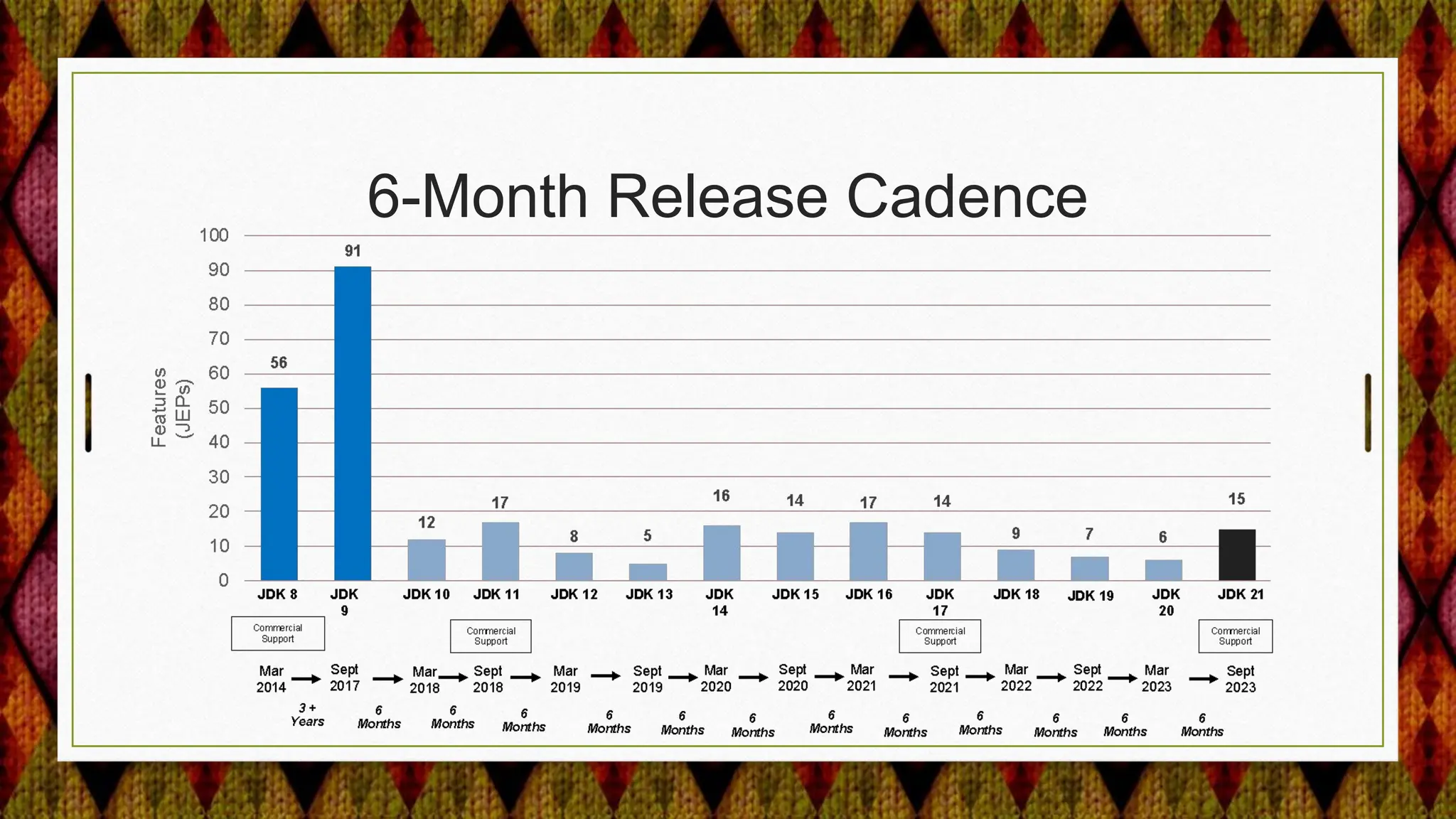
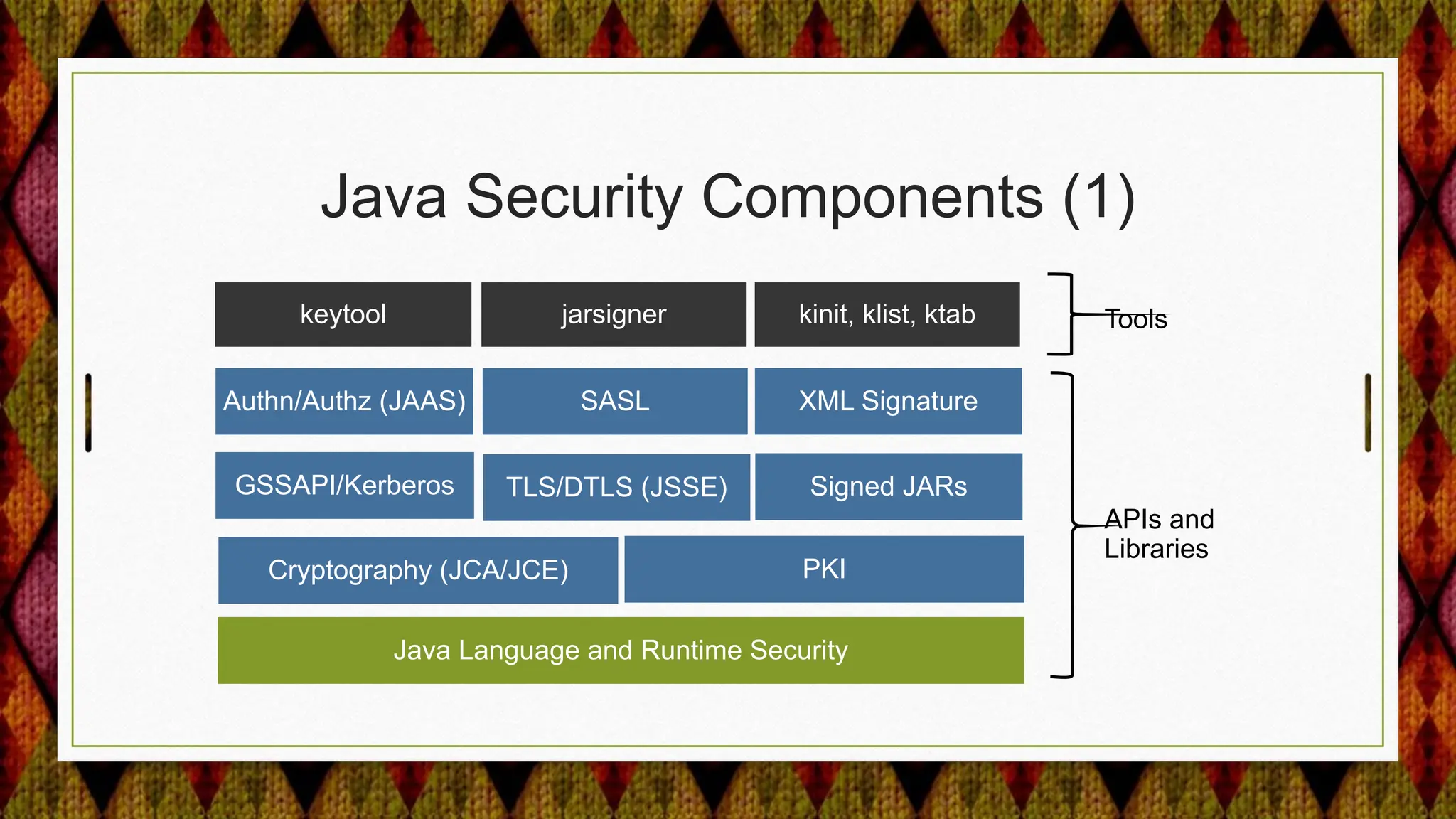
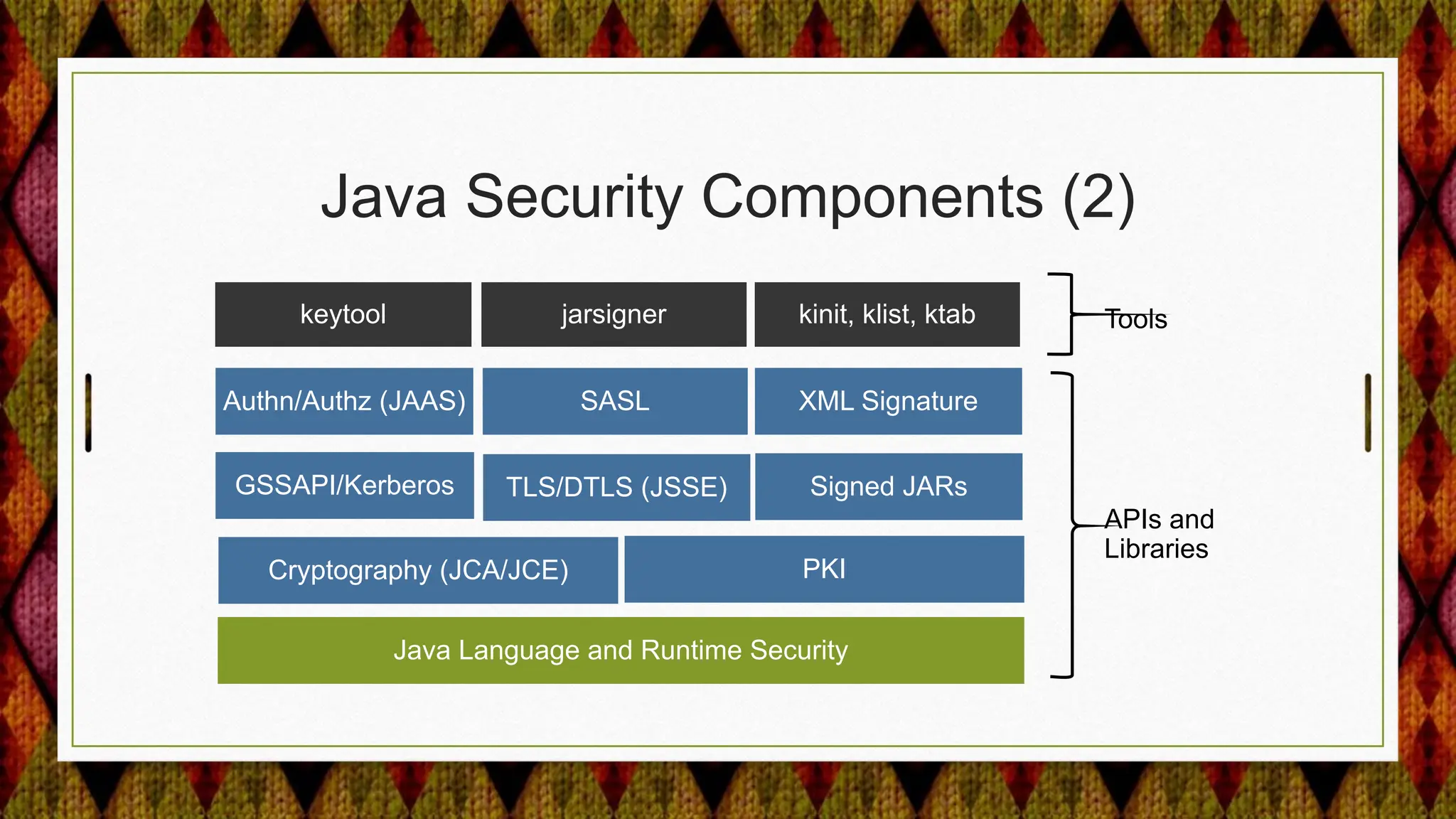
