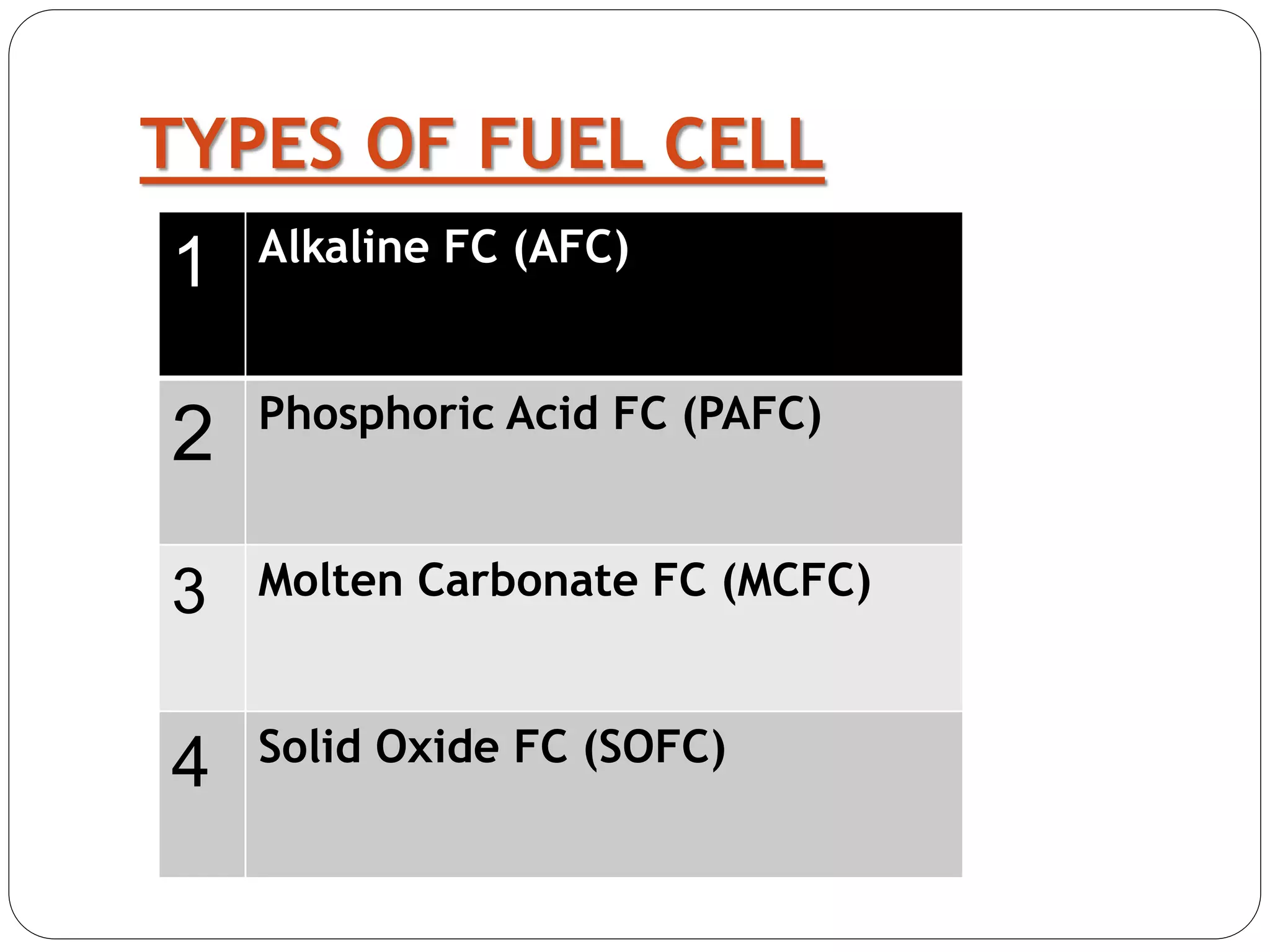
This document provides an overview of fuel cells, including their construction, working, types, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. It describes how a fuel cell works by converting chemical energy from hydrogen into electrical energy through an electrochemical reaction with oxygen. The main types of fuel cells covered are alkaline fuel cells, phosphoric acid fuel cells, molten carbonate fuel cells, and solid oxide fuel cells. The advantages include high efficiency, zero emissions, and quiet operation. Disadvantages include the high cost of the technology and fuel production. Applications mentioned include power generation, transportation, portable electronics, and backup power supplies.