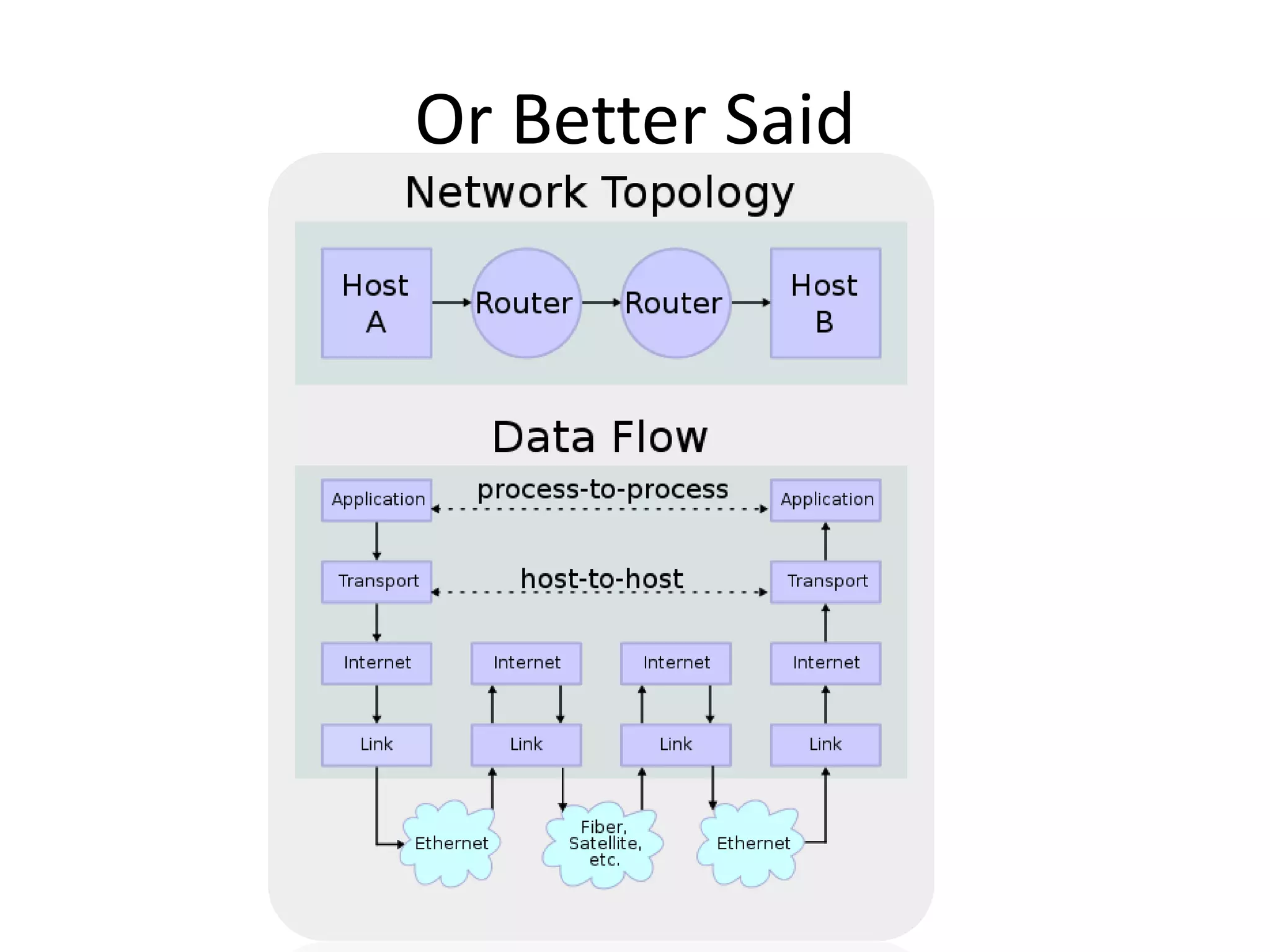
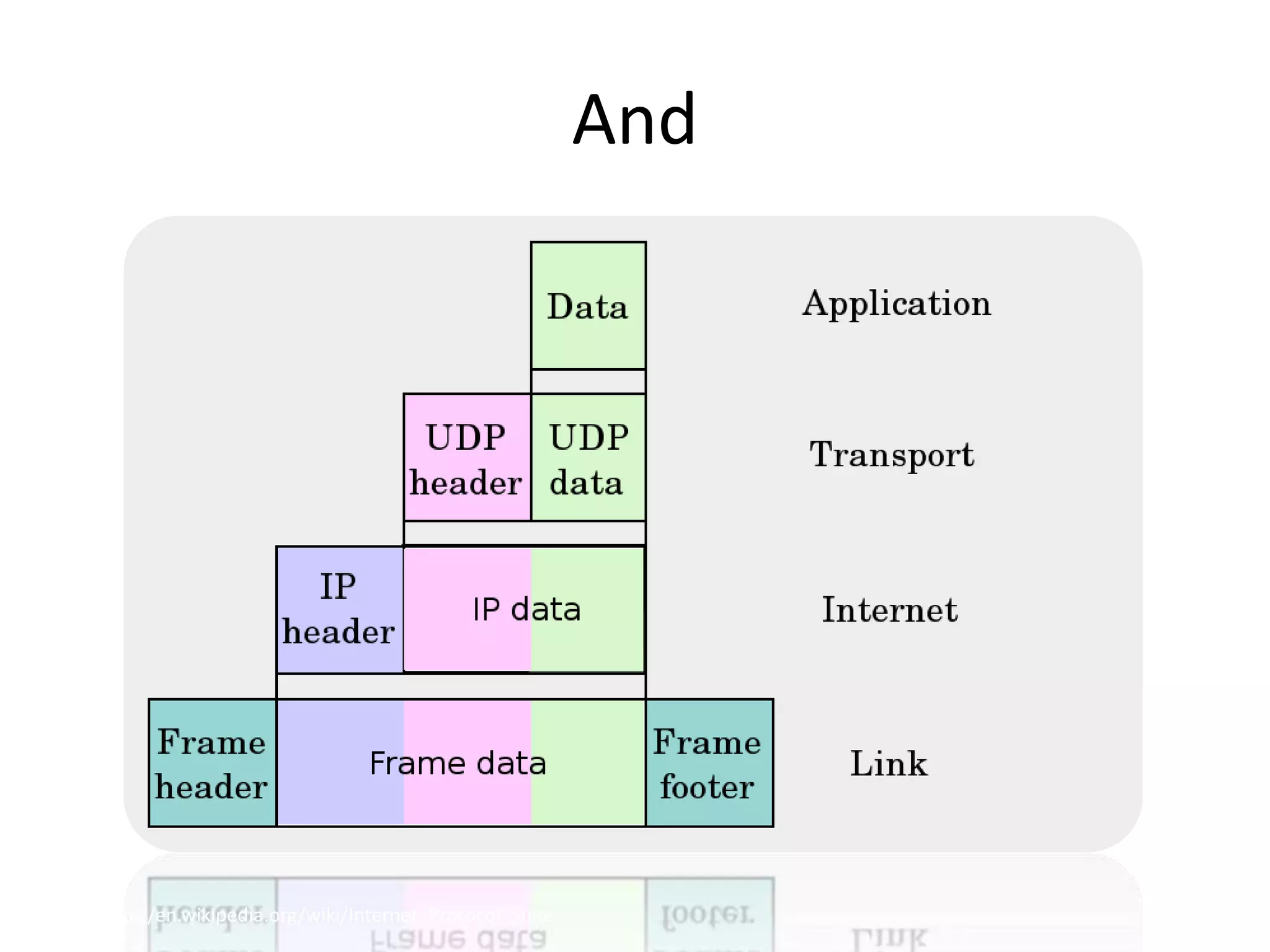
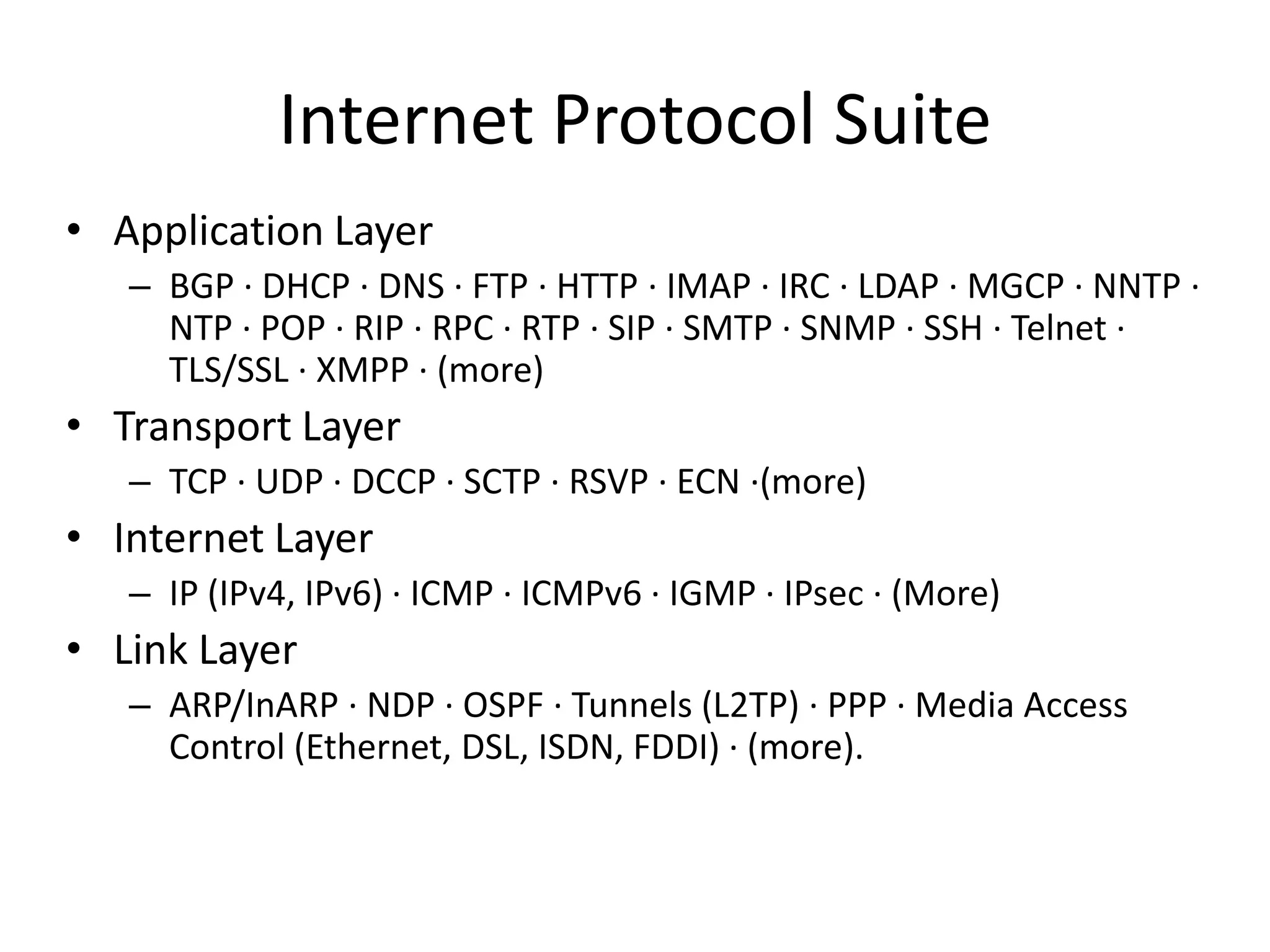
