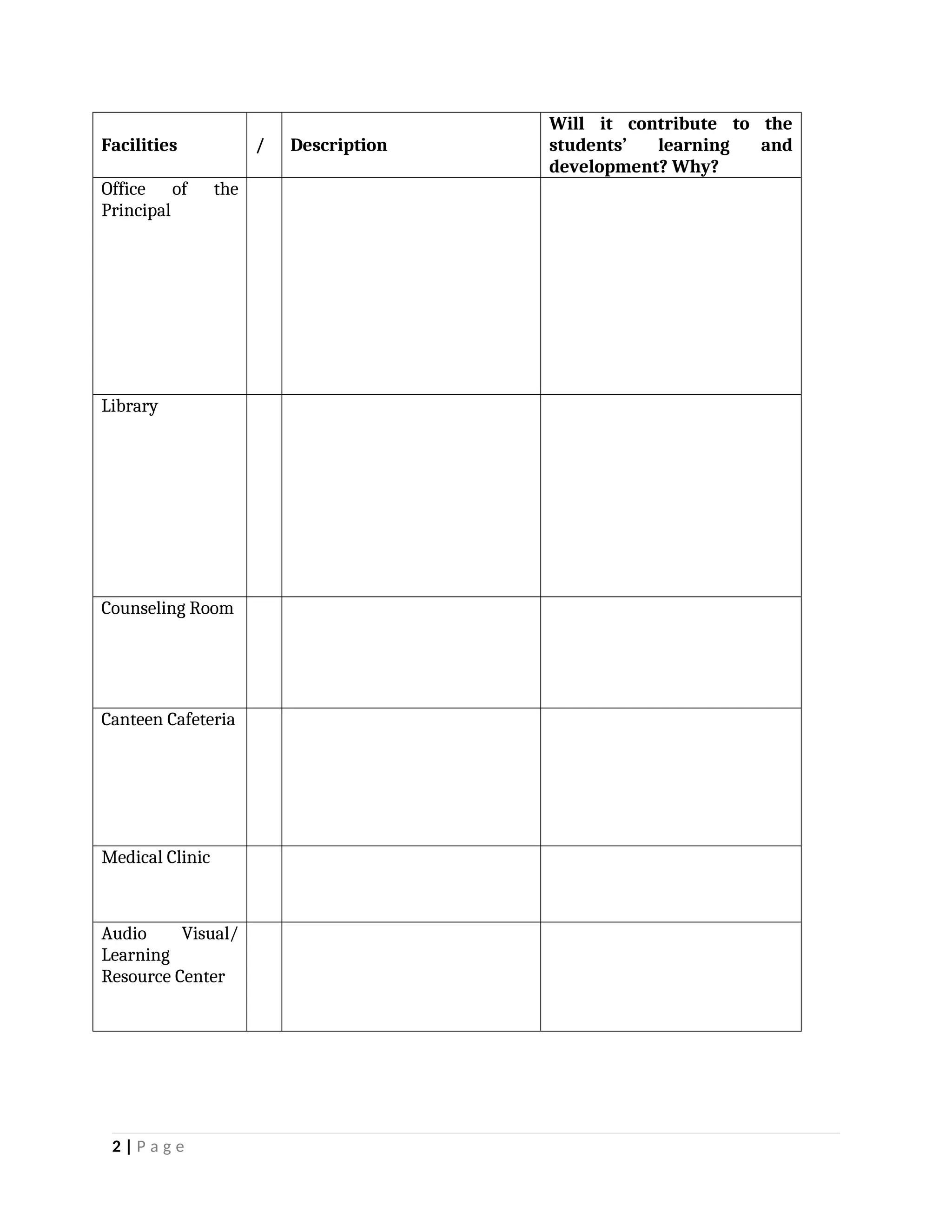
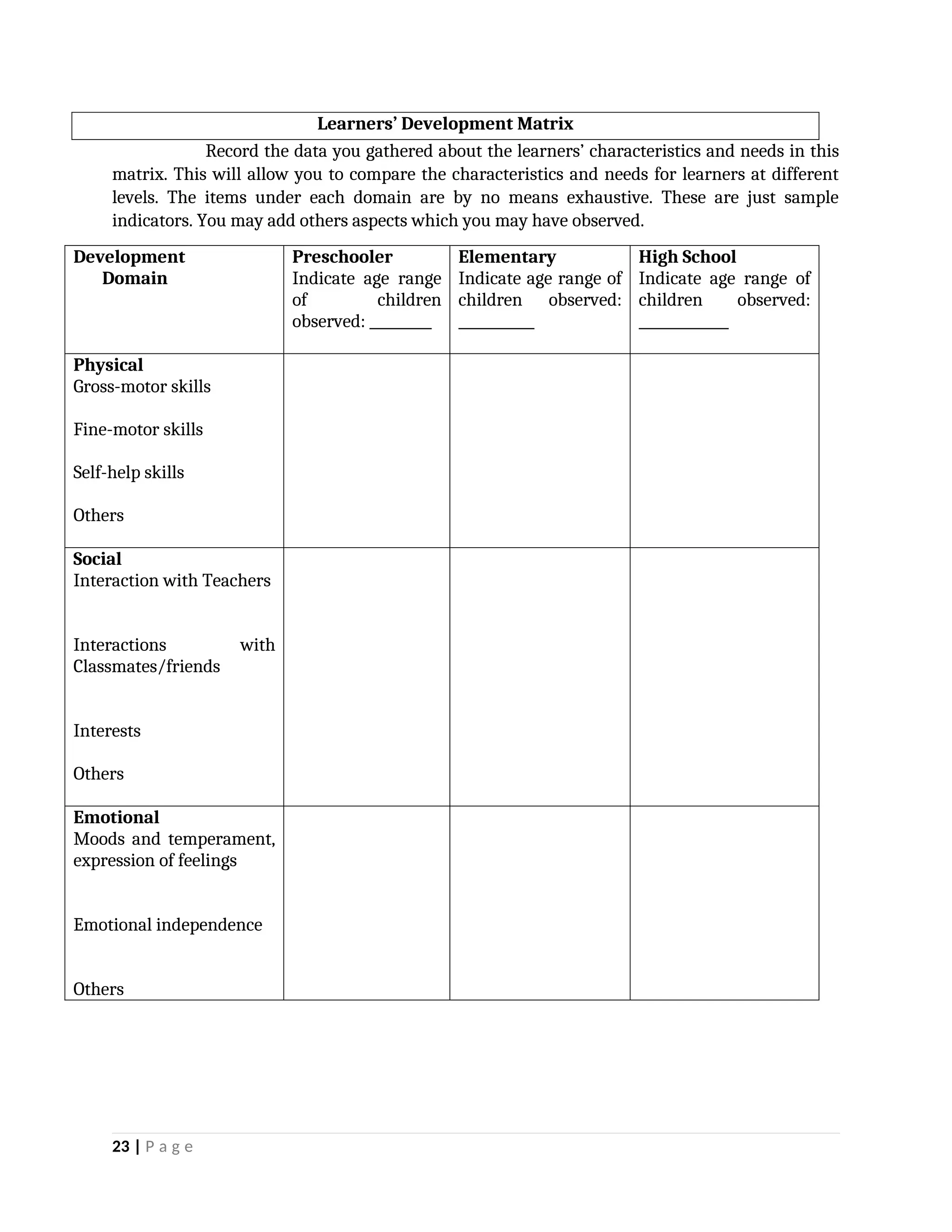
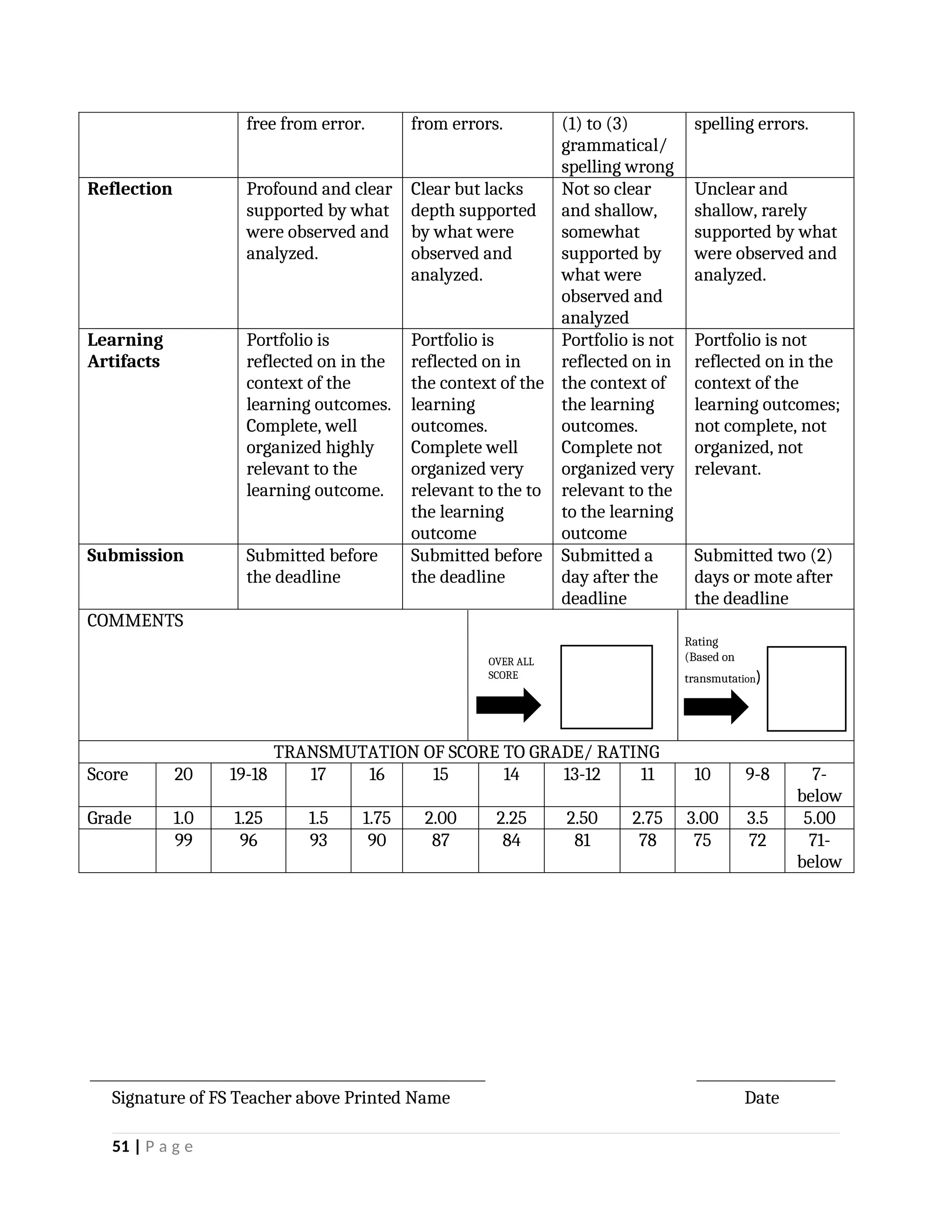
