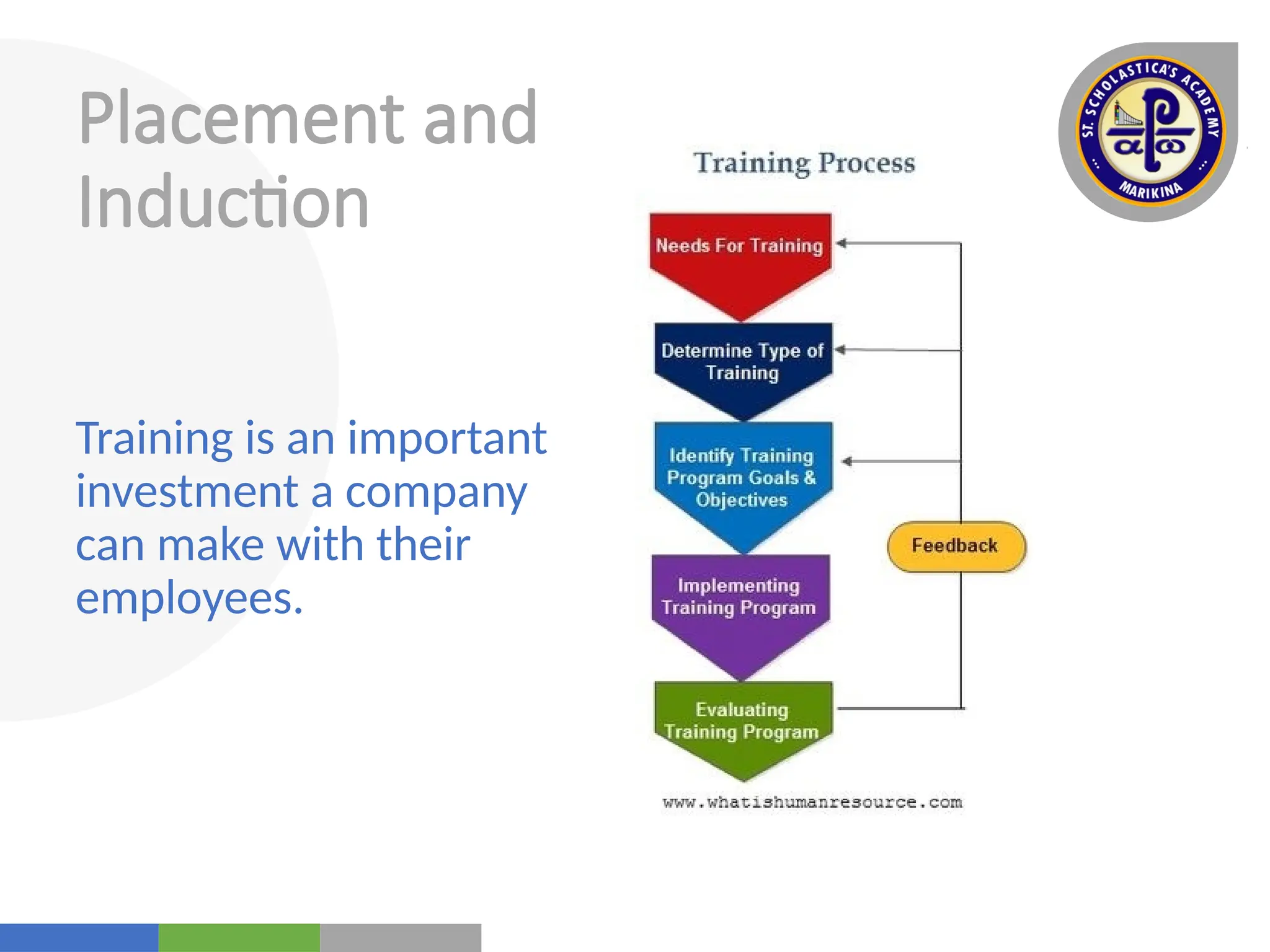
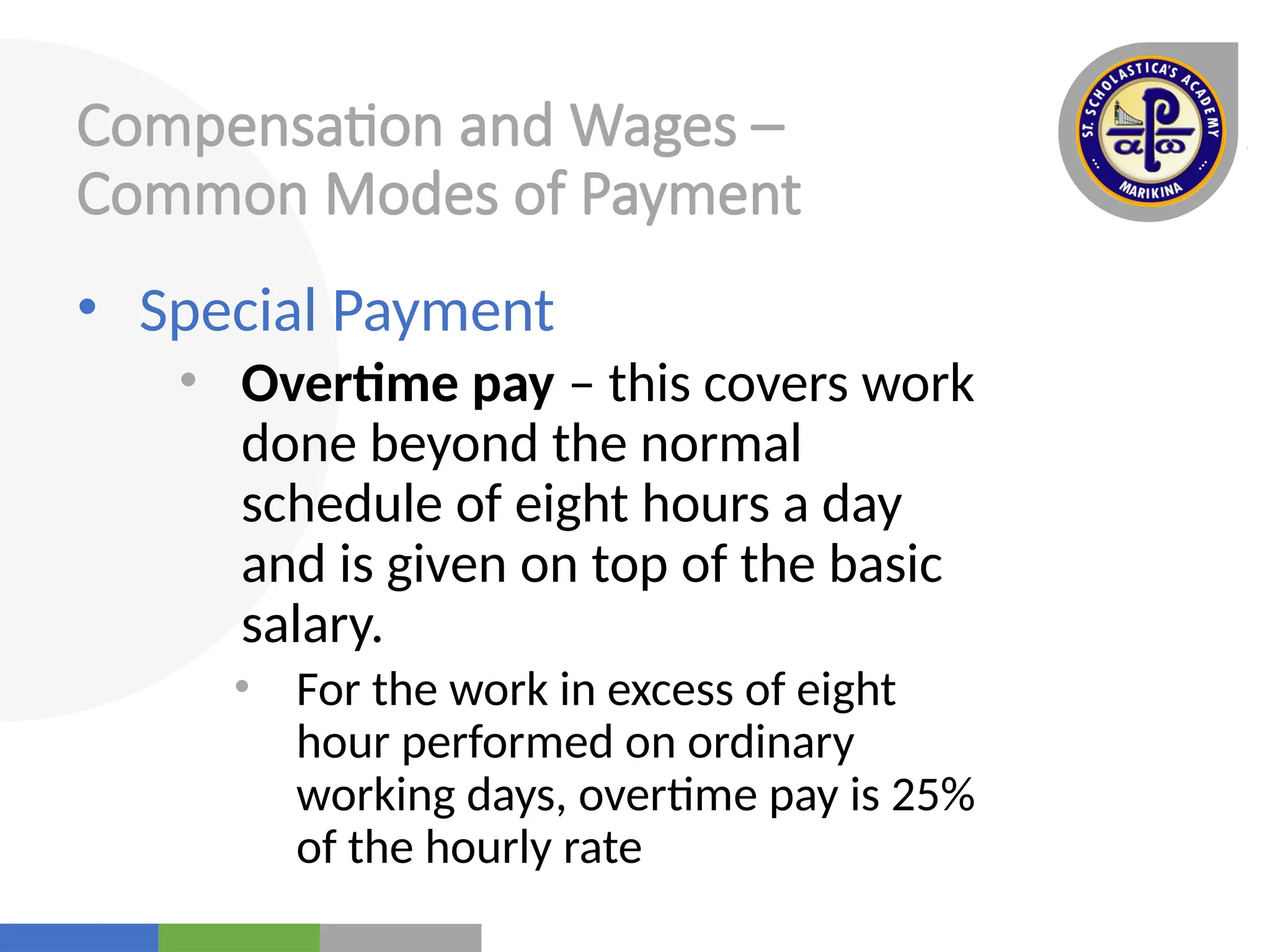
The document outlines the functions of management with a focus on staffing, including human resource planning, recruitment, selection, placement, compensation, and performance appraisal. It emphasizes the importance of finding and developing suitable employees while ensuring equal employment opportunities and offering a range of benefits. Additionally, it addresses employee movements and the various factors influencing organizational dynamics.