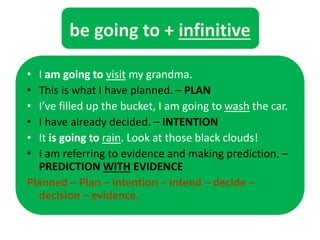
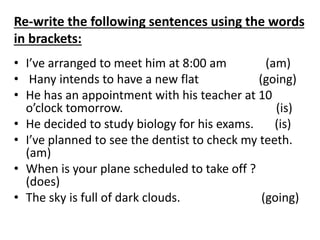
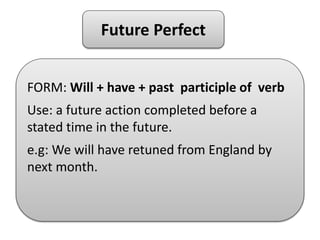
This document discusses various ways to express future actions and events in English, including will, be going to, present continuous, present simple, future continuous, and future perfect tenses. It provides examples of how each is used to indicate plans, predictions, arrangements, schedules, and other nuances involving future time. Key distinctions are drawn between planned vs. spontaneous intentions (will vs. be going to), arrangements vs. decisions (present continuous vs. be going to), and recurring vs. one-time events (present simple vs. others). Exercises are included for practice applying the tenses based on prompts.