From Java 17 to 21, the JDK made several security enhancements, including:
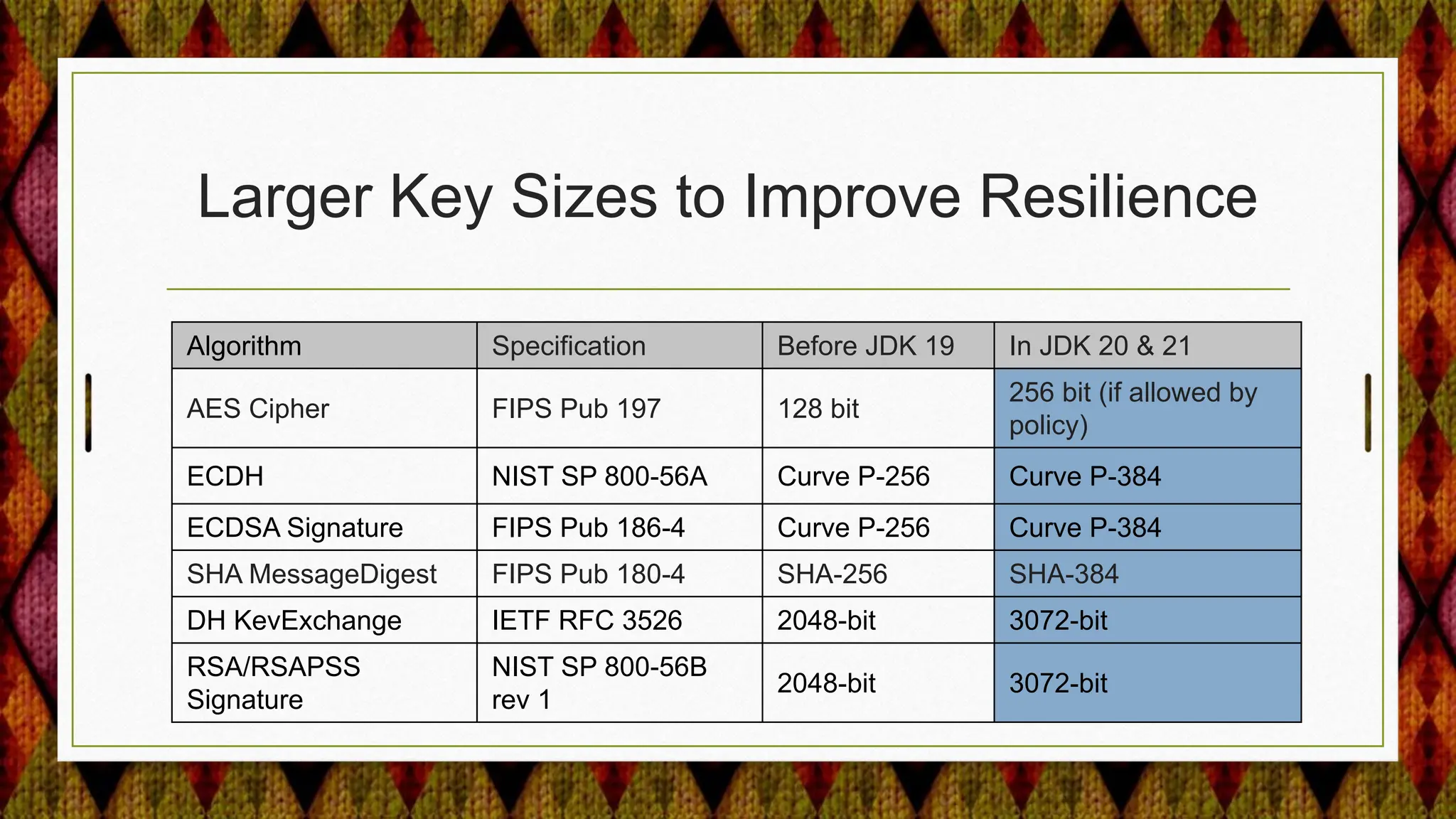
