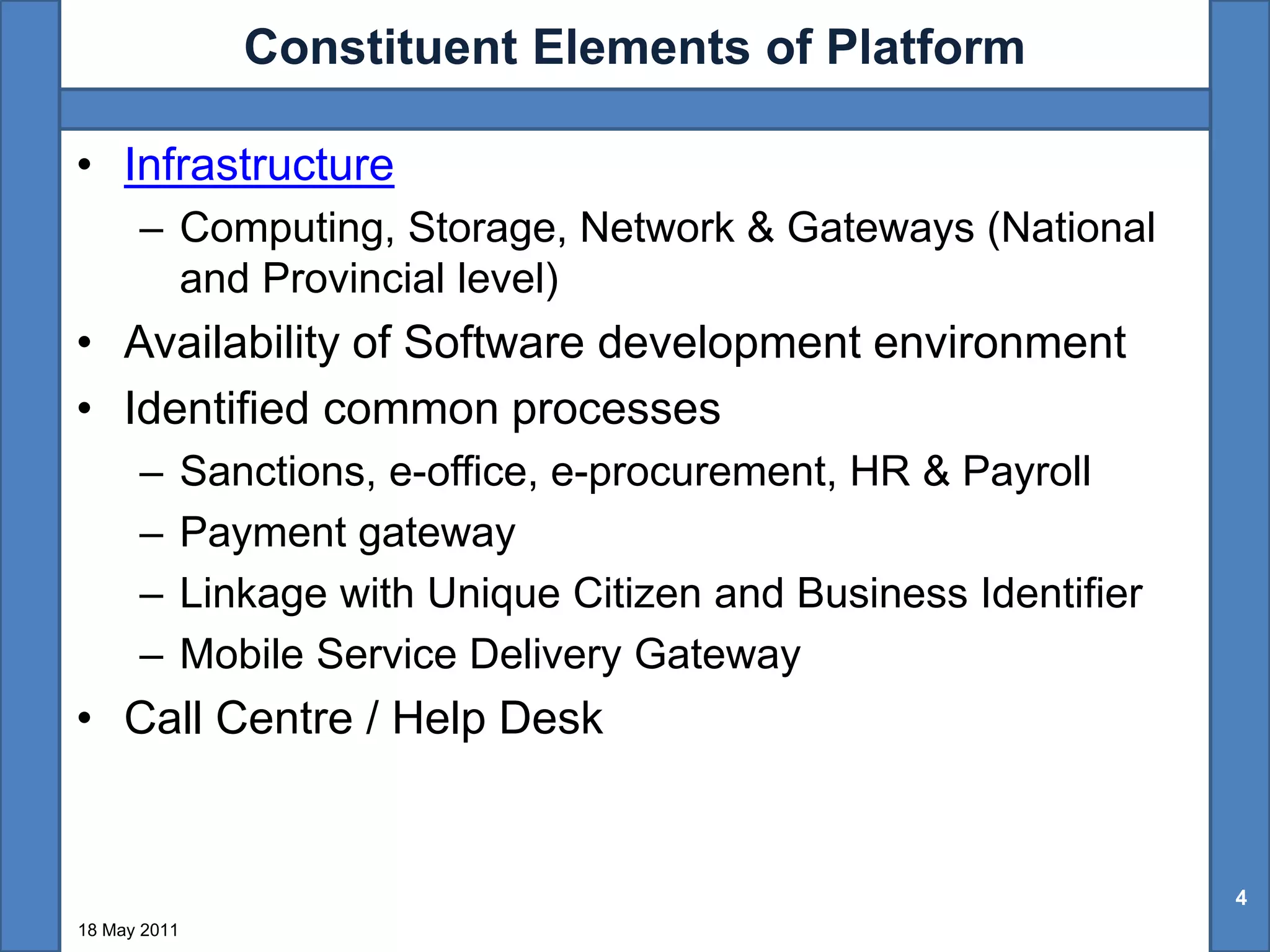
