The document discusses potential future internet use cases in several areas:
1) Utilities and environment use cases include monitoring air/water quality, noise, forests fires, and smart metering for electricity, water, and gas. Broader smart city uses also discussed.
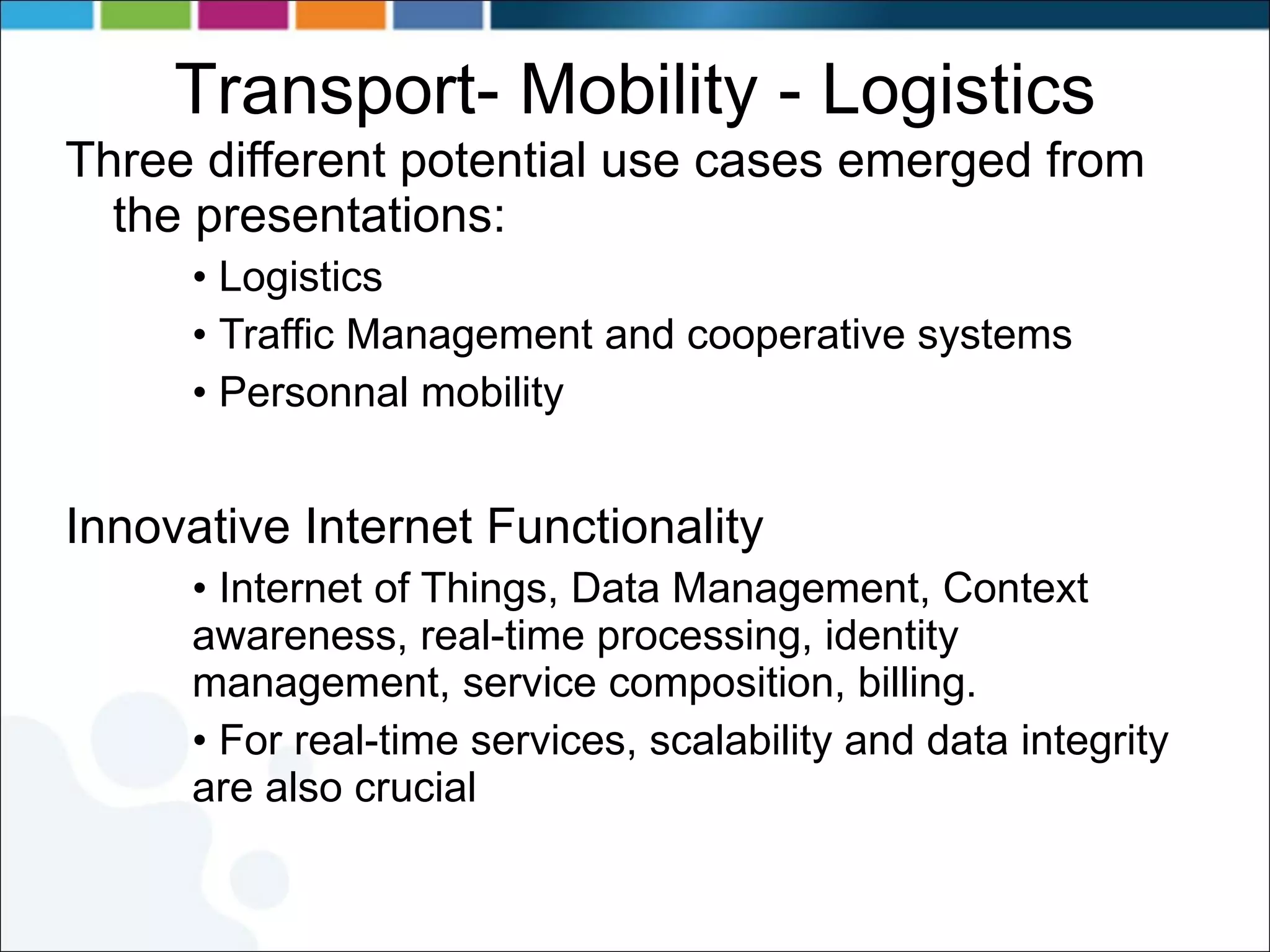
2) Transport and logistics uses cases include logistics, traffic management, cooperative systems, and personal mobility.
