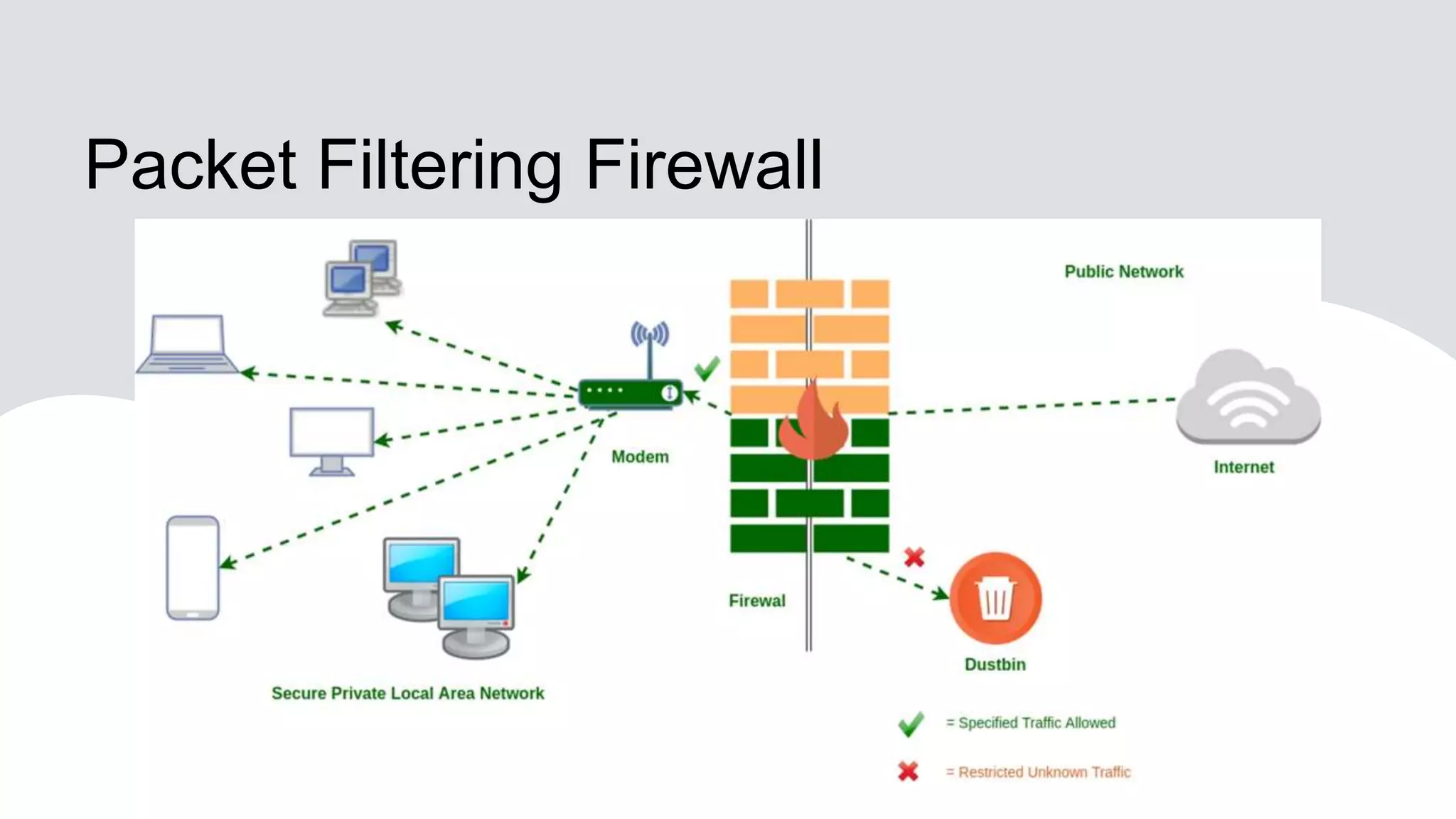
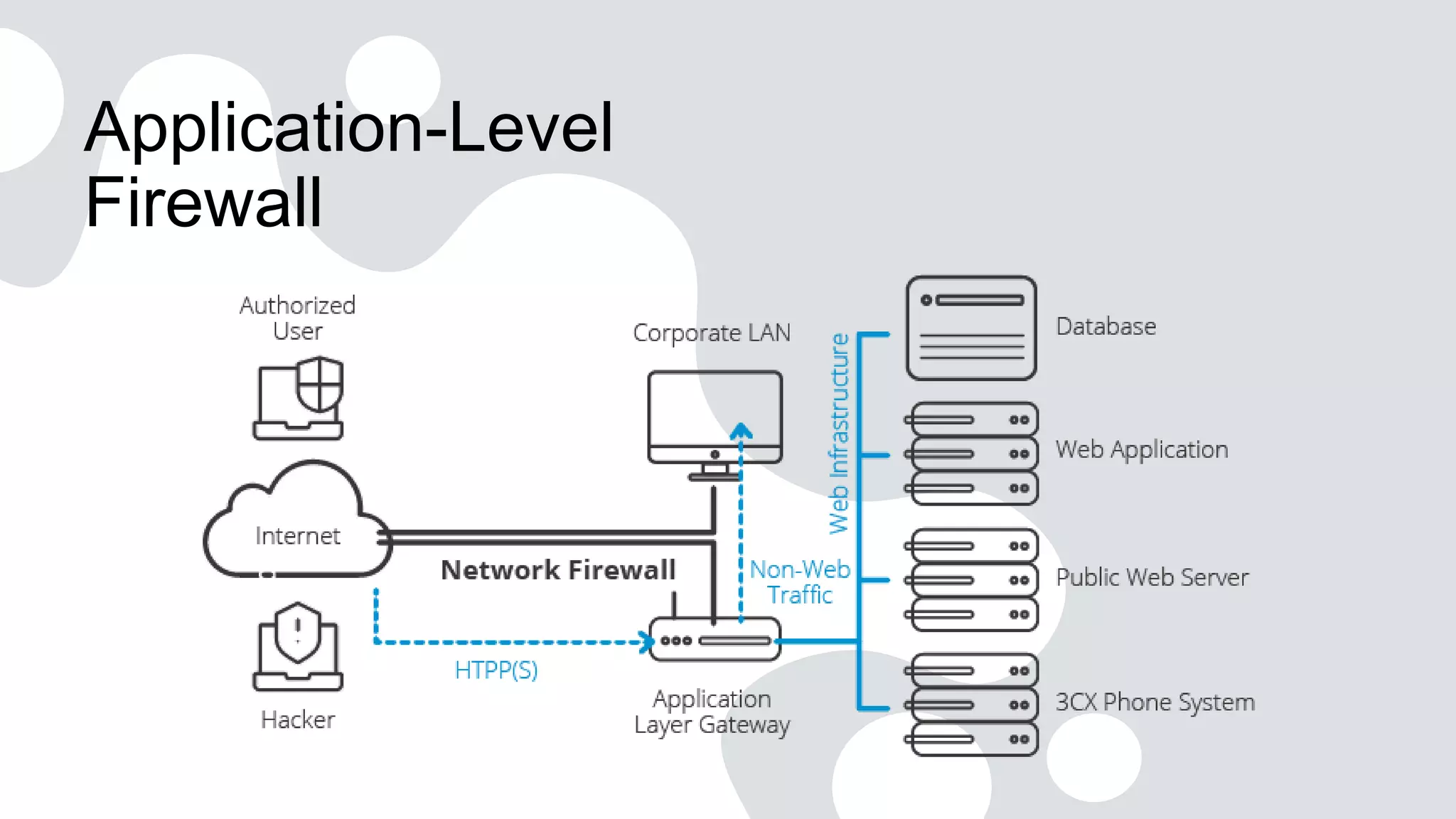
Firewall is a crucial network security component that acts as a barrier between internal networks and the external world, enforcing access control policies and protecting against unauthorized access. There are several types of firewalls including packet filtering firewalls, stateful inspection firewalls, application-level firewalls, next-generation firewalls, and unified threat management firewalls. Packet filtering firewalls operate at the network layer and examine individual packets based on rules, while stateful inspection firewalls operate at the network and transport layers and track the state of network connections. Application-level firewalls operate at the application layer and act as intermediaries between clients and servers, inspecting application-layer protocols.