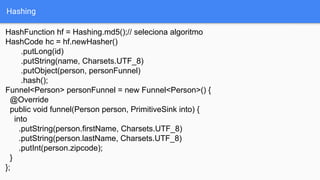
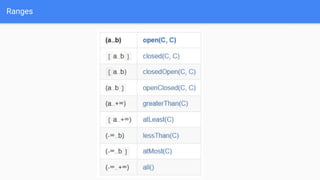
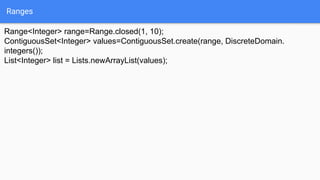
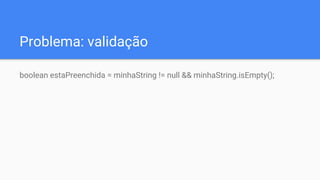
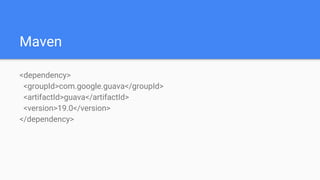
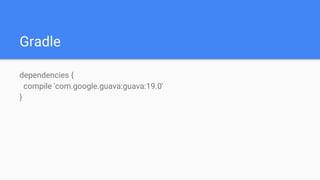
The document discusses the use of the Guava library in Java for various programming tasks, such as handling null values, implementing preconditions, and object comparison. It provides code examples illustrating features like collections management, input/output operations, and utility functions for string processing and caching. Guava enhances code quality by encouraging practices such as avoiding repetition and providing well-defined interfaces.



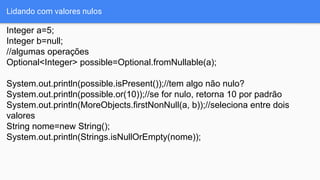
![Pré condições
import static com.google.common.base.Preconditions.checkElementIndex;
Integer[]arr=new Integer[5];
//algum código
int index=5;
checkElementIndex(index, arr.length, "index");
/*
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException: index (5) must be
less than size (5)
at com.google.common.base.Preconditions.checkElementIndex(Preconditions.java:
310)
at br.gdg.fsa.Main.main(Main.java:43)
*/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/faciliteavidacomguava-160322122905/85/Facilite-a-vida-com-guava-9-320.jpg)
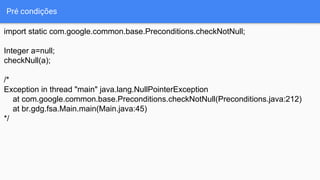

![Ordenação
Integer[]arr=new Integer[5]; arr[0]=1; arr[1]=10; arr[2]=100; arr[3]
=1000; arr[4]=10000;
List<Integer> list = Lists.newArrayList(arr);
Ordering<Integer> ordering=Ordering.natural().reverse();
System.out.println(ordering.min(list)); //10000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/faciliteavidacomguava-160322122905/85/Facilite-a-vida-com-guava-14-320.jpg)