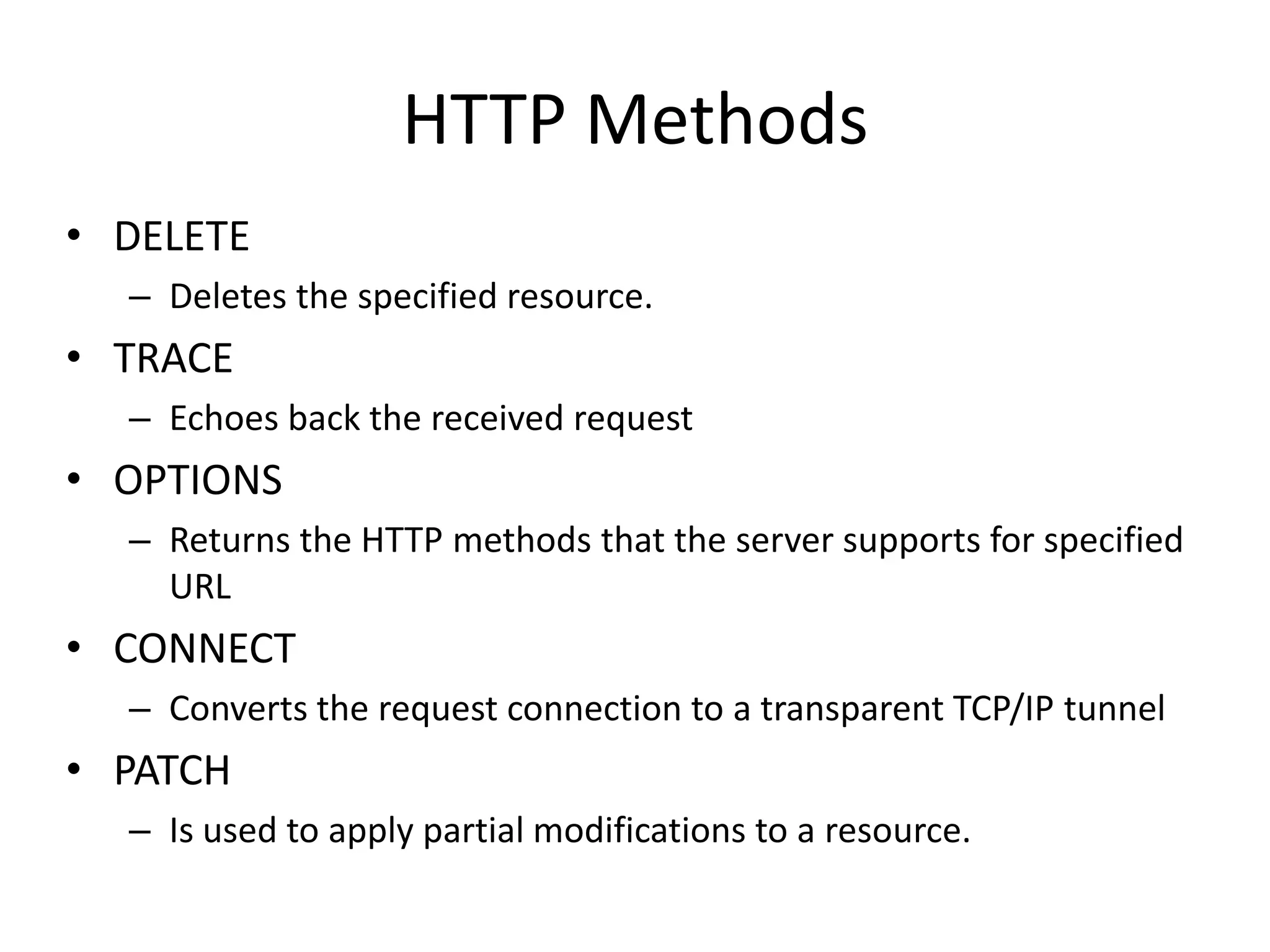
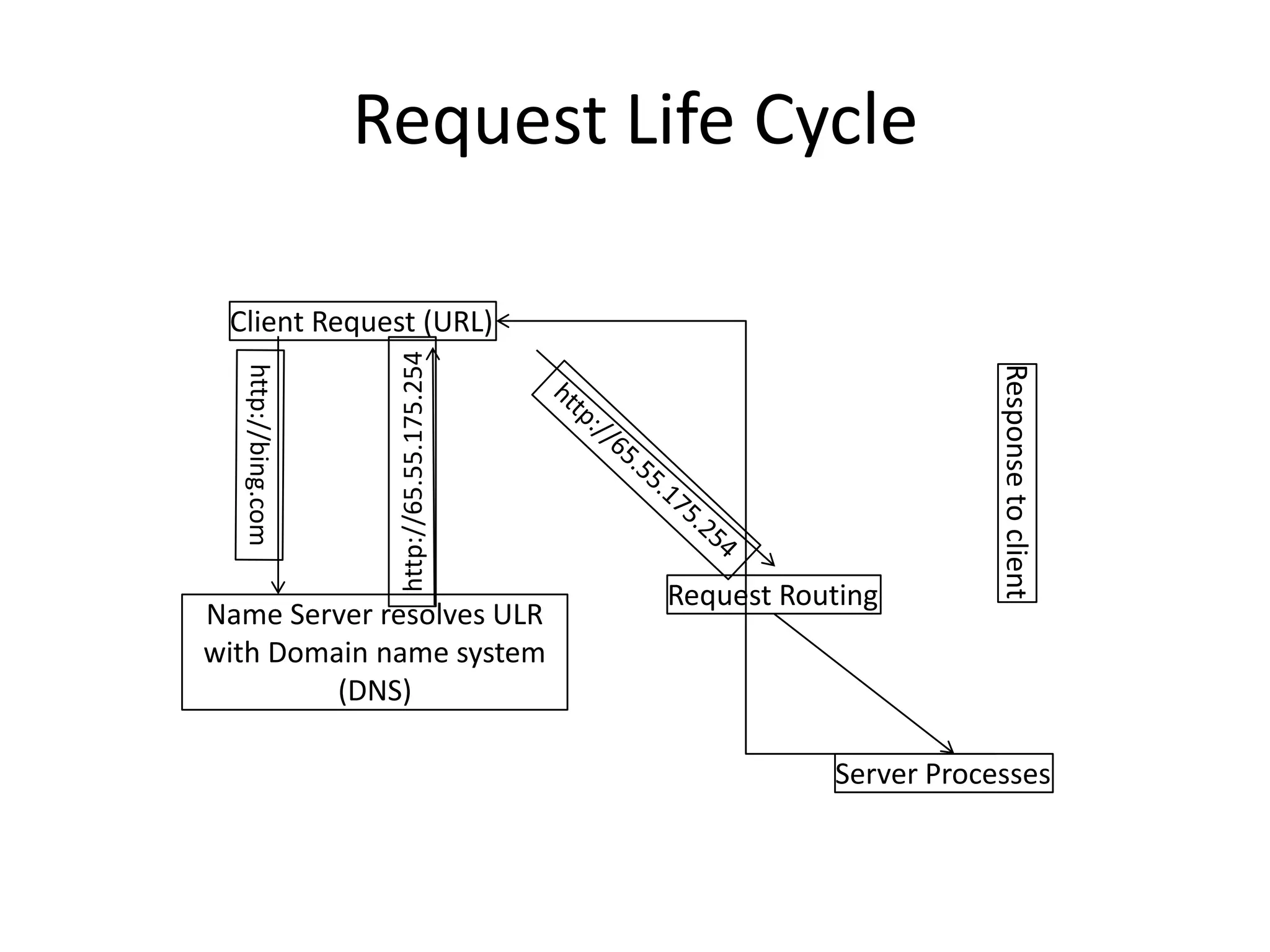