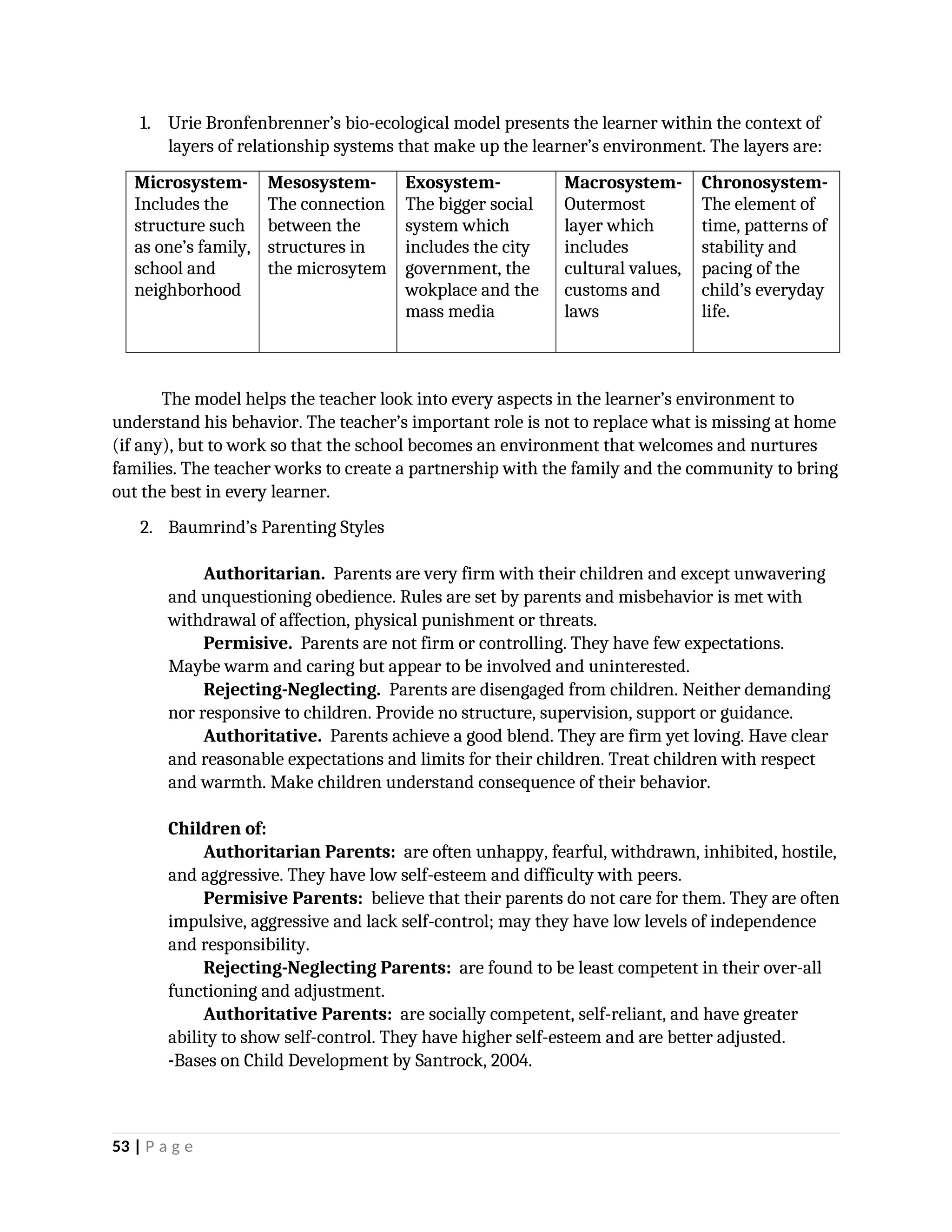
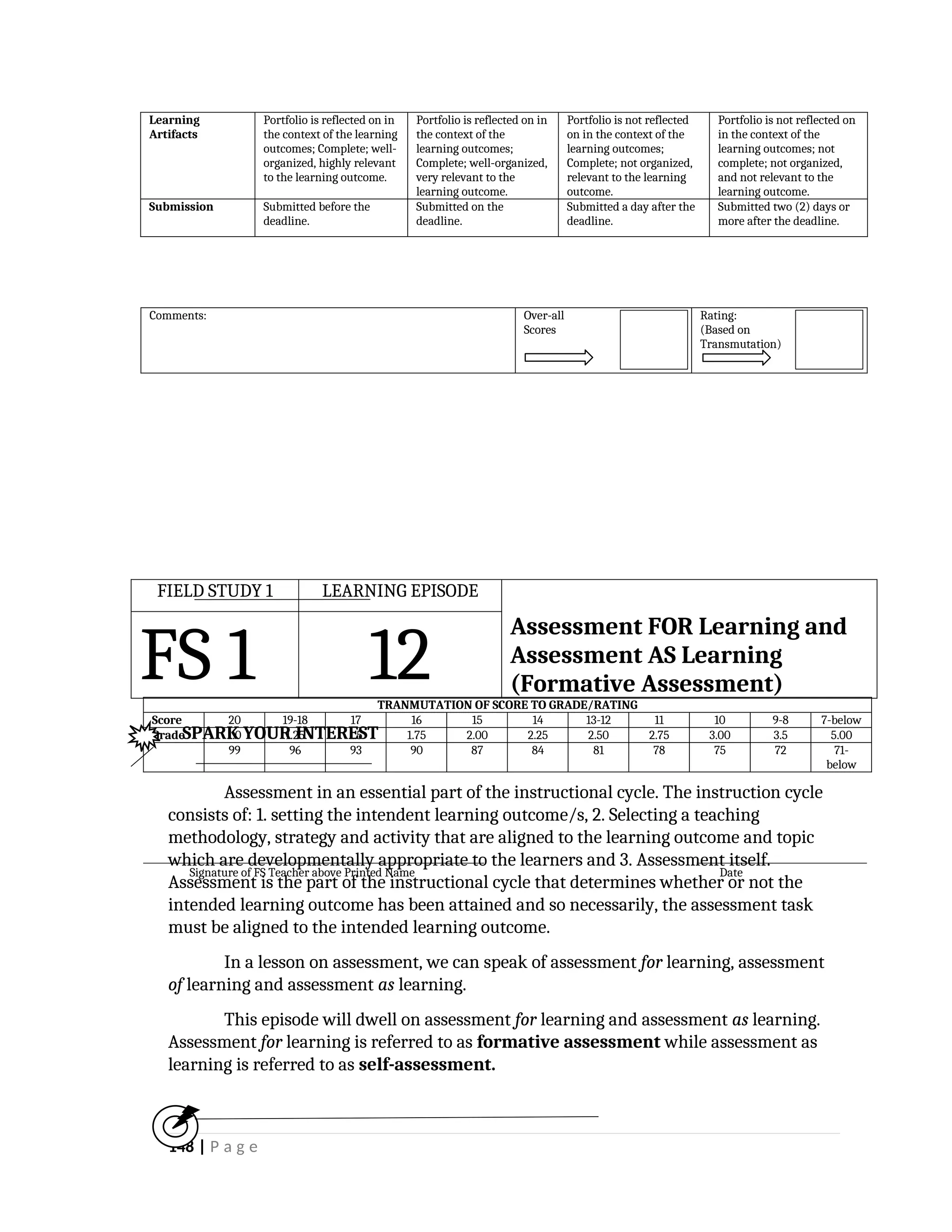
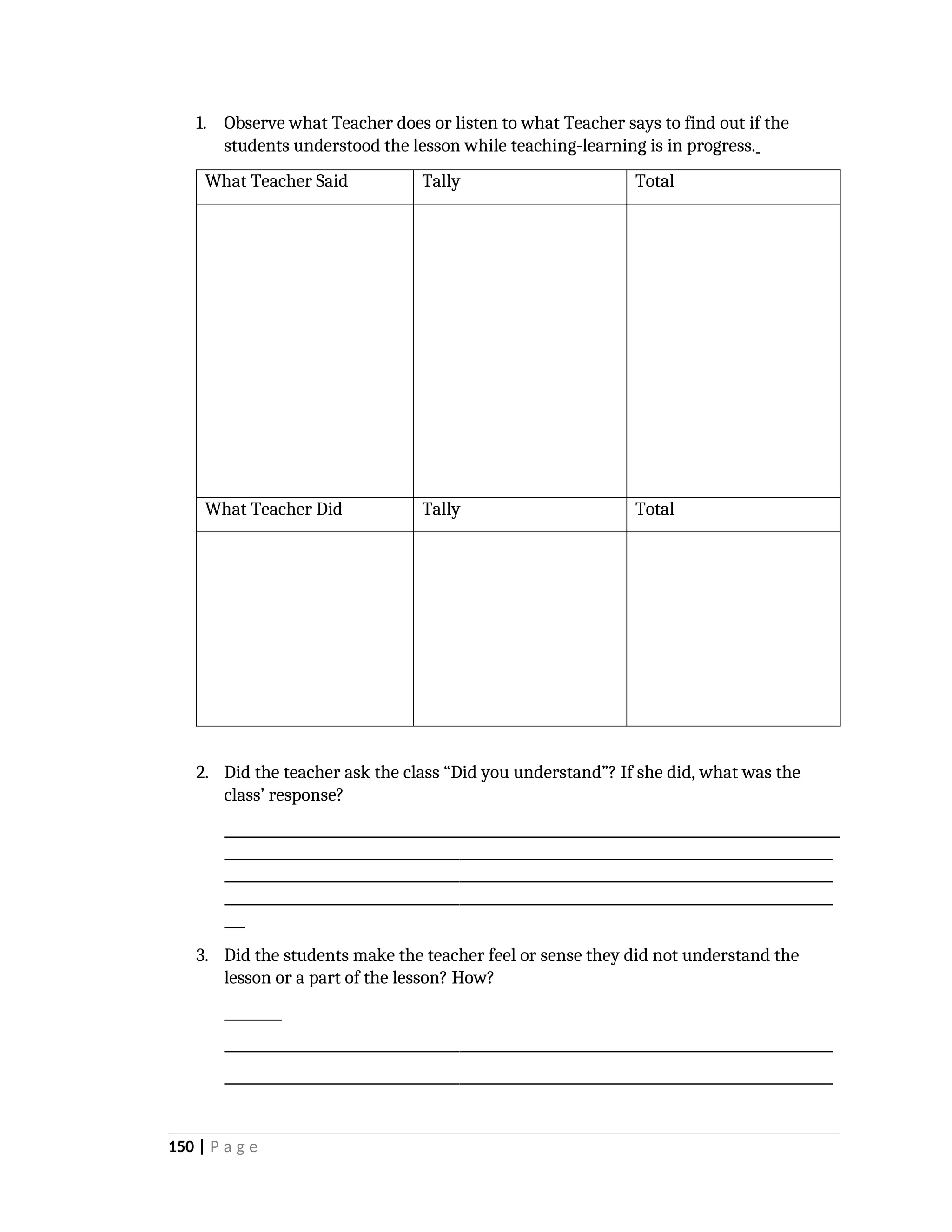
