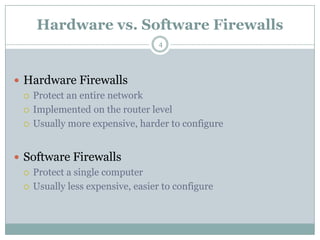
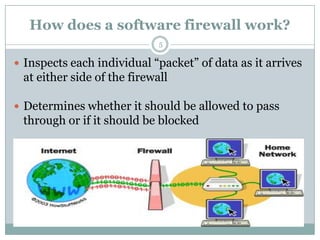
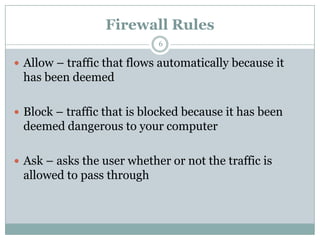
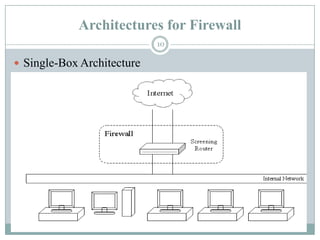
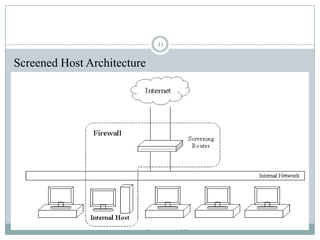
A firewall is hardware or software that protects private networks and computers from unauthorized access. There are different types of firewalls including packet filtering, application-level gateways, and circuit-level gateways. Firewalls work by inspecting packets and determining whether to allow or block them based on rules. They can protect networks and devices from hackers, enforce security policies, and log internet activity while limiting exposure to threats. However, firewalls cannot protect against insider threats, new types of threats, or viruses. Firewall configurations should be tested to ensure they are properly blocking unauthorized traffic as intended.