1) Using larger key sizes by default for cryptographic algorithms like AES, ECDSA, and DH to improve resilience against attacks.
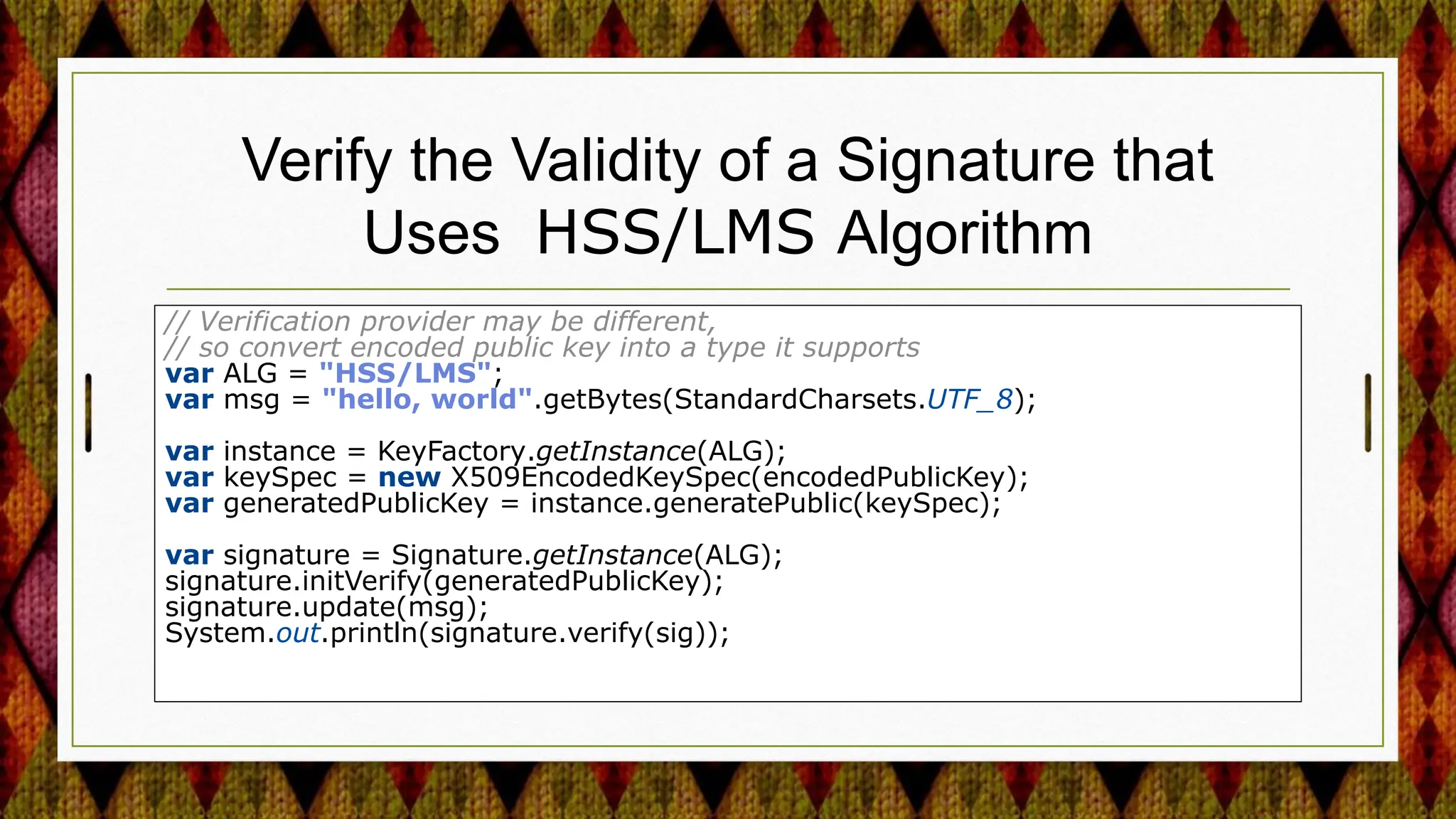
2) Adding support for post-quantum cryptography algorithms like