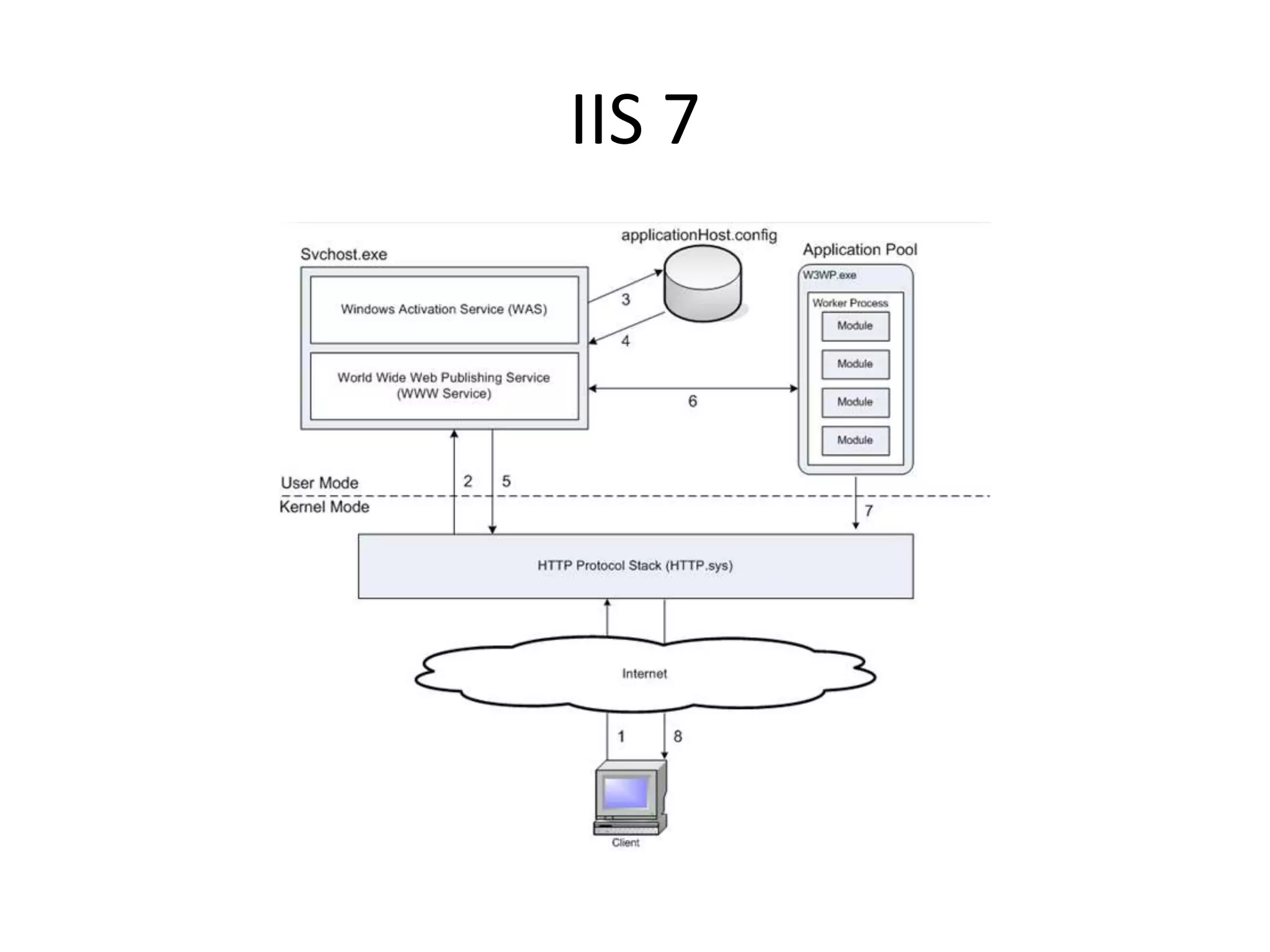
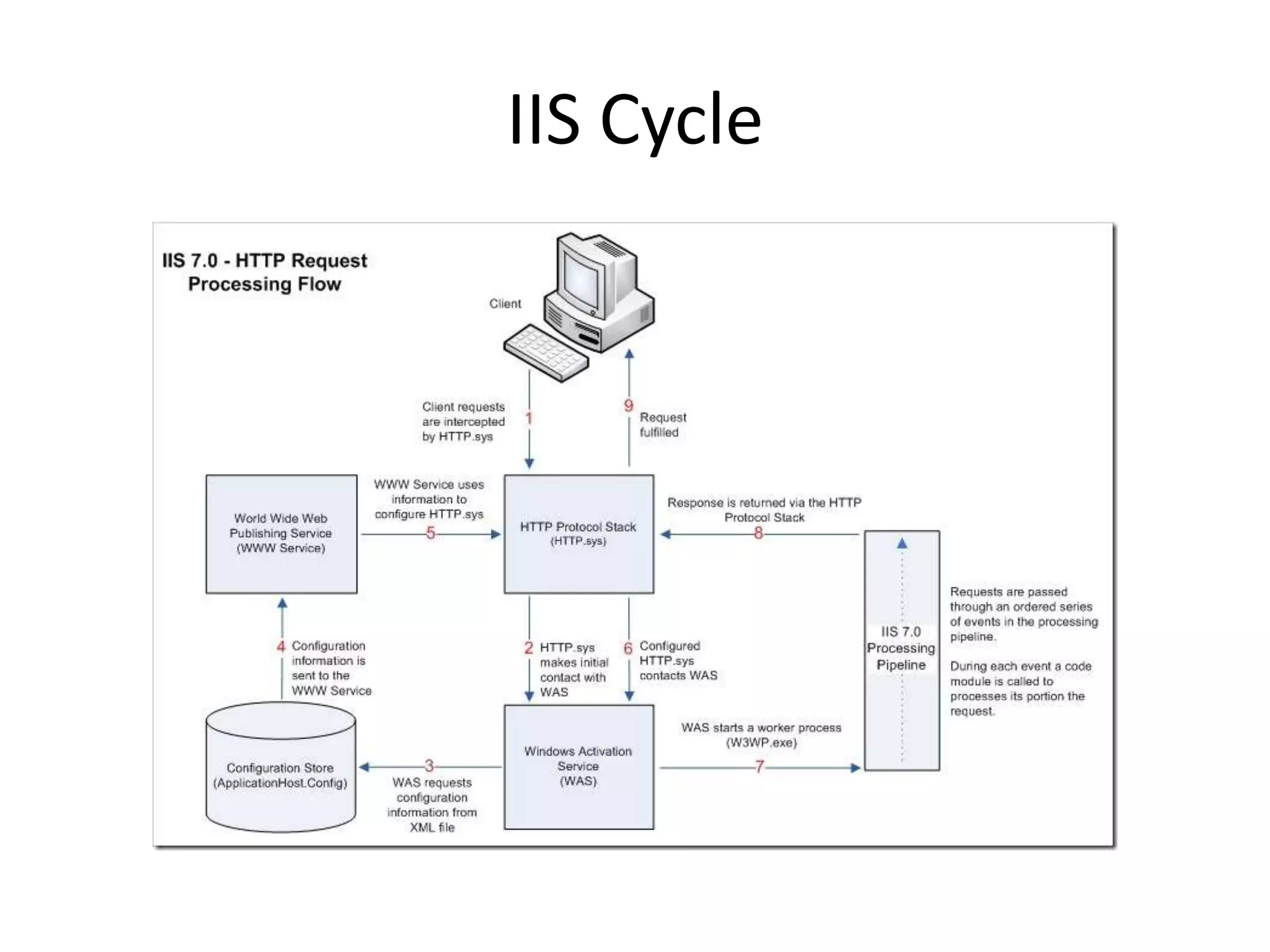
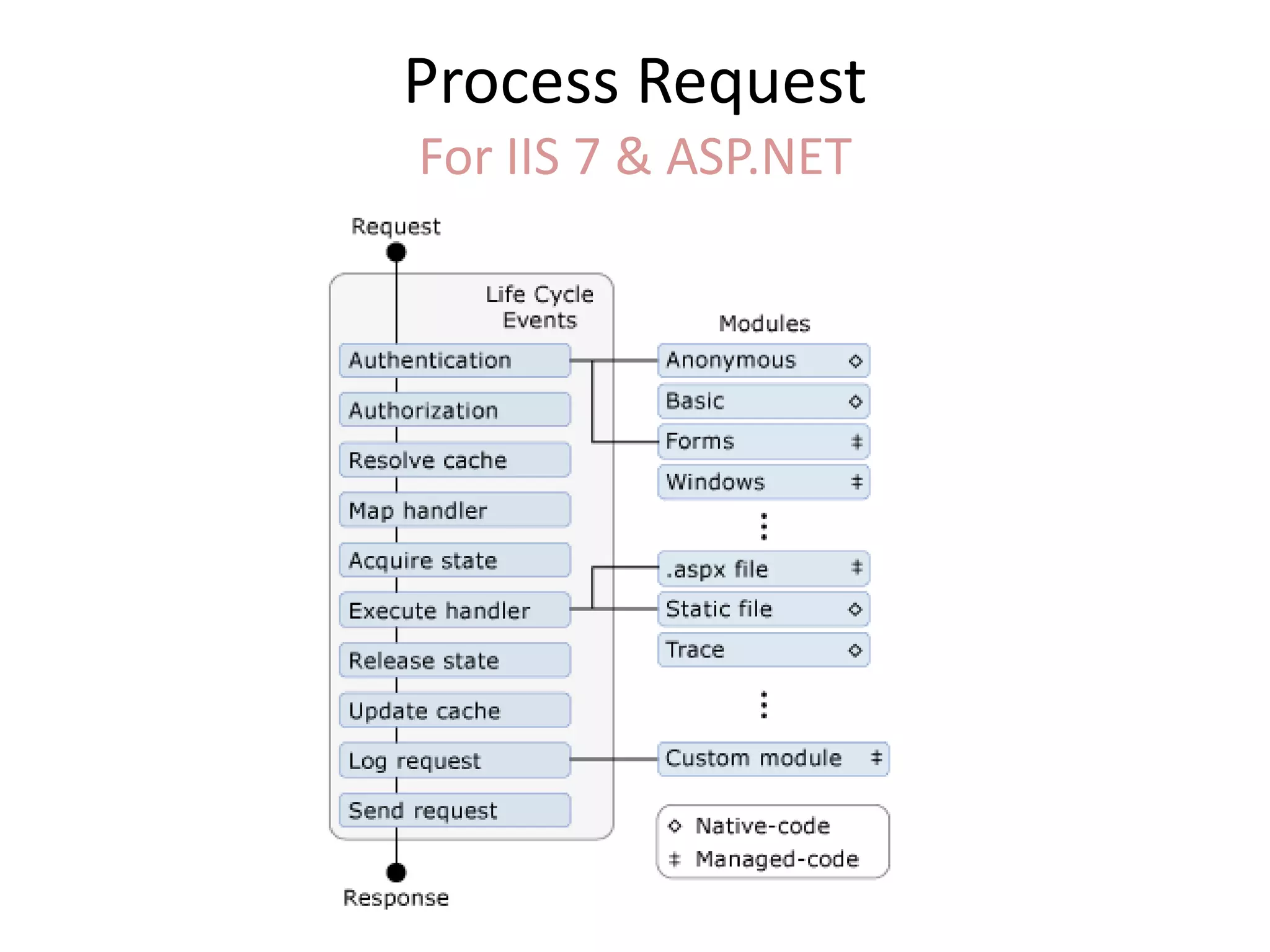
