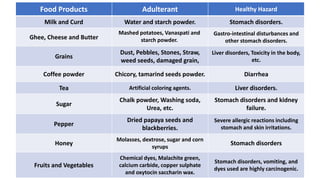
This document discusses food adulteration, including definitions, types, causes, health hazards, and methods for detection. It defines food adulteration as adding non-food substances to increase quantity or reduce quality. There are four main types of adulteration: intentional, metallic, incidental, and packaging. Common causes include profit motive and meeting high population demand. Health hazards range from cancer and organ damage to allergic reactions. Detection methods include tests for impurities, iodine levels, acid value, brix, and pH. Practical examples provided include procedures for testing salt, oil, and fruit juice quality.