HSS/LMS signature verification.
3) Restricting or disabling weak algorithms like SHA-1, 3DES, and RC4 by default.
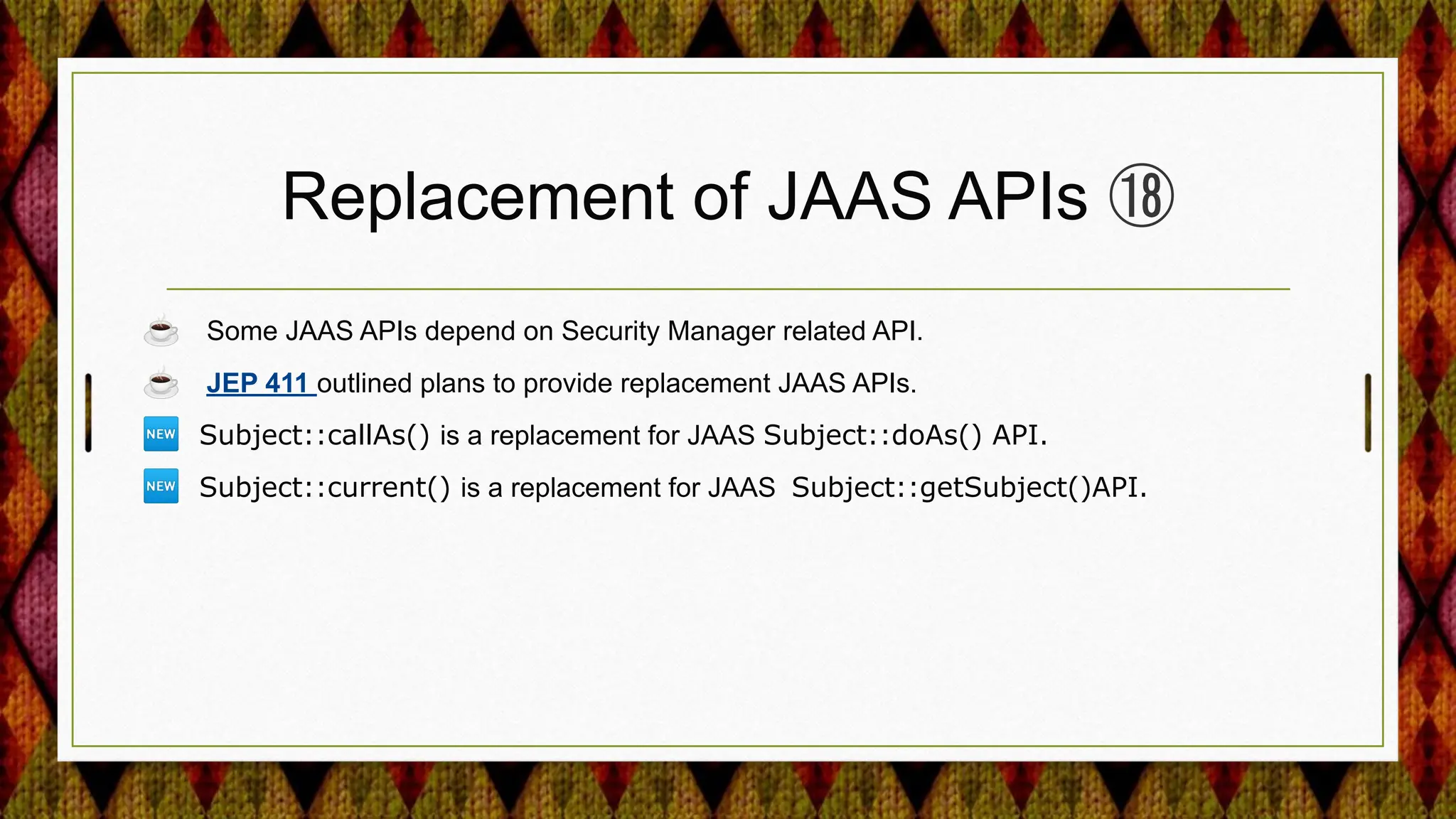
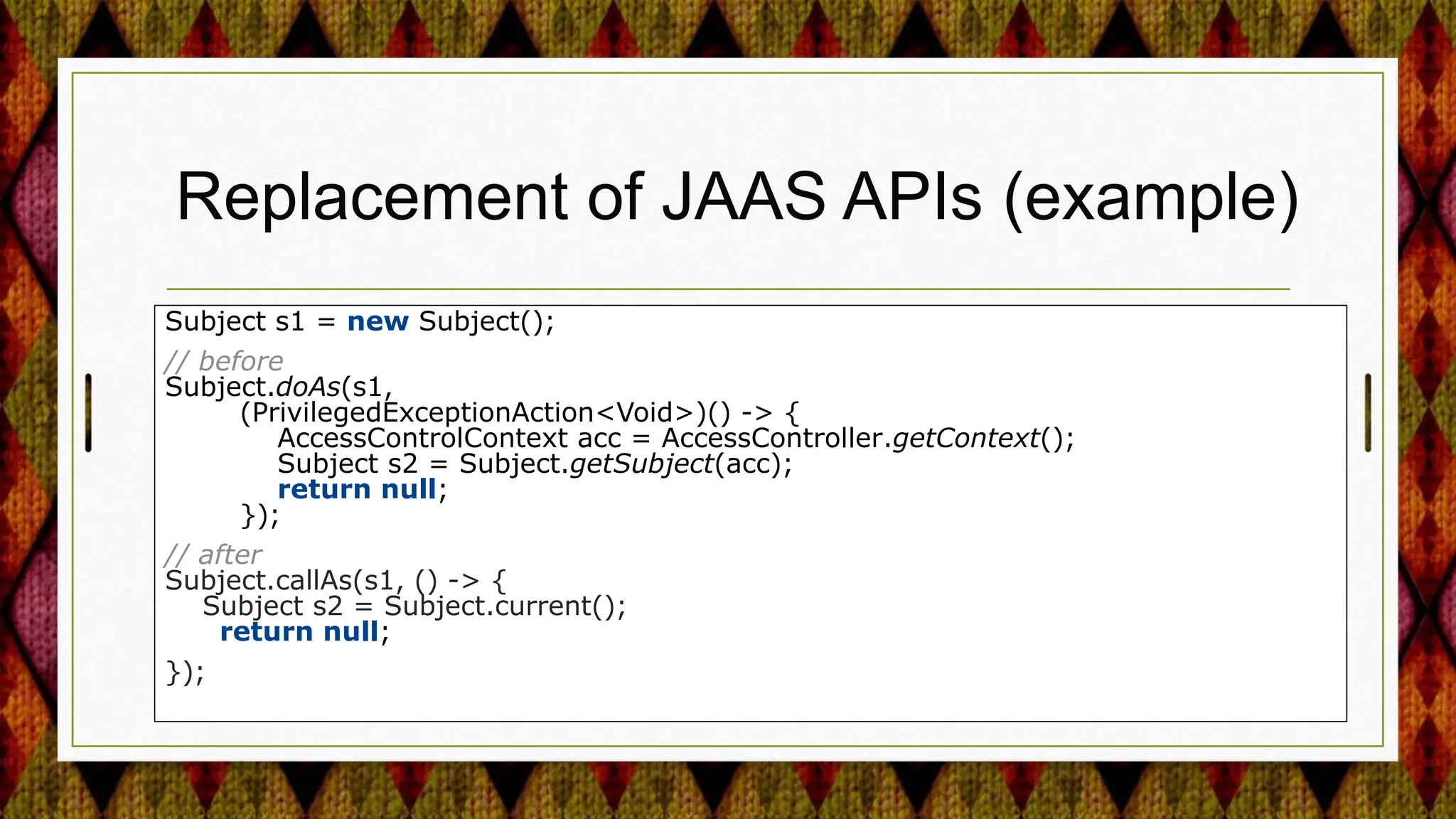
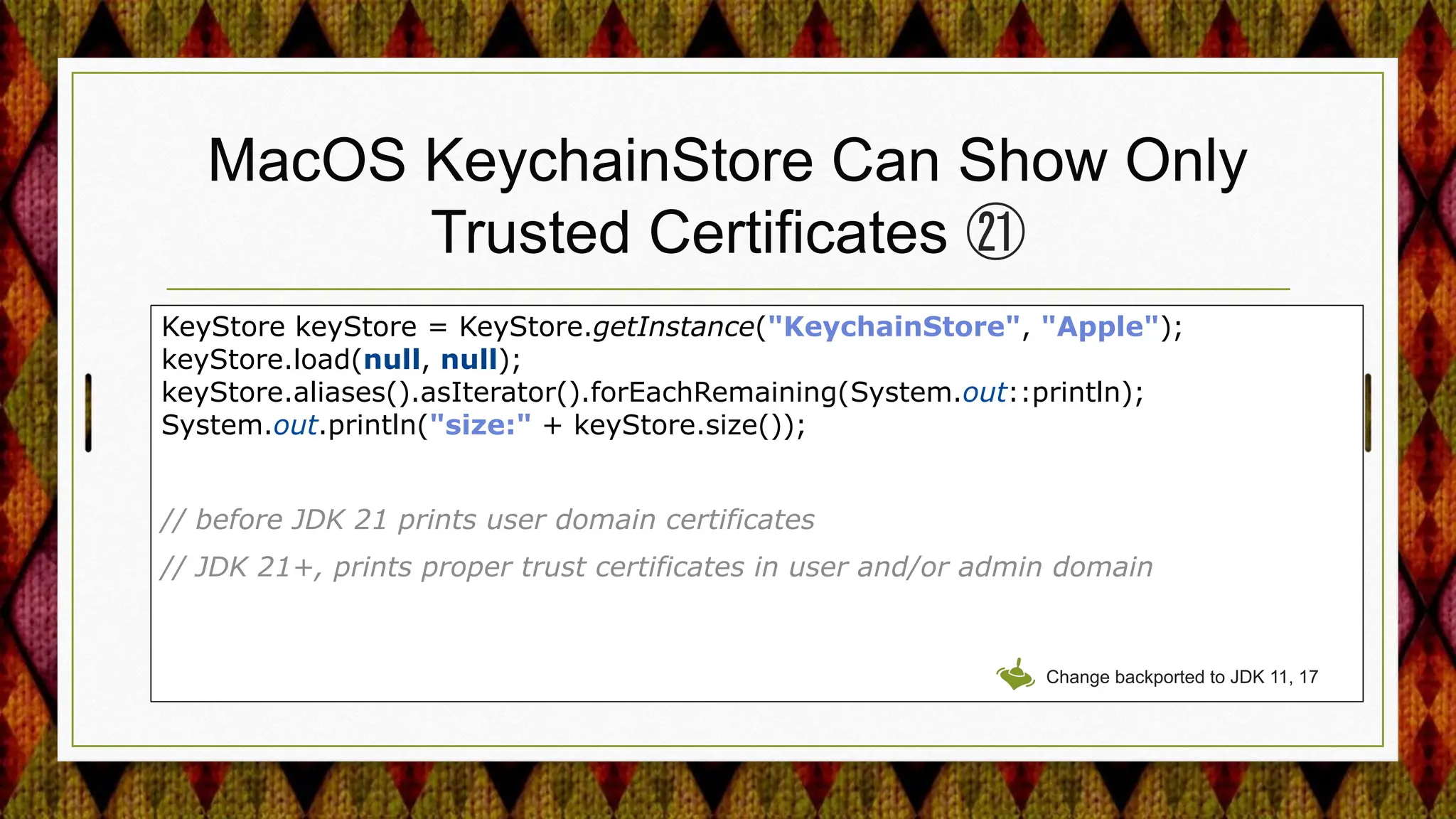
4) Improving security APIs and providing replacements for deprecated ones like the Security Manager and parts of JAAS.














