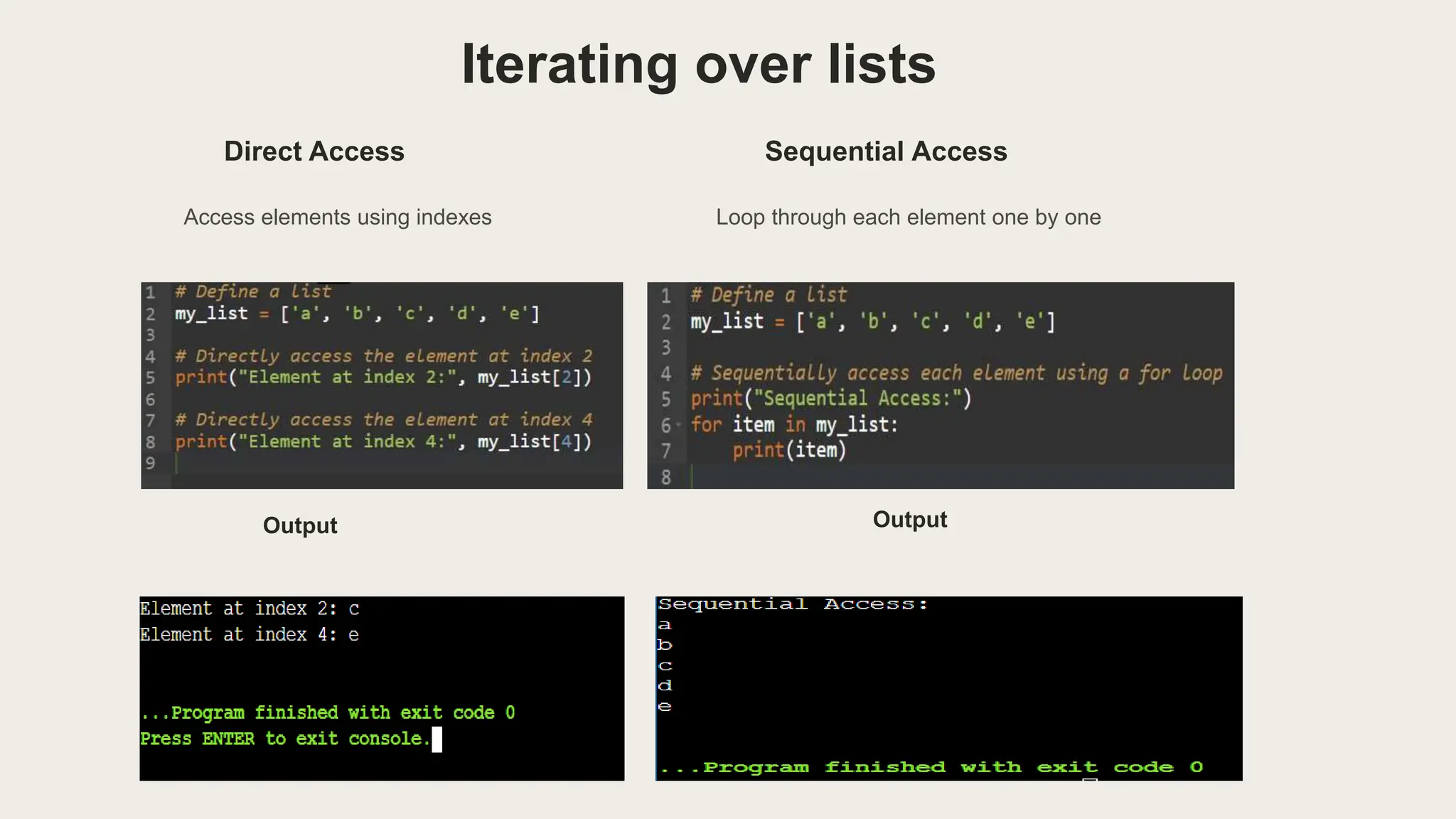
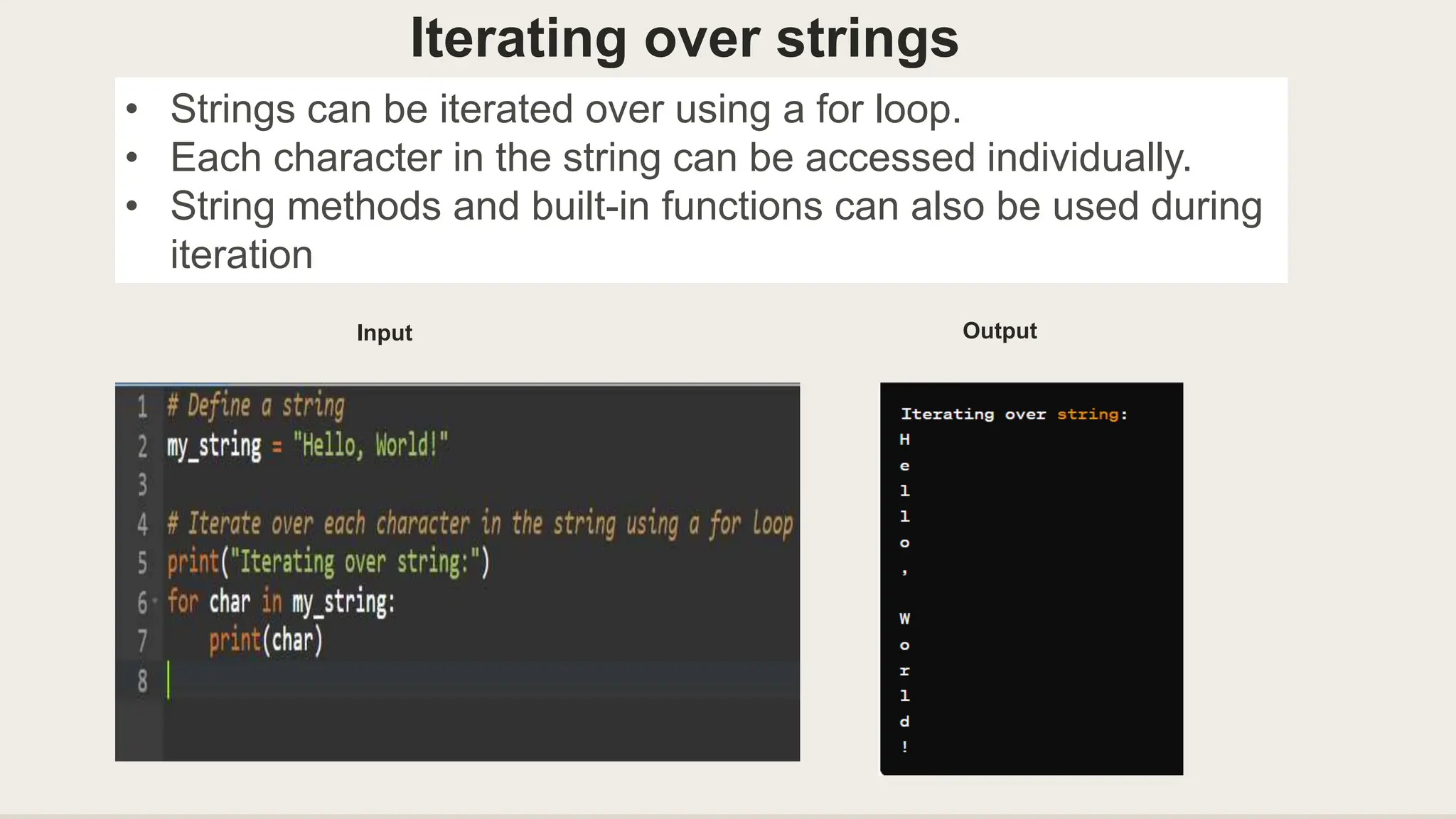
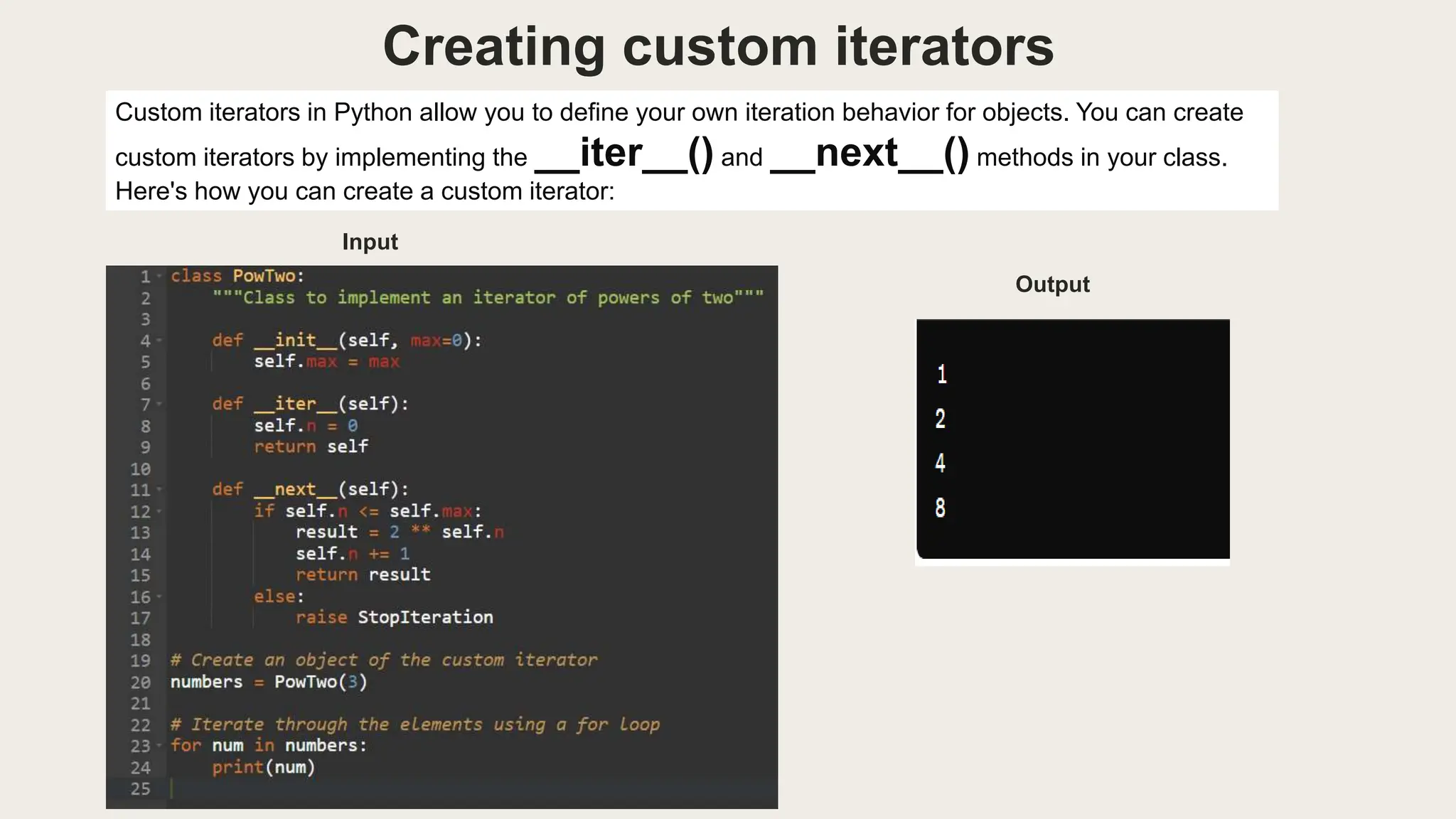
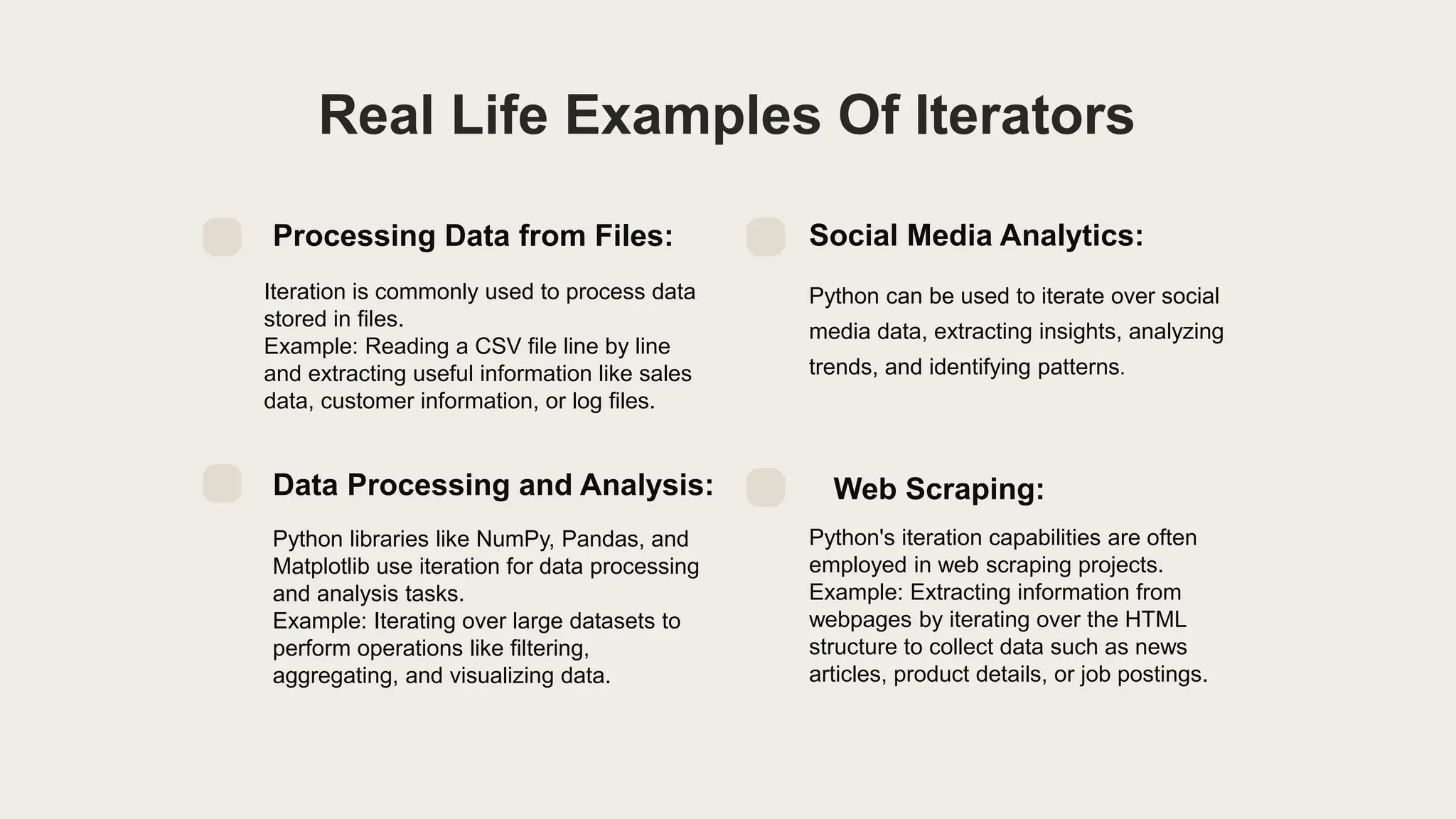
Iterators allow sequential access to elements in lists, strings, dictionaries, sets, and custom objects. For lists, you can directly access elements by index or loop through each element. For strings, you can iterate over each character. When iterating over dictionaries, you can access keys, values, or both using methods like .keys() and .items(). Real-life examples of iterators include processing data from files like CSVs, analyzing social media data, processing large datasets for analysis, and extracting data from webpages during web scraping.