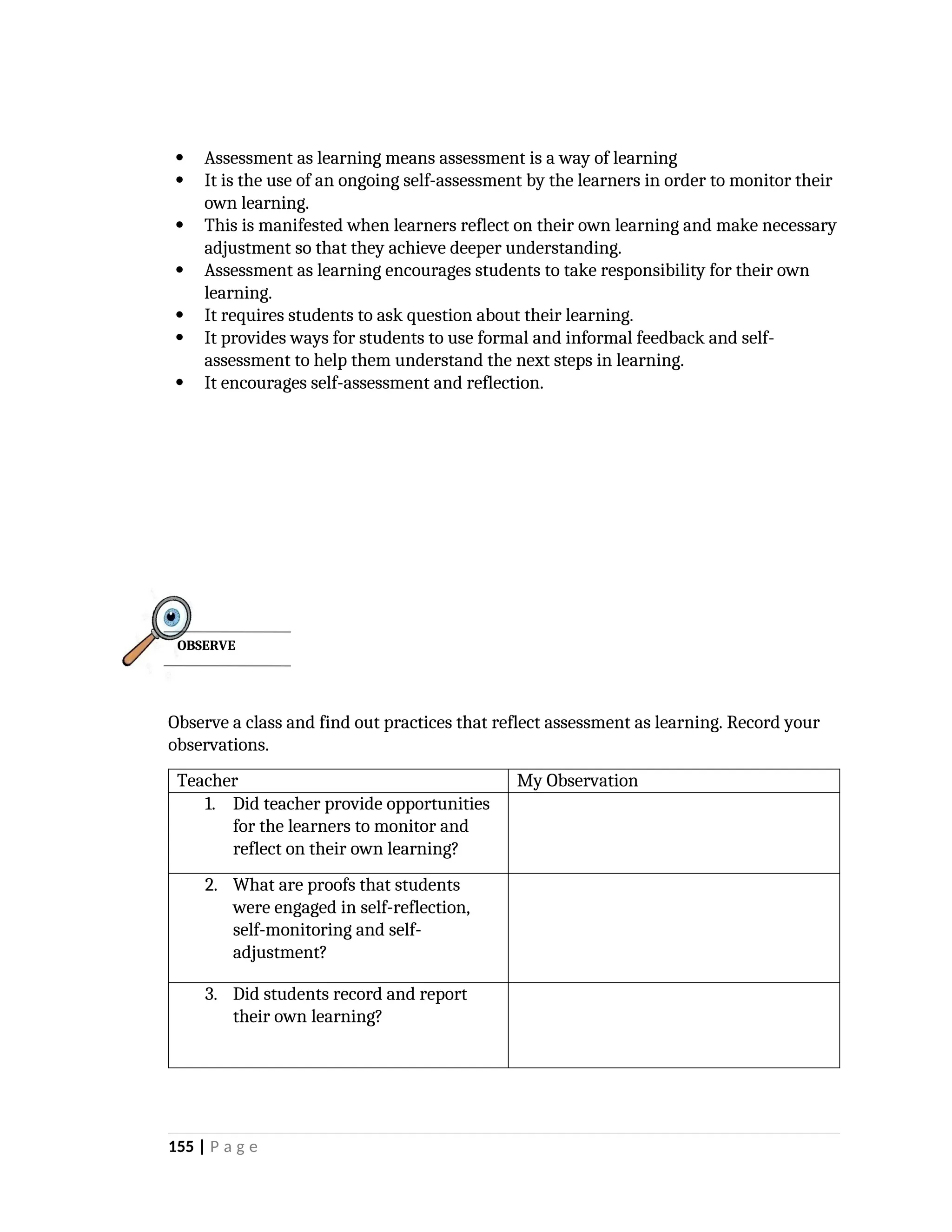
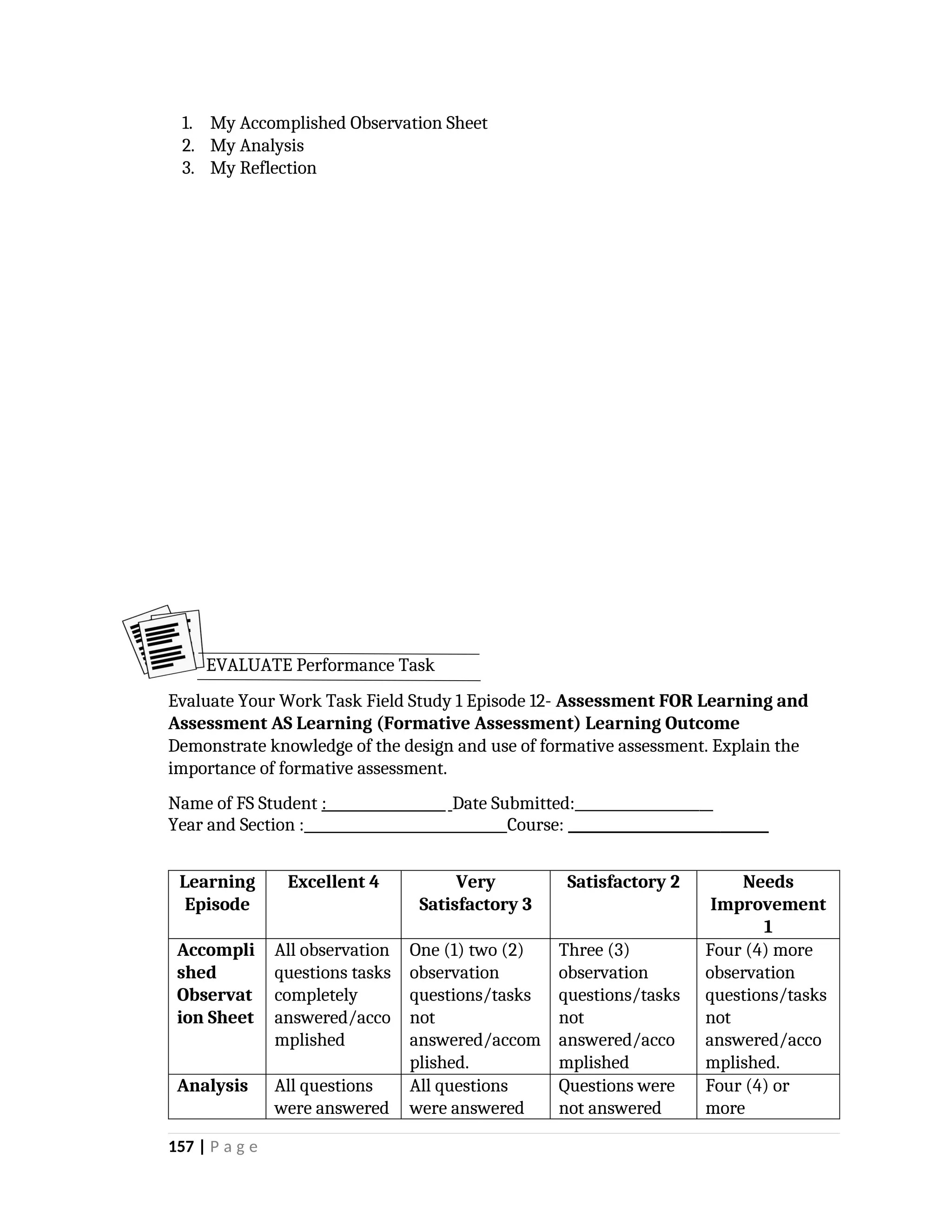
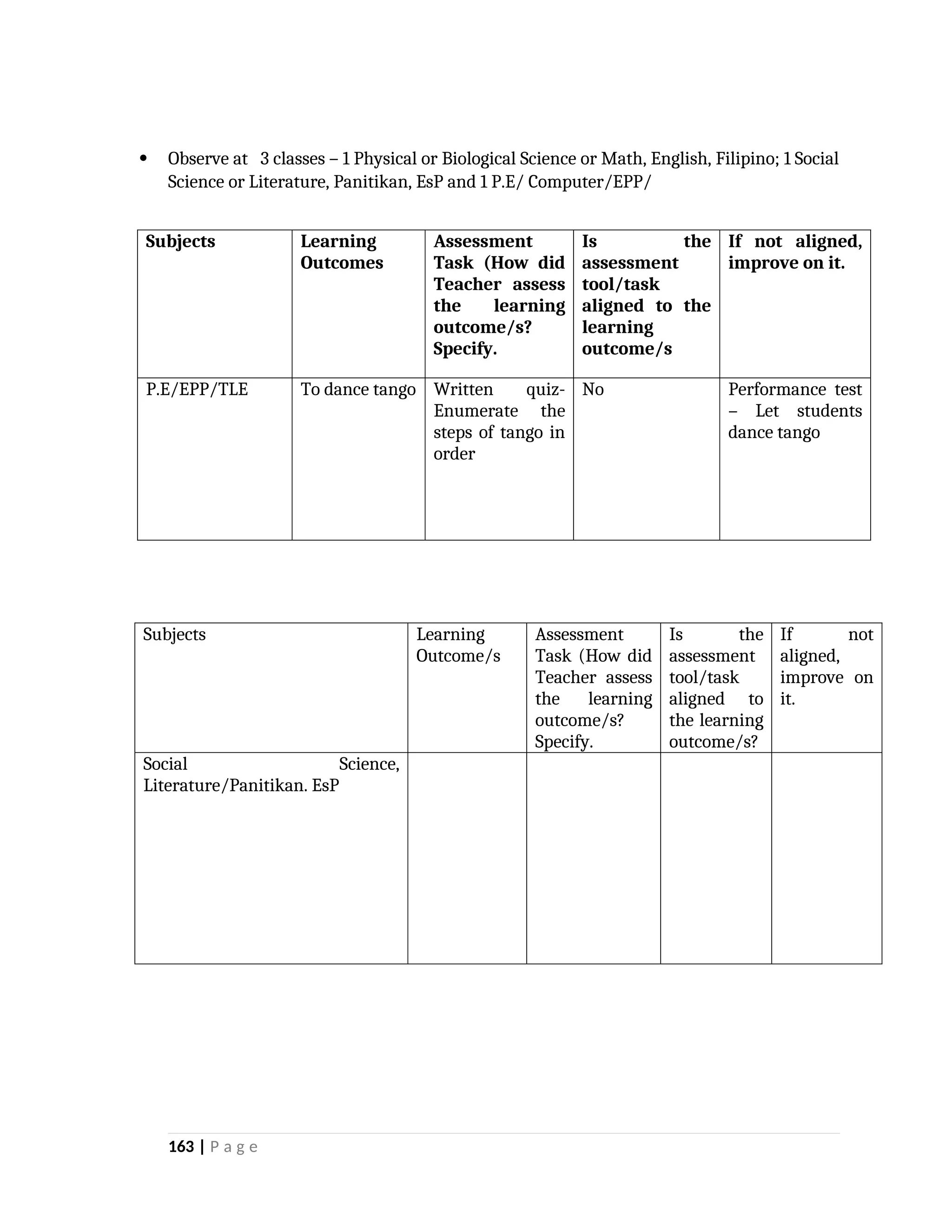
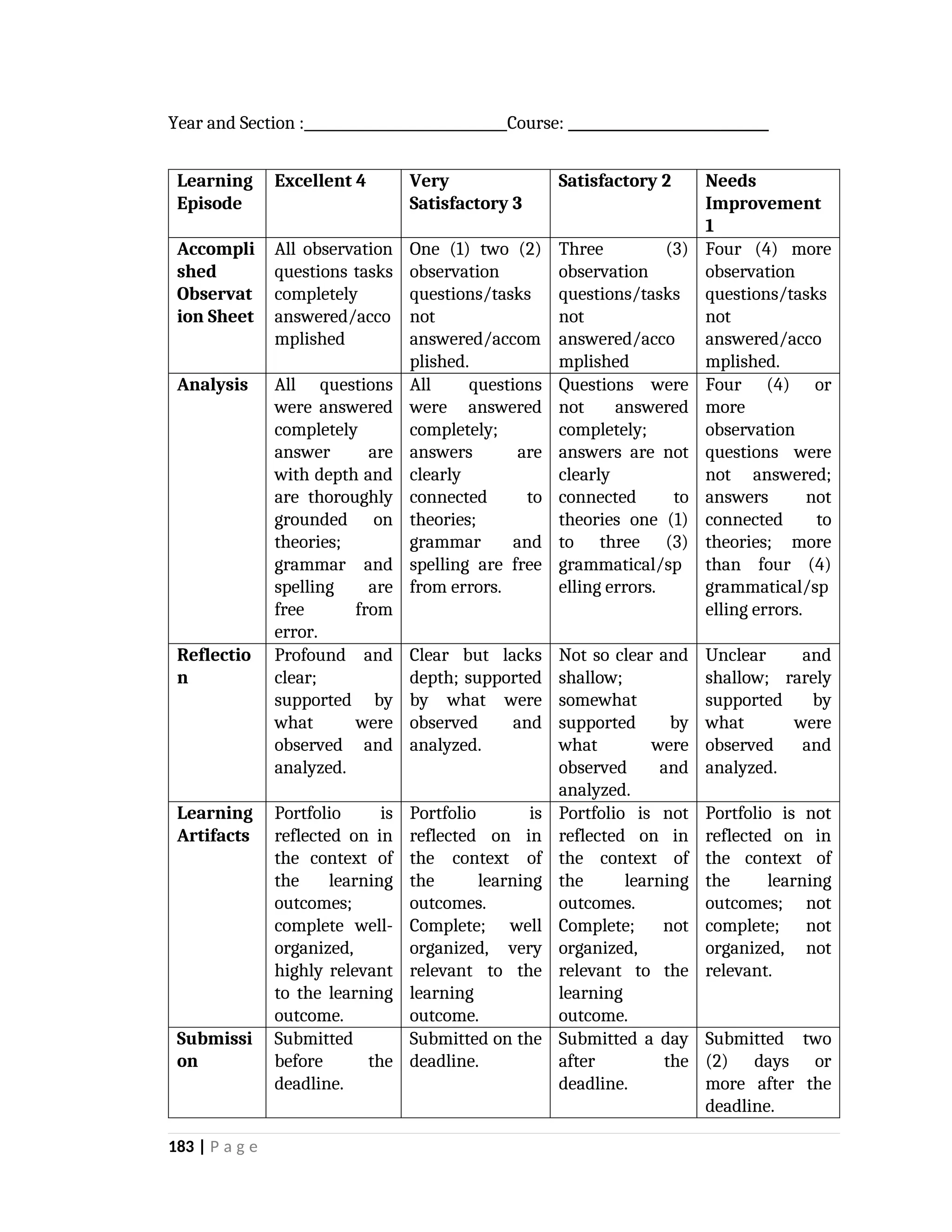
