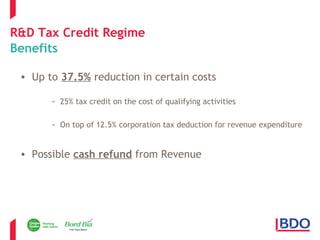
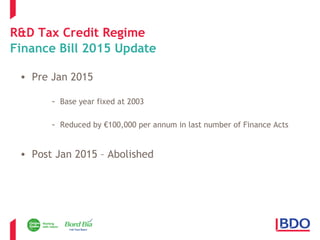
This document discusses Ireland's R&D tax credit regime and how sustainability efforts can qualify. It outlines that the tax credit provides up to a 37.5% reduction in qualifying R&D costs. Sustainability activities like reducing emissions, energy/water usage, and waste can potentially qualify if they involve scientific or technological advancement to resolve uncertainties. Examples provided include material substitutions, process optimizations and improvements, packaging changes, and waste product alternative uses. Non-qualifying activities are also defined. The presentation addresses common myths that activities are disqualified if grants were received, failures occurred, results would not be patentable, or intellectual property is not retained. Questions are invited at the end.