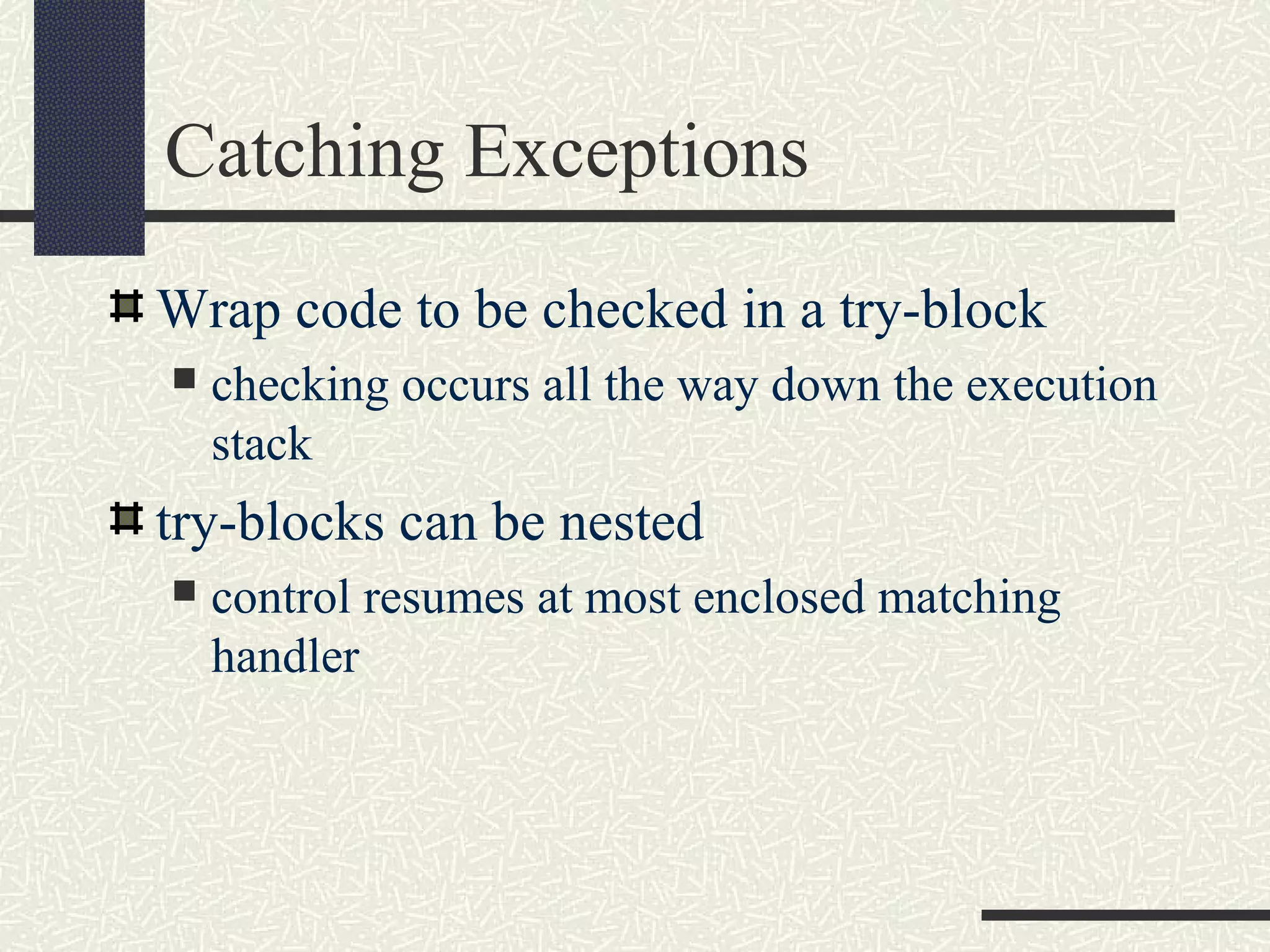
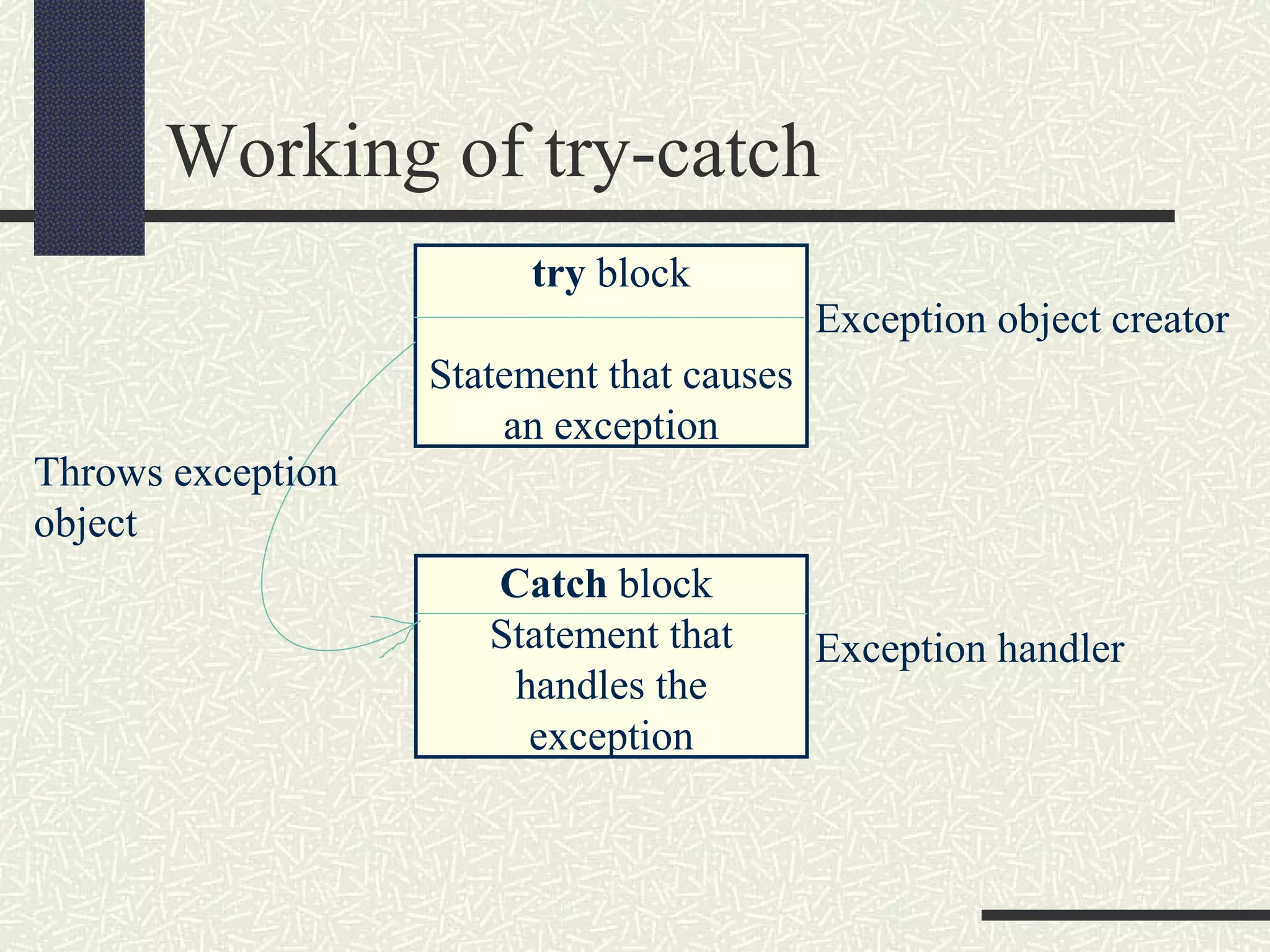
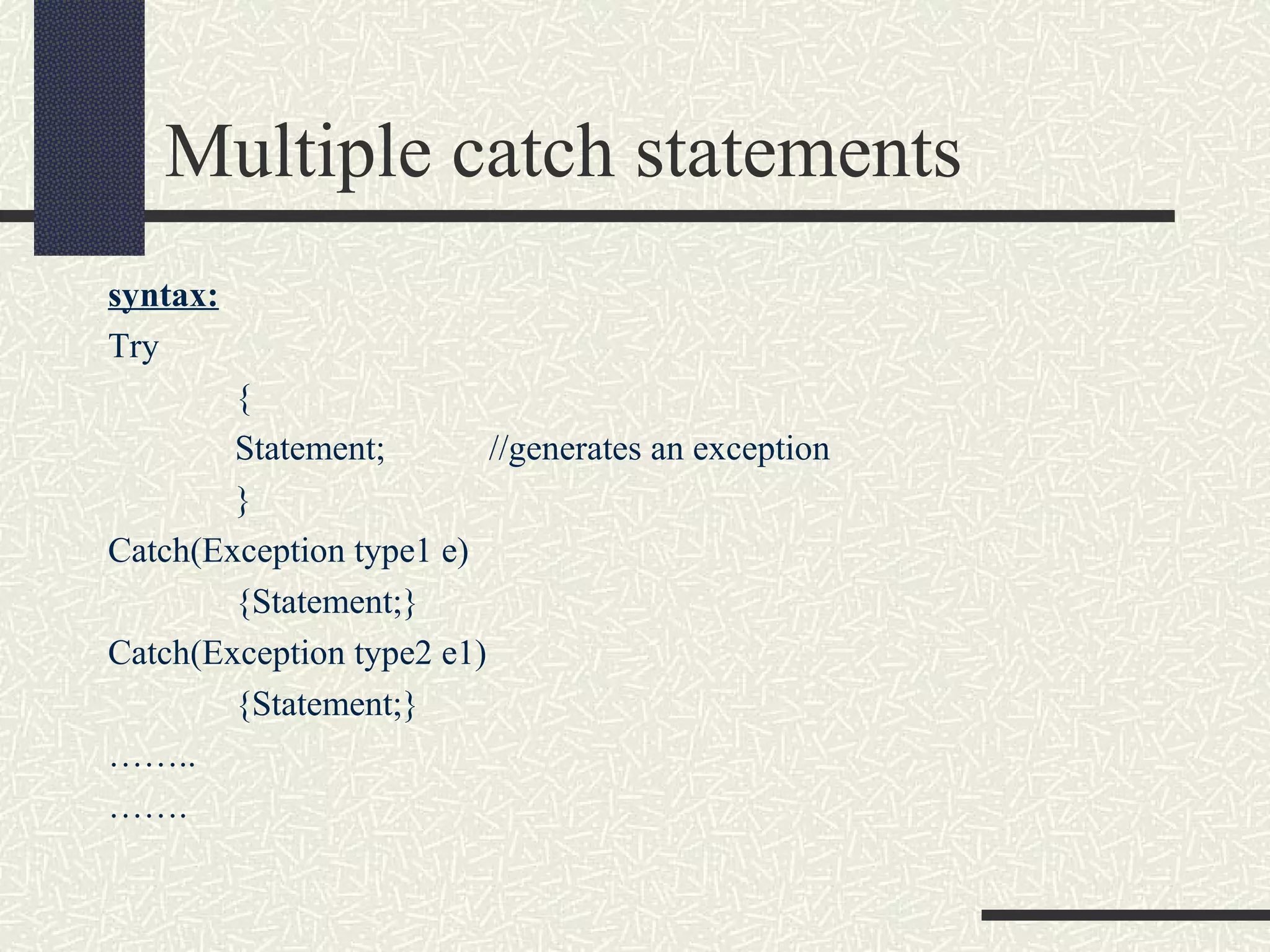
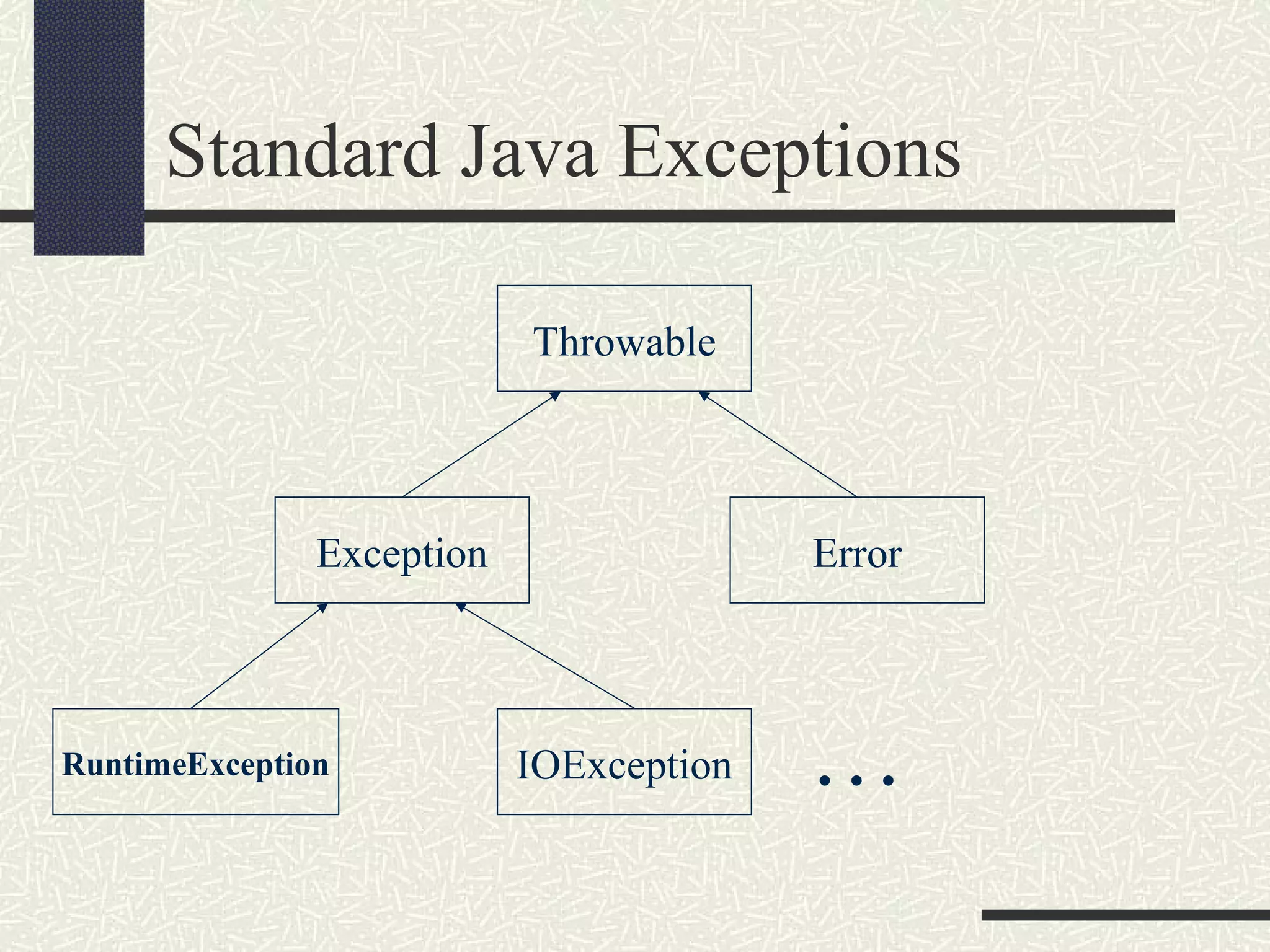
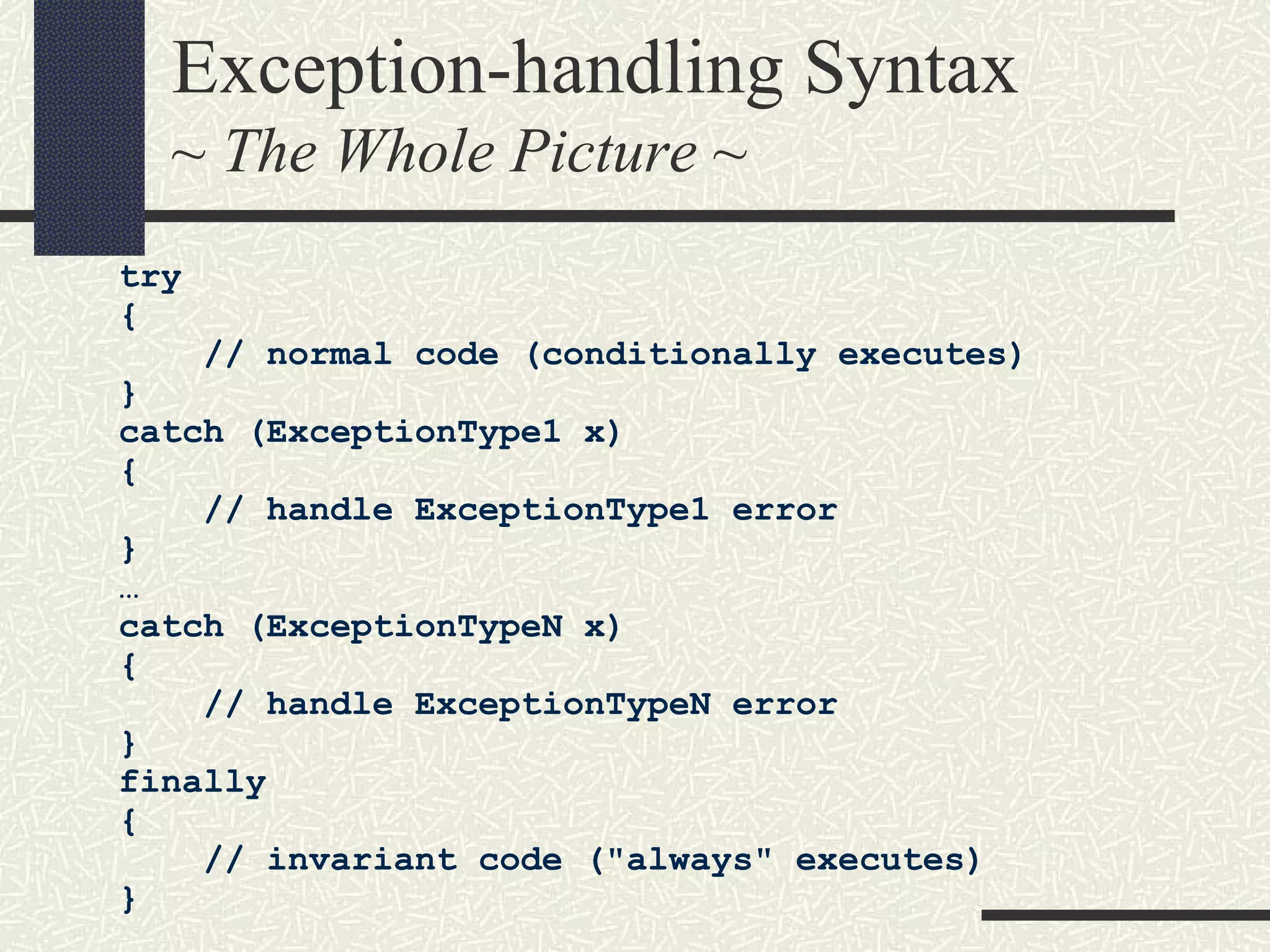
Java exceptions allow programs to handle and recover from errors and unexpected conditions. Exceptions are thrown when something abnormal occurs and the normal flow of execution cannot continue. Code that may throw exceptions is wrapped in a try block. Catch blocks handle specific exception types. Finally blocks contain cleanup code that always executes regardless of exceptions. Common Java exceptions include IOException for I/O errors and NullPointerException for null reference errors. Exceptions bubble up the call stack until caught unless an uncaught exception causes thread termination.





![import java.io.*;
class OpenFile
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
if (args.length > 0)
{
try
{
// Open a file:
FileReader f =
new FileReader(args[0]);
System.out.println(args[0]
+ " opened");
f.close();
}
catch (IOException x)
{
System.out.println(x);
}
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-170405100112/75/Exception-handling-6-2048.jpg)













![public static void main(String[] args)
{
try
{
f();
}
catch(Exception x)
{}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-170405100112/75/Exception-handling-26-2048.jpg)






![Program
import java.lang.Exception;
class my extends Exception {
my(String msg);}
class test
{ public static void main(String a[])
{ int x=5,y=1000;
try {float z=(float) x / (float) y;
if(z<0.01)
{ throw new my(“Number is to small”); }
}
Catch(my e)
{ S.o.p(“Caught my exception”);
S.o.p(“e.getMessage()); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-170405100112/75/Exception-handling-33-2048.jpg)
