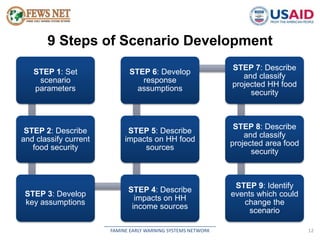
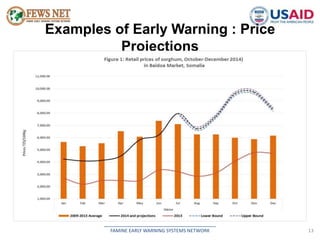
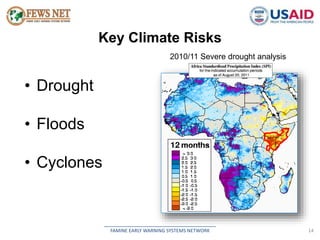
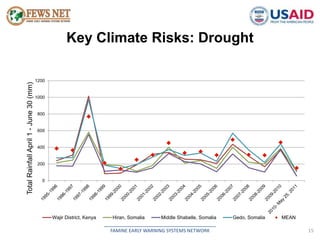
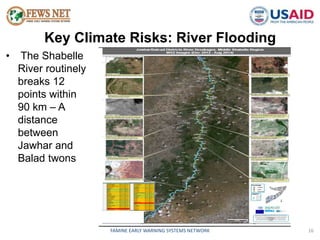
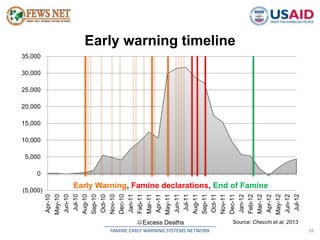
The document discusses early warning systems in Somalia, specifically through the Famine Early Warning Systems Network (FEWS NET), which provides vital information and analysis on food security to various stakeholders since 1995. It highlights key climate risks such as drought, floods, and cyclones that impact food security and includes contributions from various humanitarian and data collection organizations. The document outlines a framework for scenario development and intervention, detailing steps taken to assess current and projected food security conditions in the region.