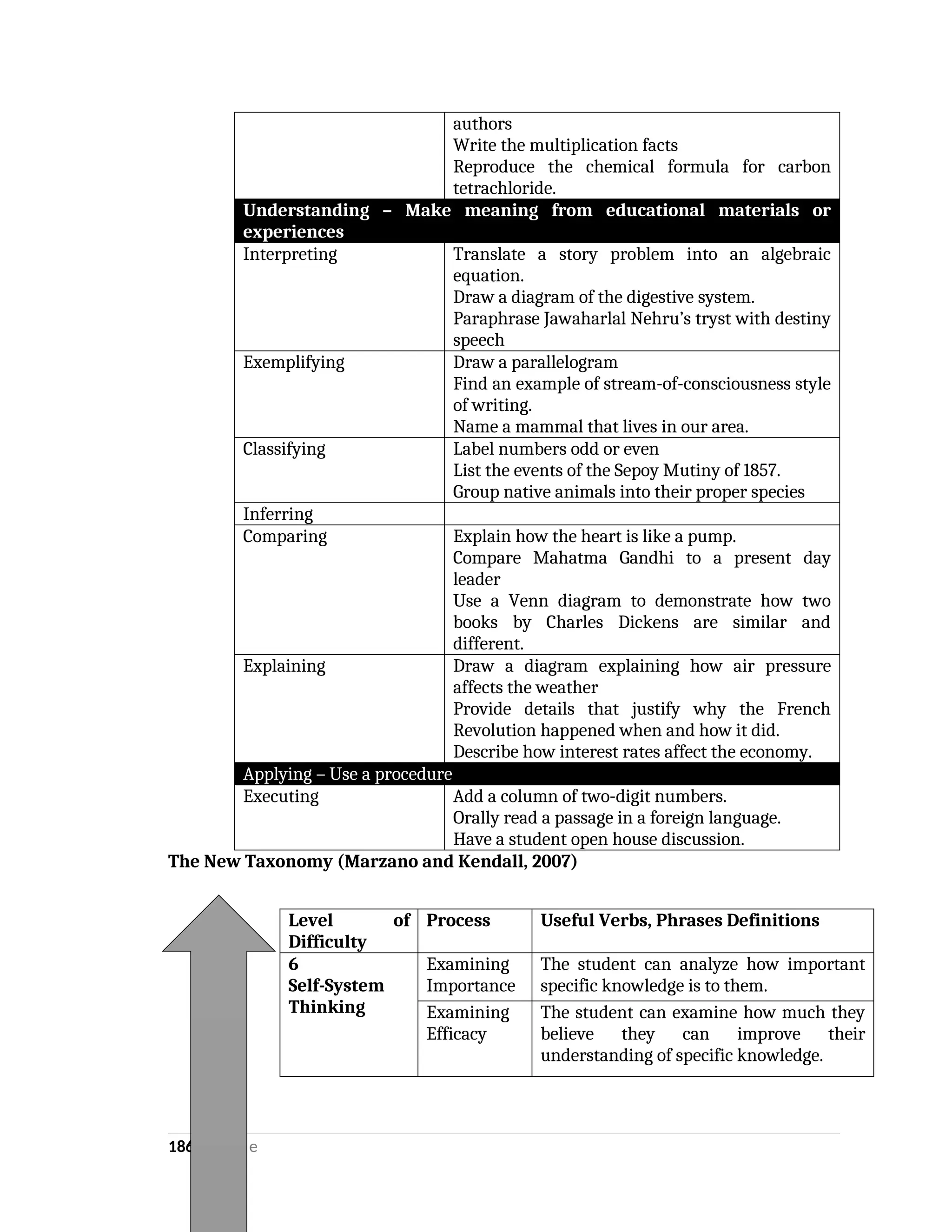
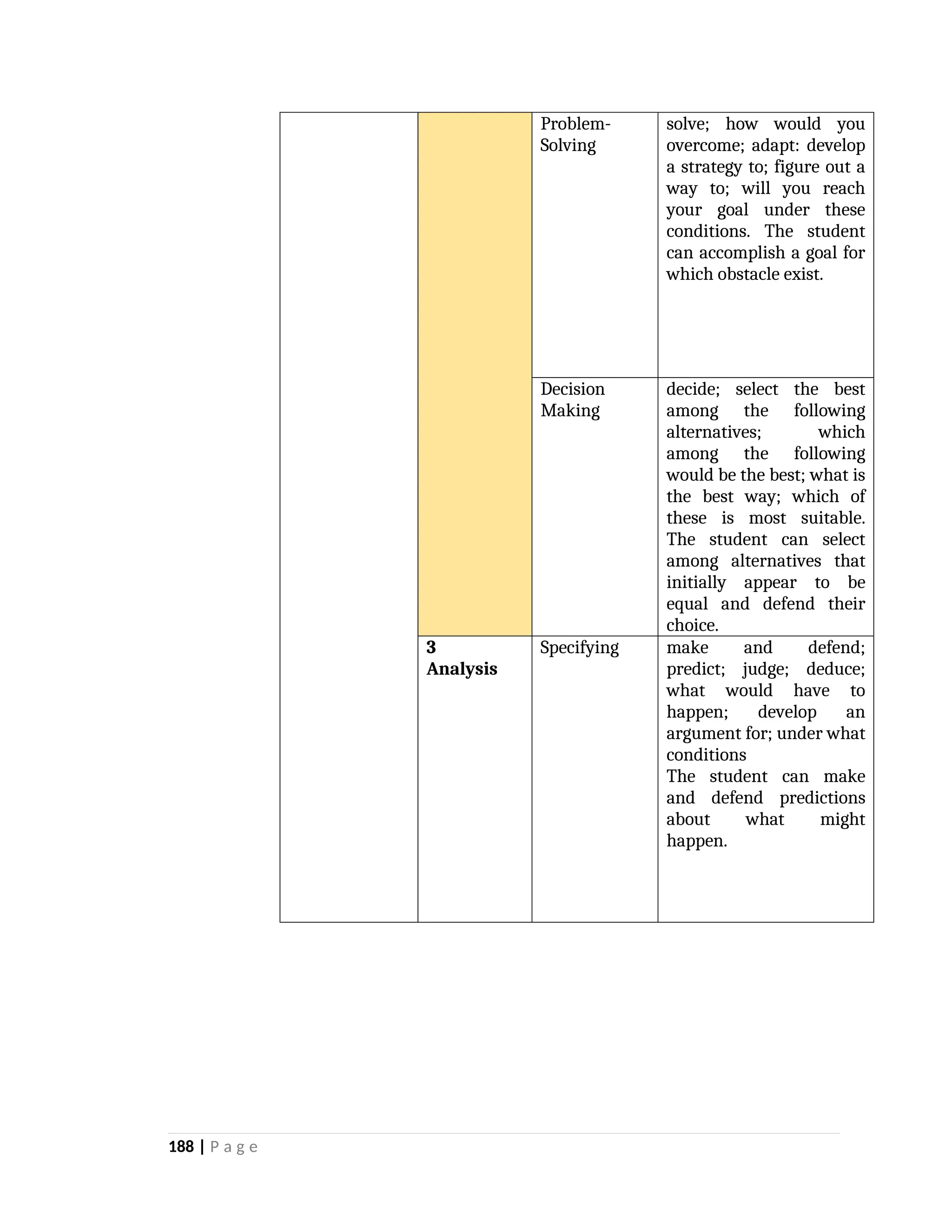
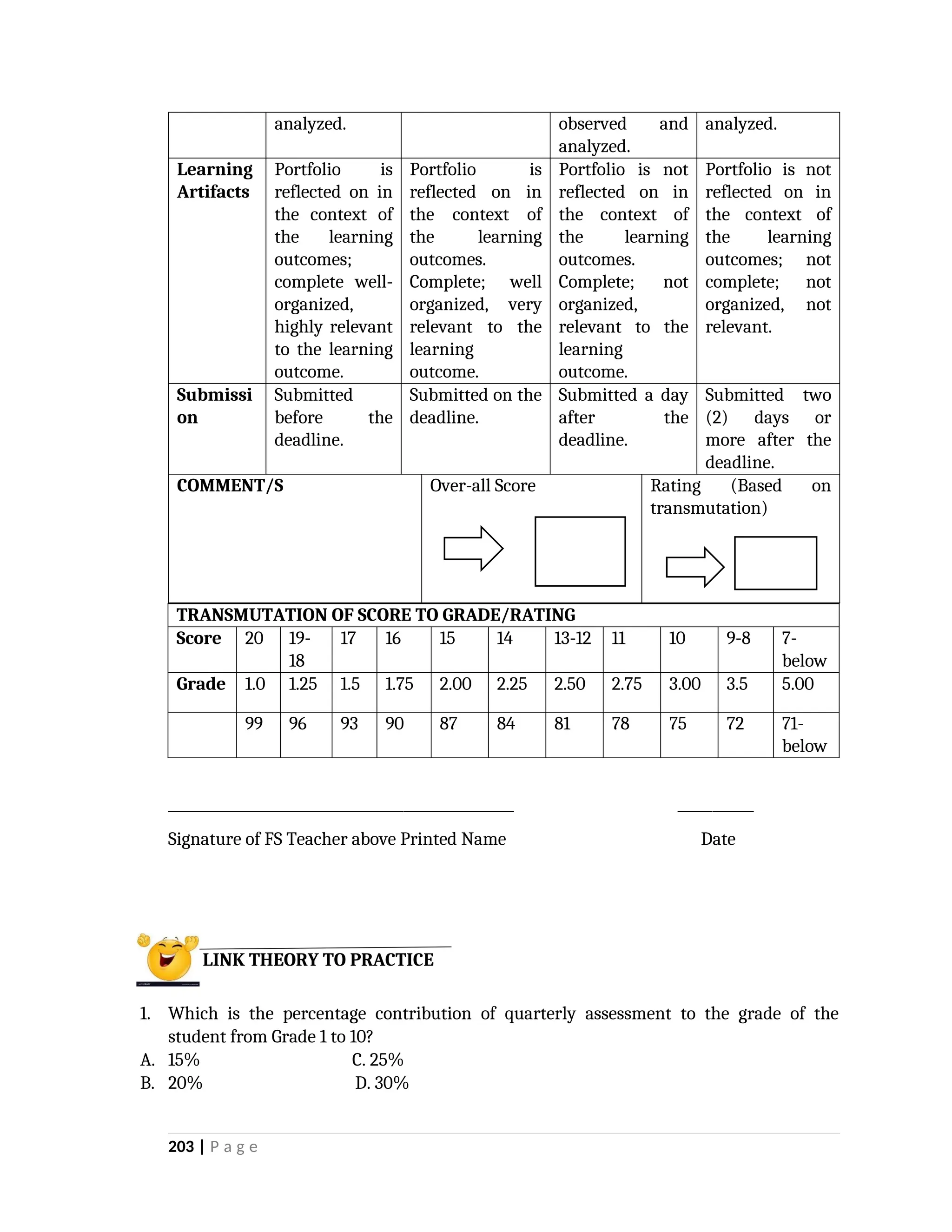