![Removed Weak Kerberos Encryption
Types
#krb5.conf
[libdefaults]
allow_weak_crypto = false
permitted_enctypes =
es256-cts-hmac-sha1-96
aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96
des3-cbc-sha1 …
☕ DES,3DES and RC4 have been removed
from the default list of Kerberos encryption
types. ⑱
⛔ If allow_weak_crypto = true, any of the
weak encryption types could then be used!
☕ You can selectively enable weak algorithms in
Kerberos, by specifically adding the weak
algorithm(s) name to permitted_enctypes in
krb5.conf.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fromjava17to21-ashowcaseofjdksecurityenhancements-240204082615-b6f734e6/75/From-Java-17-to-21-A-Showcase-of-JDK-Security-Enhancements-21-2048.jpg)





![APIs to Customize TLS and DTLS
Signature Schemes ⑲
SSLParameters sslParams = new SSLParameters();
sslParams.setEndpointIdentificationAlgorithm("HTTPS");
String[] sigSchemes = {"rsa_pkcs1_sha512", "rsa_pkcs1_sha384"};
sslParams.setSignatureSchemes(sigSchemes);
New javax.net.ssl.SSLParameters::setSignatureSchemes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fromjava17to21-ashowcaseofjdksecurityenhancements-240204082615-b6f734e6/75/From-Java-17-to-21-A-Showcase-of-JDK-Security-Enhancements-29-2048.jpg)
![APIs to Customize TLS and DTLS Named
Groups ⑳
SSLParameters params = new SSLParameters();
params.setNamedGroups(new String[] { "x25519", "secp256r1" });
New javax.net.ssl.SSLParameters::setNamedGroups](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fromjava17to21-ashowcaseofjdksecurityenhancements-240204082615-b6f734e6/75/From-Java-17-to-21-A-Showcase-of-JDK-Security-Enhancements-30-2048.jpg)





![Fine Tune Usage of XPath here()Function ㉑
<!-- select node-sets for use in XPath
transforms..-->
<XPath xmlns:dsig="&dsig;">
count(ancestor-or-self::dsig:Signature |
here()/ancestor::dsig:Signature[1]) >
count(ancestor-or-self::dsig:Signature)</XPat
h>
☕ here() is not a standard XPath function
🆕 jdk.xml.dsig.hereFunctionSupported
☕ The security property has default value true.
Also backported to JDK 8u,11u, 17u](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fromjava17to21-ashowcaseofjdksecurityenhancements-240204082615-b6f734e6/75/From-Java-17-to-21-A-Showcase-of-JDK-Security-Enhancements-37-2048.jpg)






![Keytool Improvements (2)
☕ Uses larger default key sizes in -genkeypair if -keysize option is not specified.
☕ -genseckey and -importpass options warn when using weak password-based encryption
algorithms. ㉑
$ keytool -genseckey -alias secret -keypass changeit -keyalg RC4
-keysize 128 -keystore example.p12 -storepass changeit
-storetype PKCS12 -v
Generated 128-bit ARCFOUR secret key [Storing example.p12]
Warning: The generated secret key uses the ARCFOUR algorithm which is
considered a security risk.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fromjava17to21-ashowcaseofjdksecurityenhancements-240204082615-b6f734e6/75/From-Java-17-to-21-A-Showcase-of-JDK-Security-Enhancements-45-2048.jpg)