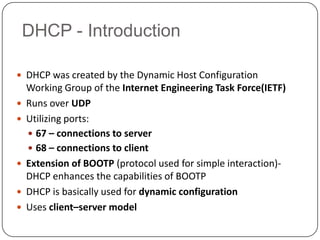
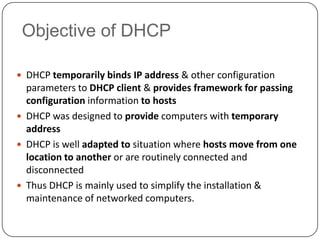
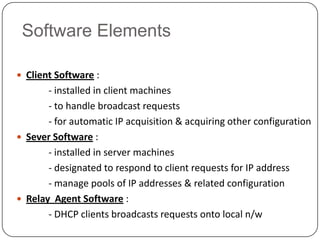
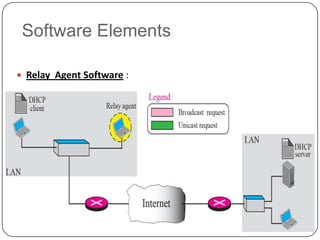
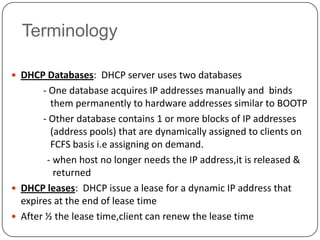
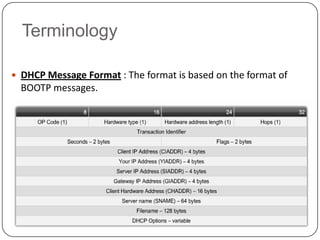
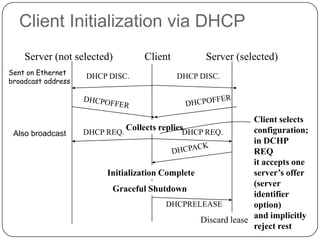
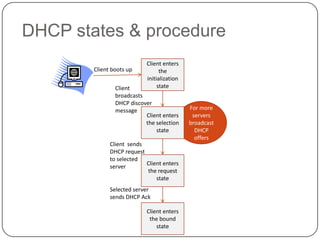
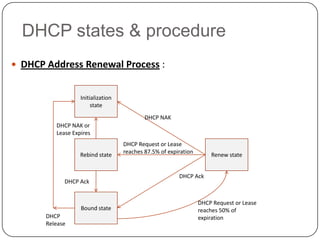
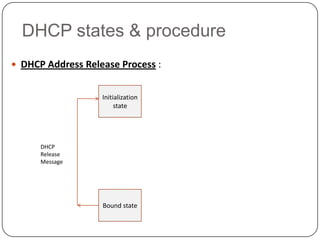
DHCP is a protocol that dynamically assigns IP addresses and other network configuration parameters to devices on a network. It uses a client-server model where DHCP clients make requests to DHCP servers which maintain pools of addresses. A DHCP client will broadcast requests at initialization and use a 4-step process to get an address assigned. It will later enter renewal states to extend its lease before initialization again if needed. This allows for efficient dynamic allocation and management of IP addresses on a network.