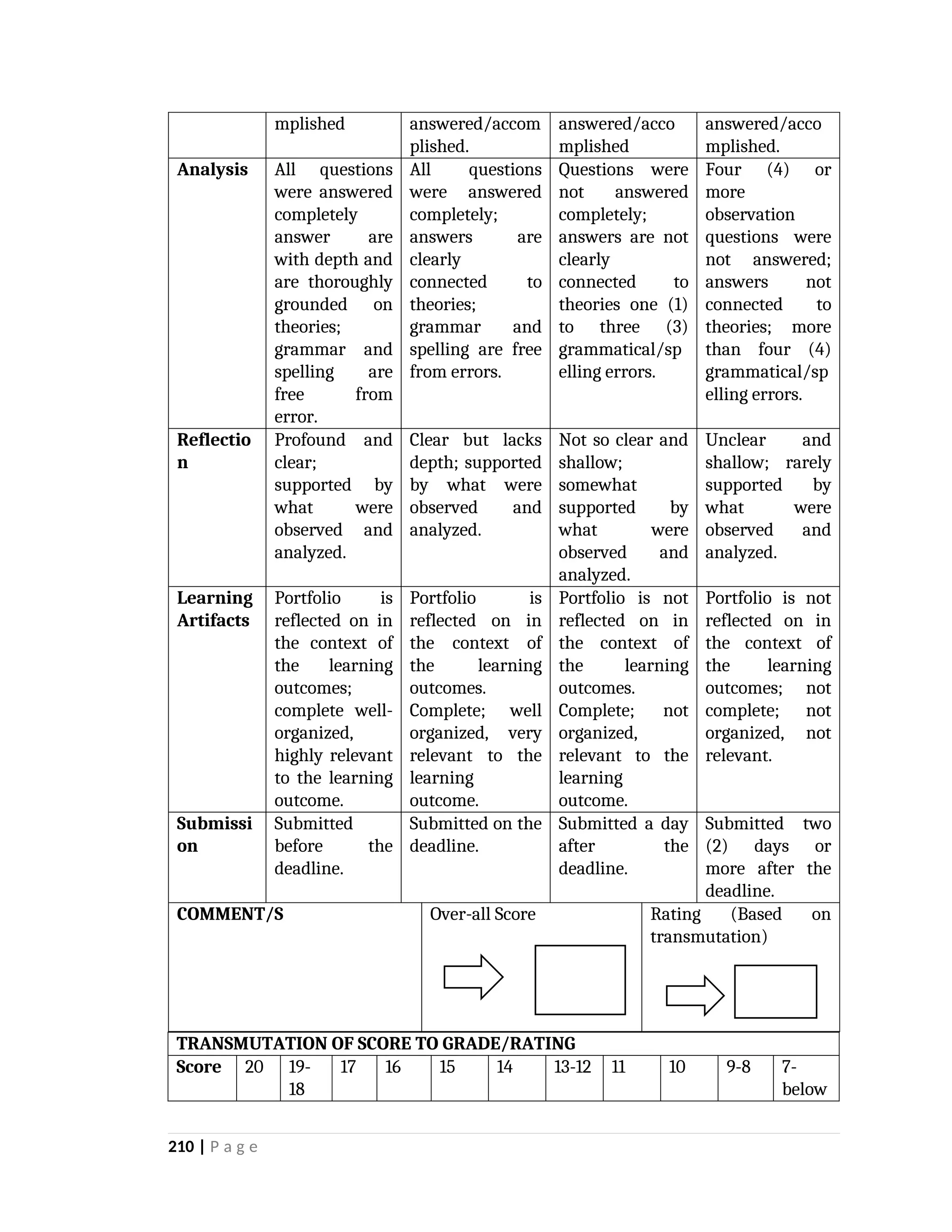
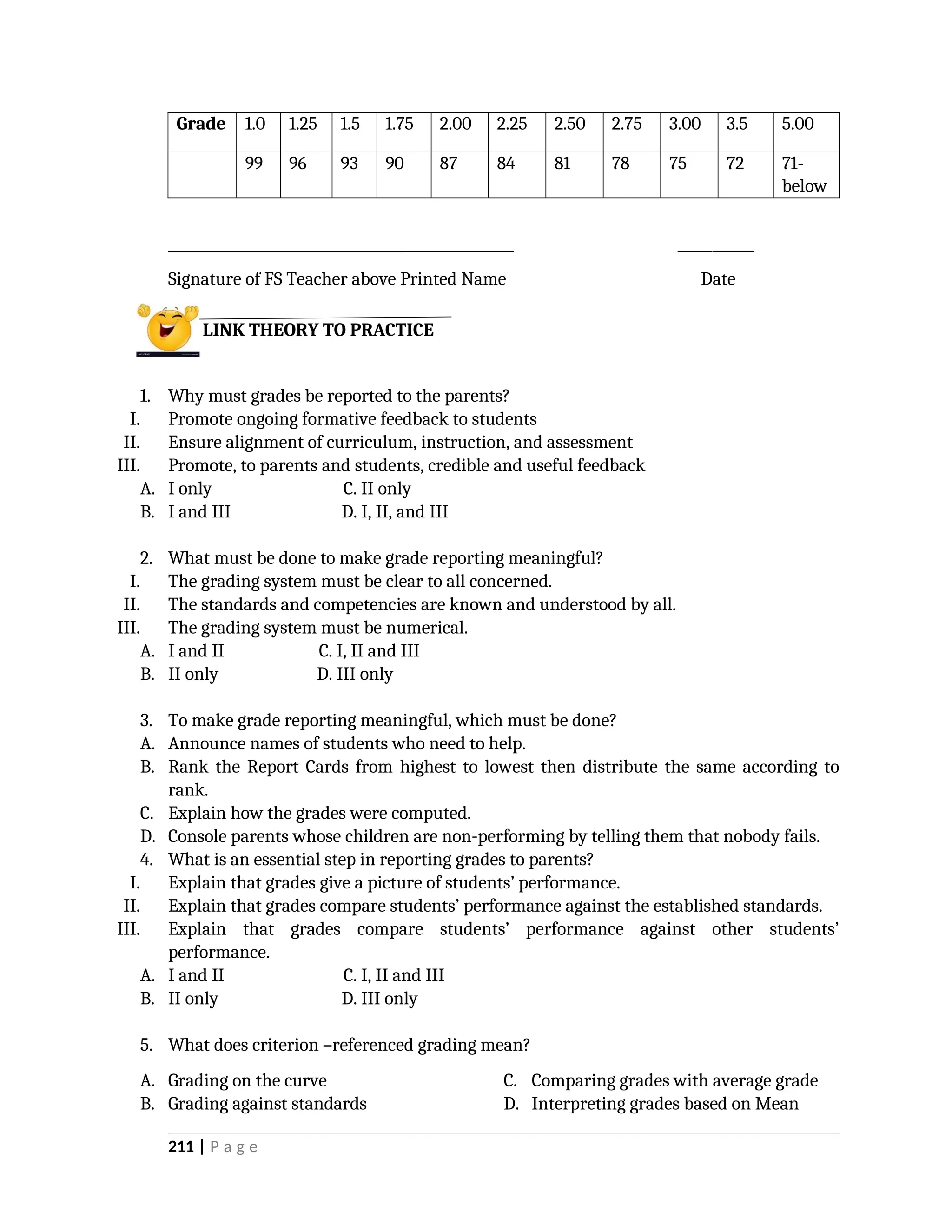
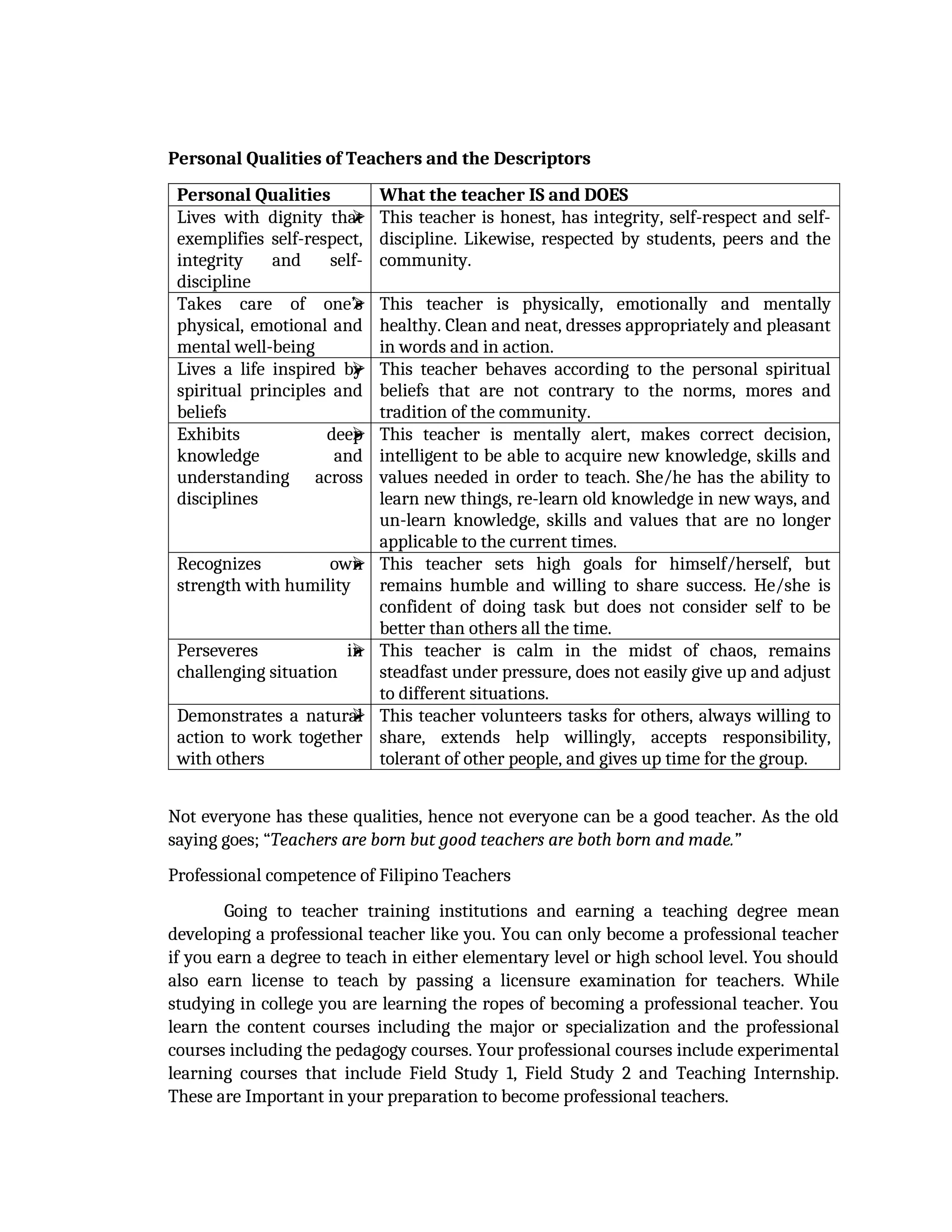