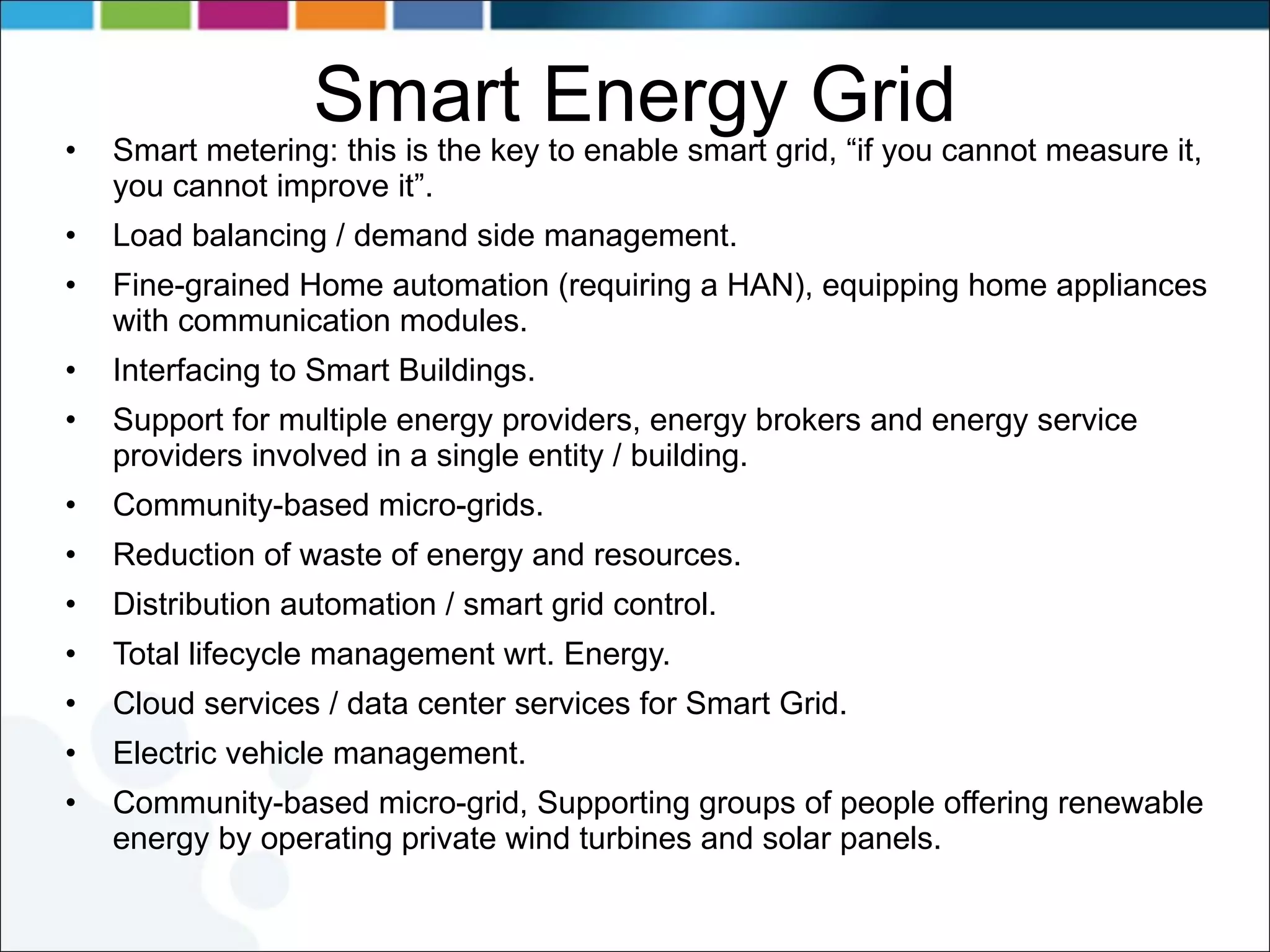
3) Other areas discussed include smart energy grid, eHealth, finance, and eTourism uses cases.





![Miguel Ponce de Leon, Chief Technologist, TSSG, WIT. Email: [email_address] Tel: +353 51 302952 (w) Web: www.tssg.org/people/miguelpdl twitter: miguelpdl](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20110107miguelpdlfipppusecaseexamplessfi-110410162014-phpapp01/75/FI-PPP-Use-Case-Examples-2011-8-2048.jpg)