Embed presentation
Download to read offline




![Example
Example of exception handling in Java:
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int[] arr = new int[3];
arr[4] = 5;
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("An array index is out of bounds.");
}
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandlingppt-230728120949-51a1b292/85/Exception-handling-ppt-pptx-7-320.jpg)

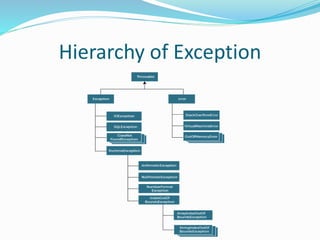
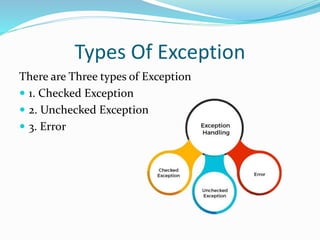
This document discusses exception handling in Java. It introduces exceptions as problems that occur during program execution and disrupt normal flow. It outlines the hierarchy of exceptions and describes the main types - checked exceptions, unchecked exceptions, and errors. It also lists common exception handling keywords like try, catch, finally, throw, and throws. Finally, it provides an example Java code snippet demonstrating how to catch an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.






![Example
Example of exception handling in Java:
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int[] arr = new int[3];
arr[4] = 5;
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("An array index is out of bounds.");
}
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandlingppt-230728120949-51a1b292/85/Exception-handling-ppt-pptx-7-320.jpg)