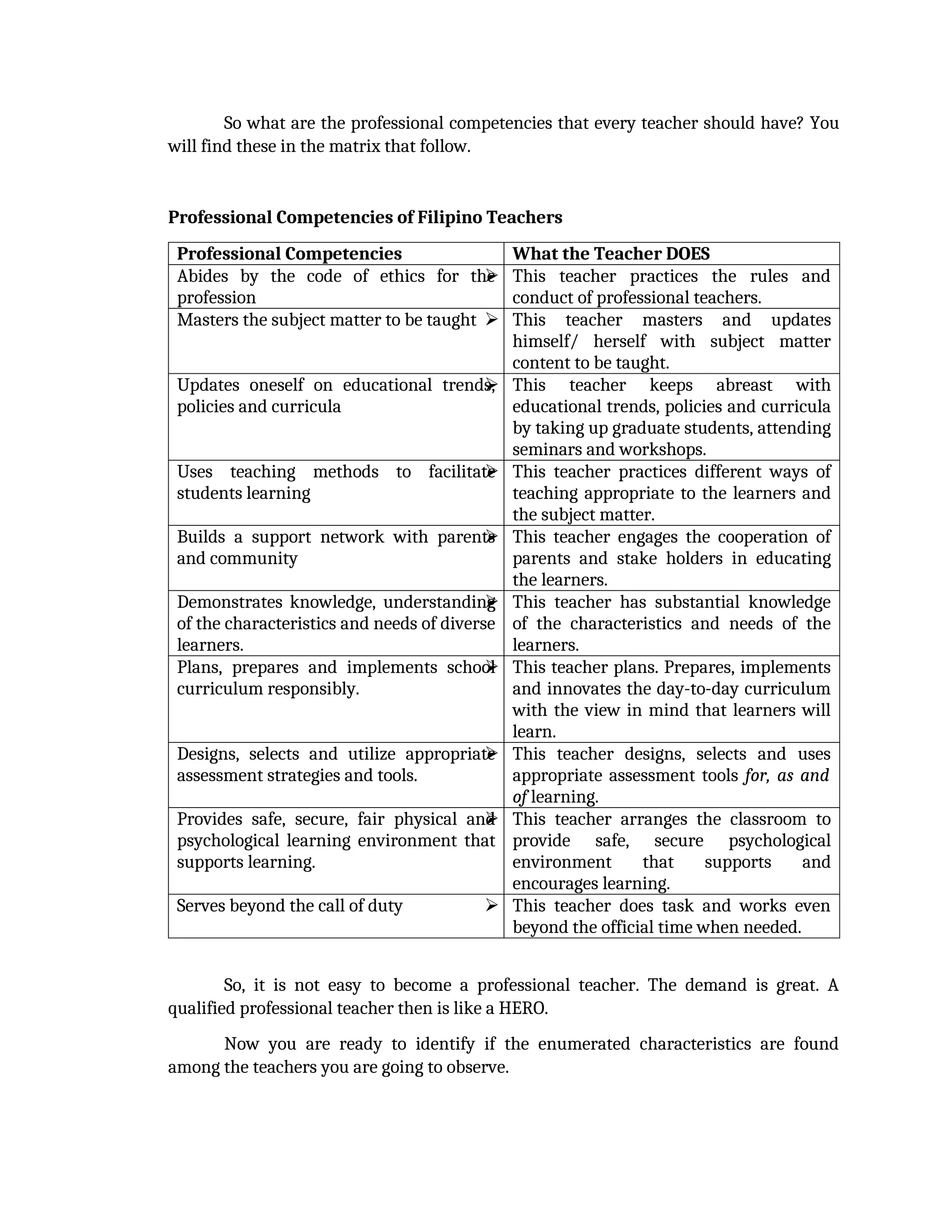
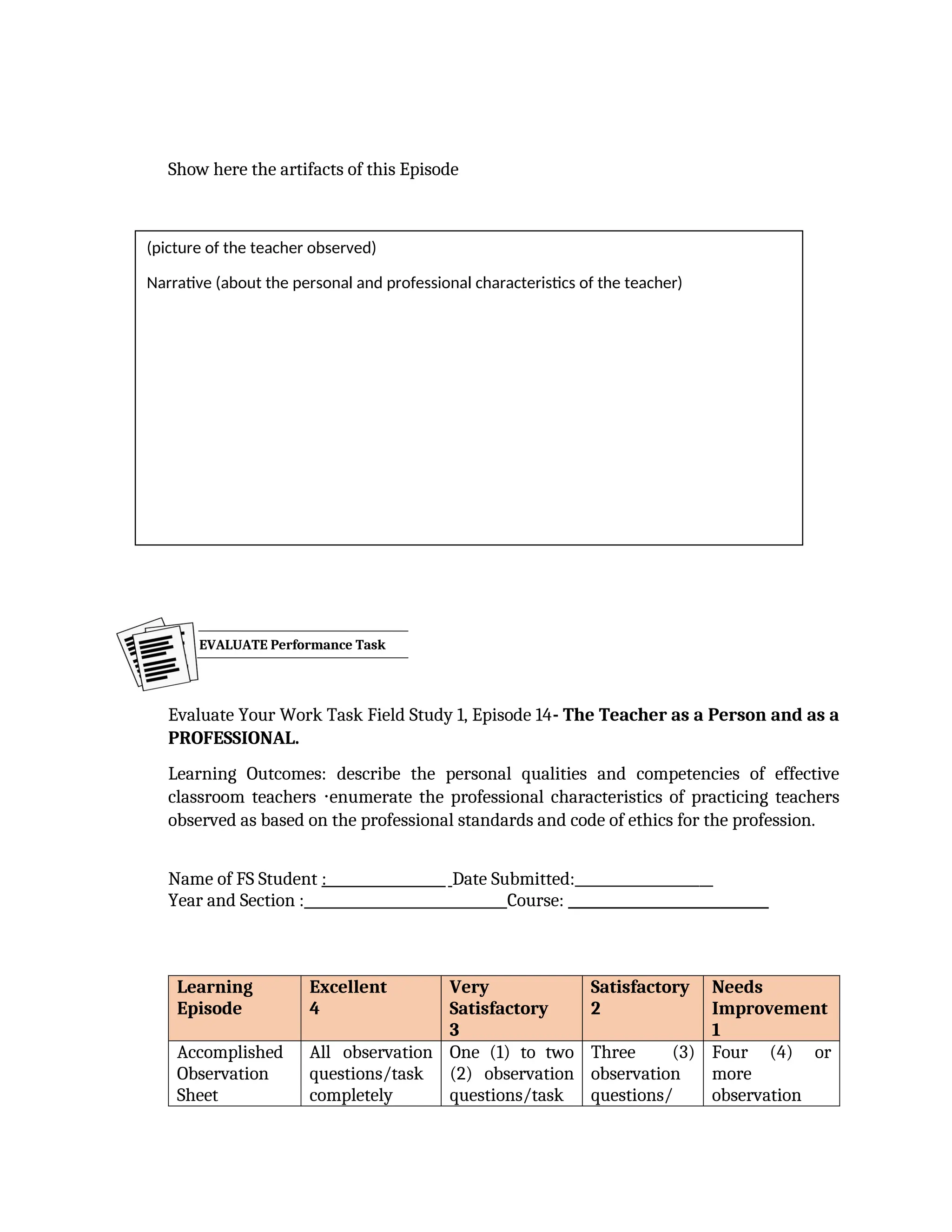
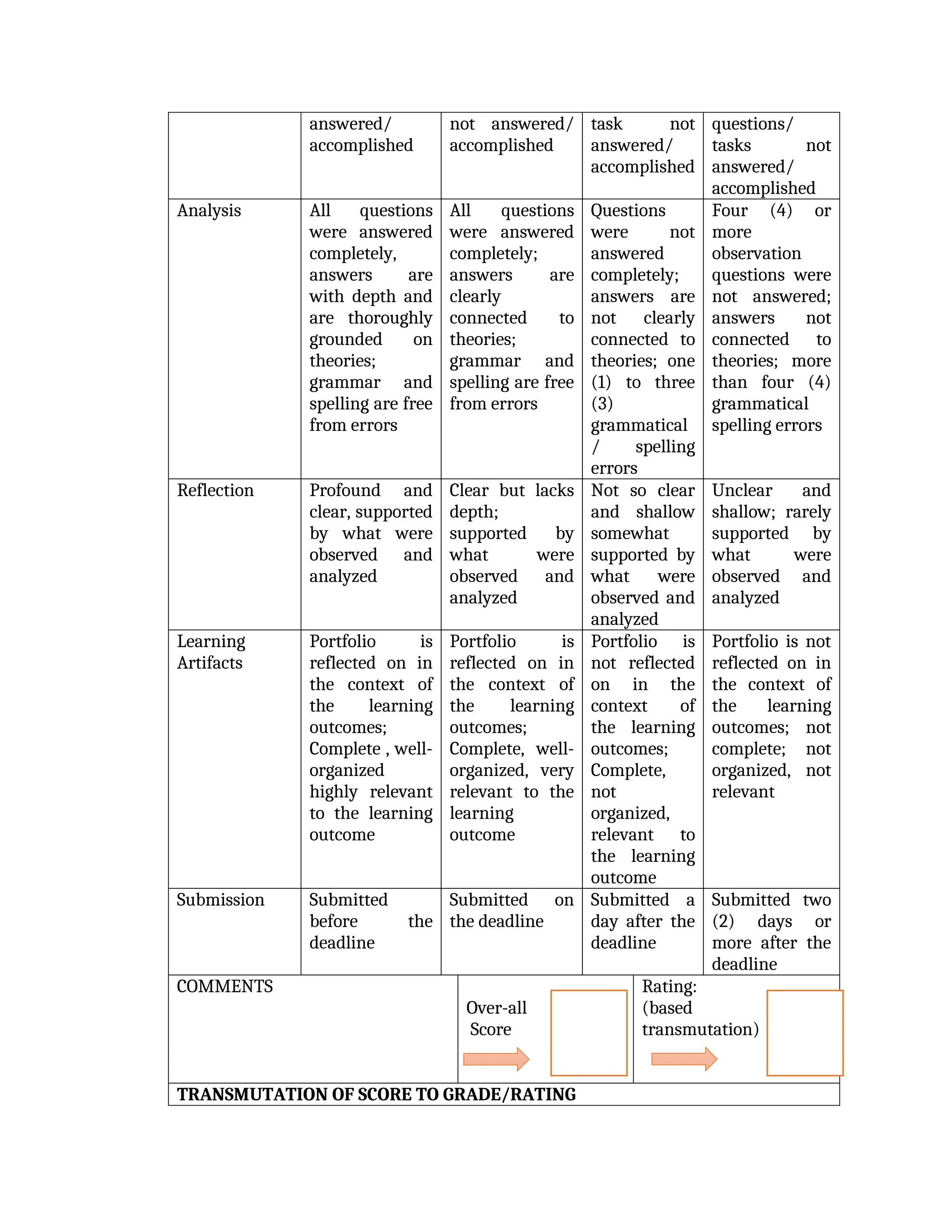
yfr6u6e6ytuytiuoi8y02qwbdhwqetfr2erfyg7qy3g73gyeurhguewrhgefbghdfbvhdsbfvdsfvbyursfgvdhfbvbvdhdhhdhdhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhdeheeeeyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyygyghhgfhdfggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggg