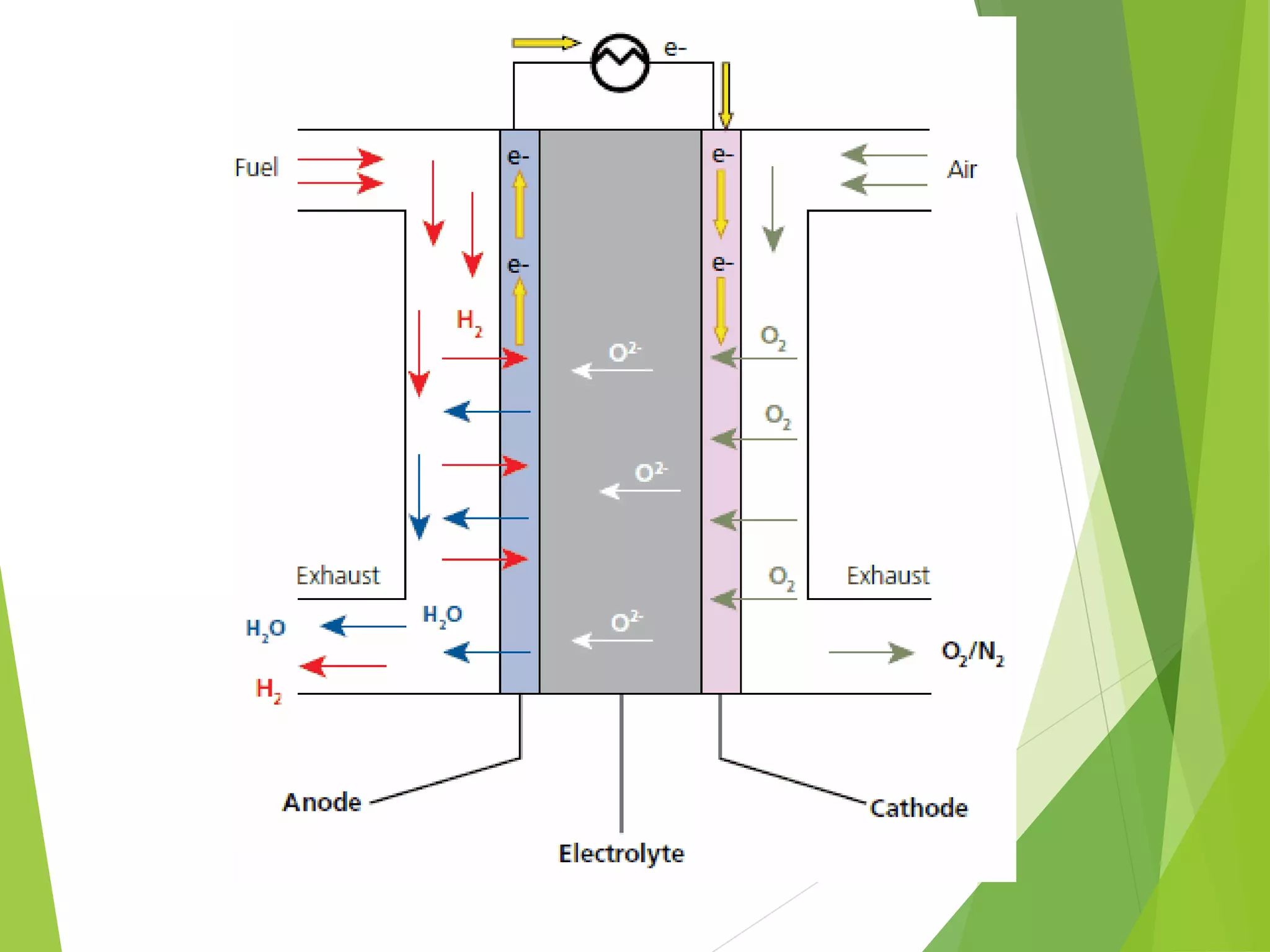
Fuel cells generate electricity through an electrochemical reaction without combustion. They convert chemical energy stored in hydrogen fuel into electricity. Fuel cells were first demonstrated in 1839 and the first practical fuel cell was developed in 1959. Key parts include an anode, cathode, catalyst and electrolyte. Hydrogen ions pass through the electrolyte and electrons travel through an external circuit to generate electricity. Fuel cells have various applications and advantages like high efficiency and low emissions but also have disadvantages like high costs. Different types of fuel cells operate at different temperatures using different fuels and electrolytes.