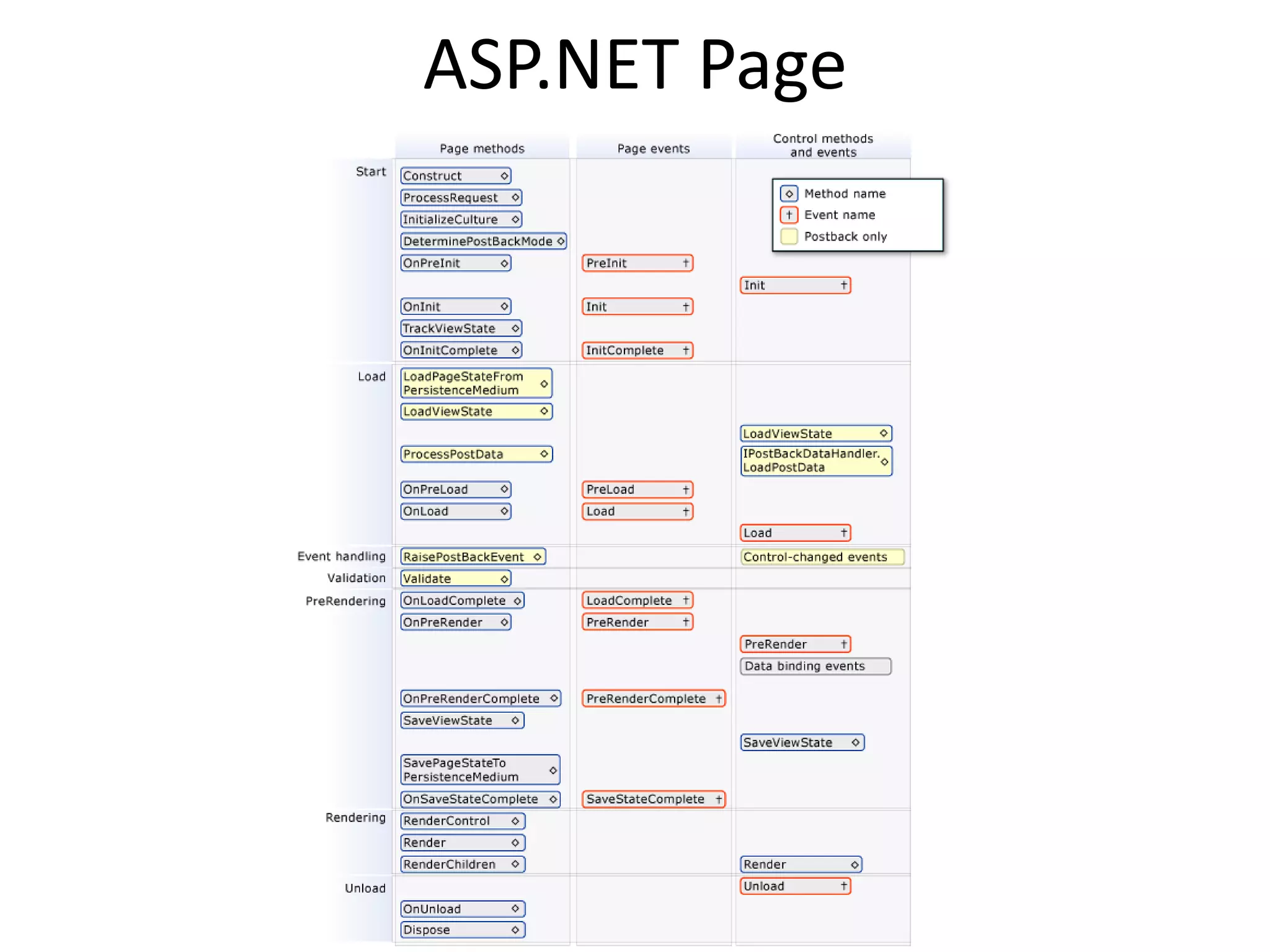
This document provides an overview of how the web developed from early packet-switched networks and protocols in the 1960s to modern web applications. It discusses the layers of the Internet Protocol Suite including application, transport, internet, and link layers. Key components that enable the web are explained such as HTTP, web servers, browsers, and how requests are processed. The document also introduces ASP.NET and the model-view-controller (MVC) framework for building web applications.