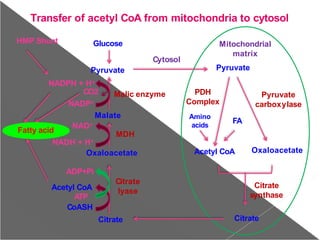
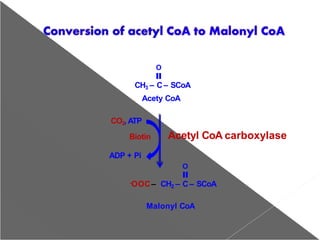
The document summarizes de novo fatty acid synthesis. It occurs in the liver, kidney, adipose tissue, and lactating mammary gland. Enzymes are located in the cytosol. Acetyl CoA from the mitochondria is the starting material and is converted to malonyl CoA by acetyl CoA carboxylase in an ATP-dependent reaction. Fatty acid synthase complex then catalyzes sequential reactions to produce palmitate through seven cycles. Production is regulated by enzymes, metabolites, hormones, and diet.