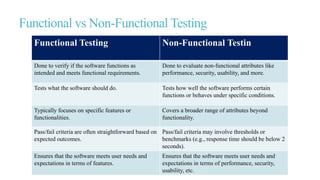
Functional testing is a crucial part of software quality assurance that verifies the functions of an application against specifications. It comprises six steps, including identifying functions, creating input data, and executing test cases, across various types like unit testing, smoke testing, and regression testing. The document also contrasts functional with non-functional testing, outlines best practices for functional testing, and emphasizes the importance of clear documentation.