The document describes the process planning and cost estimation for manufacturing a flange coupling. It includes the following:
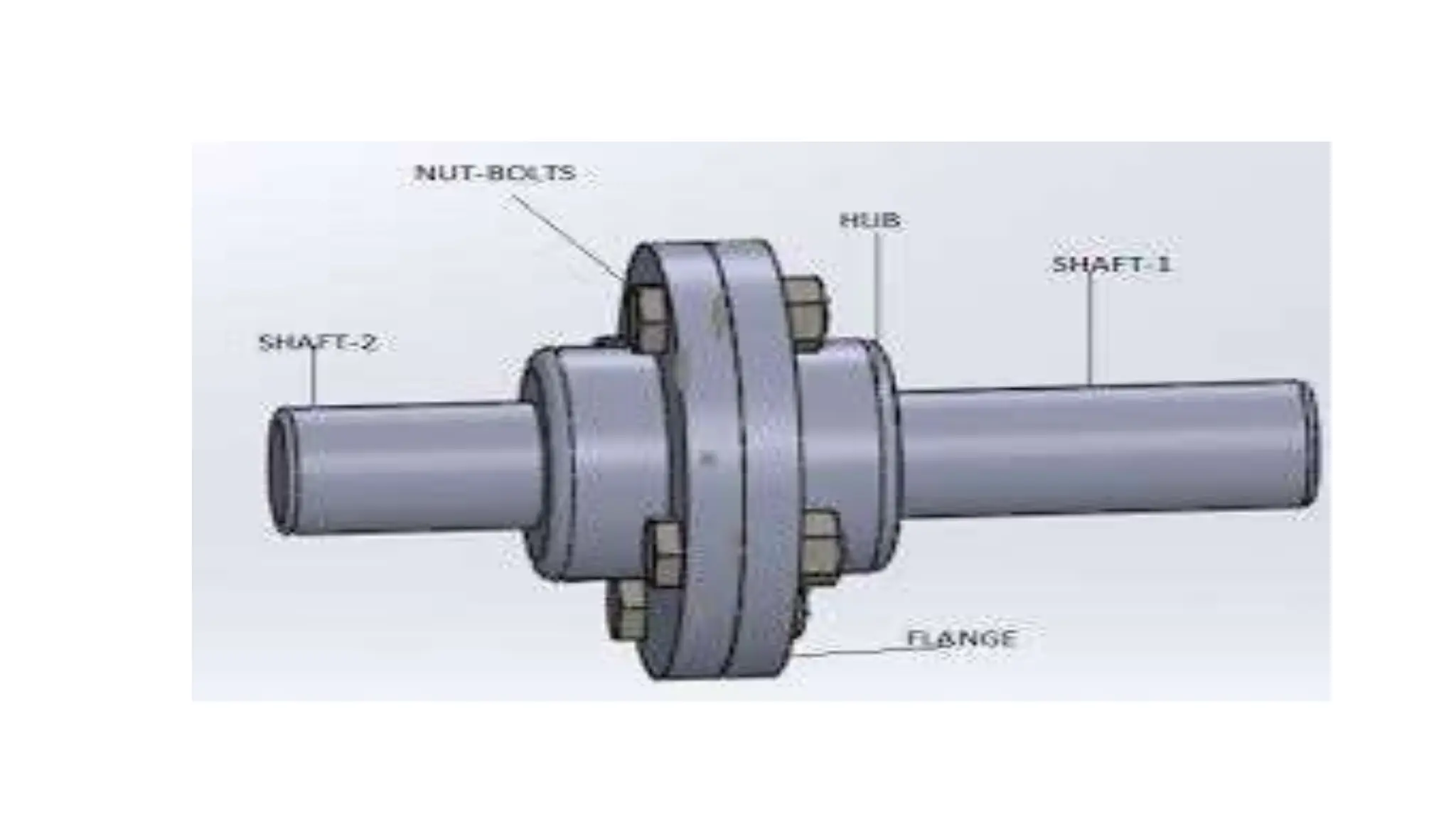
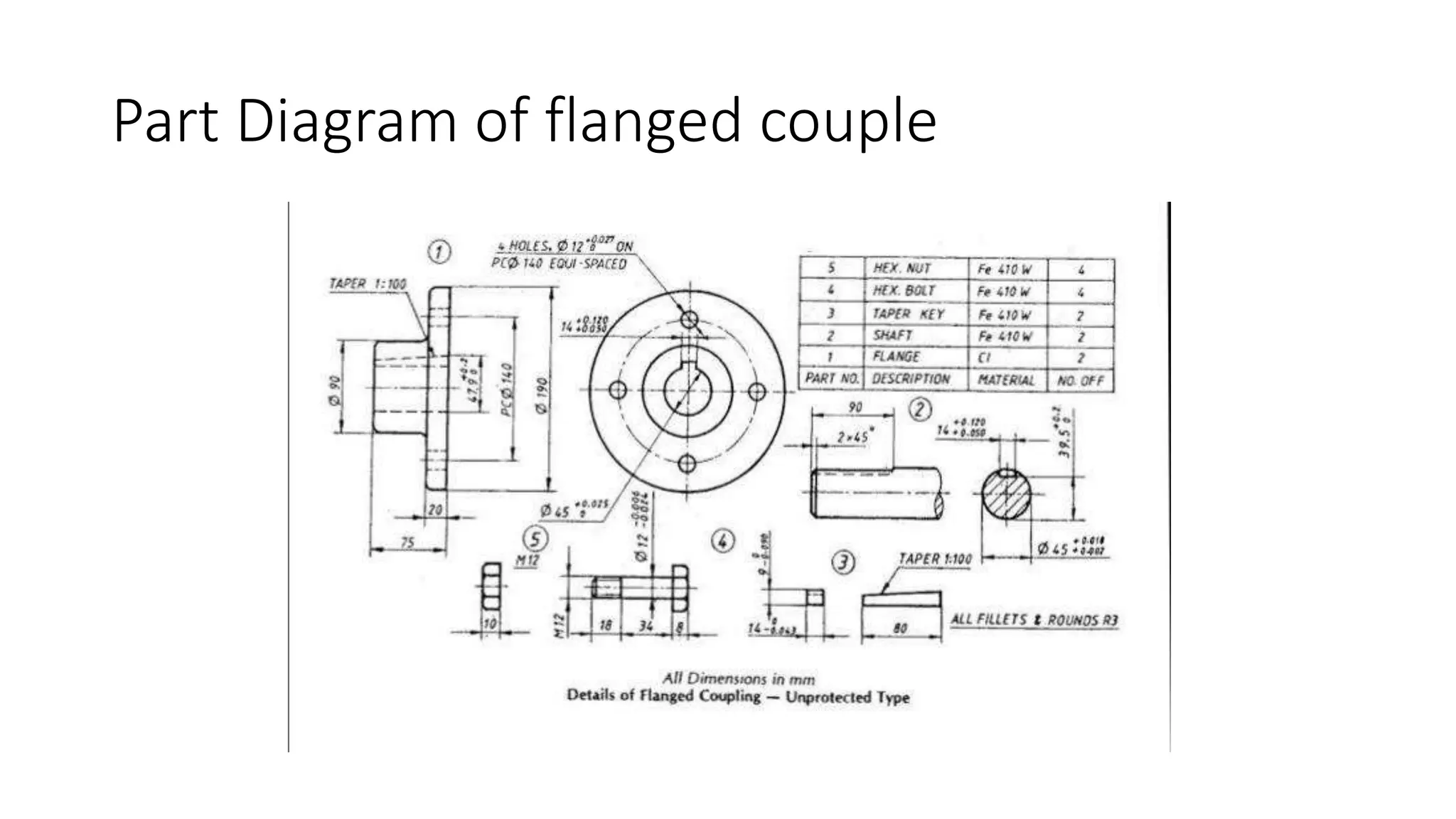
- Descriptions of the parts of a flange coupling including hexagonal nuts, bolts, taper keys, shafts, and flanges.
- Explanations of the manufacturing processes like forging and CNC turning used to make the parts.
- Calculations of the volumes, masses, and material costs for each part based on the given dimensions.
- A total material cost of Rs. 1361.915 for all parts, additional costs of Rs. 67.44 for metal lost and Rs. 16.66 for labor, for a total estimated cost of Rs. 1446