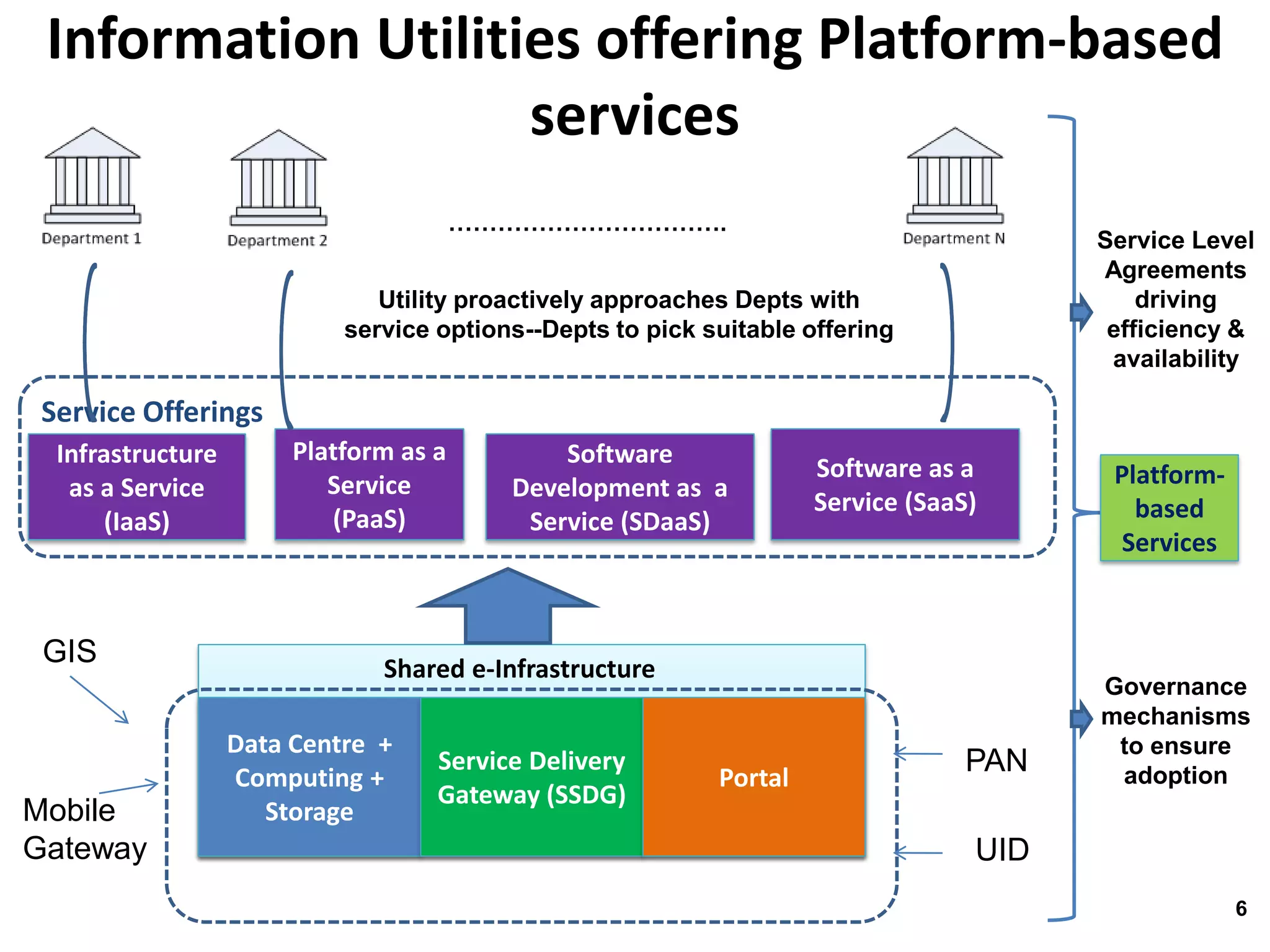
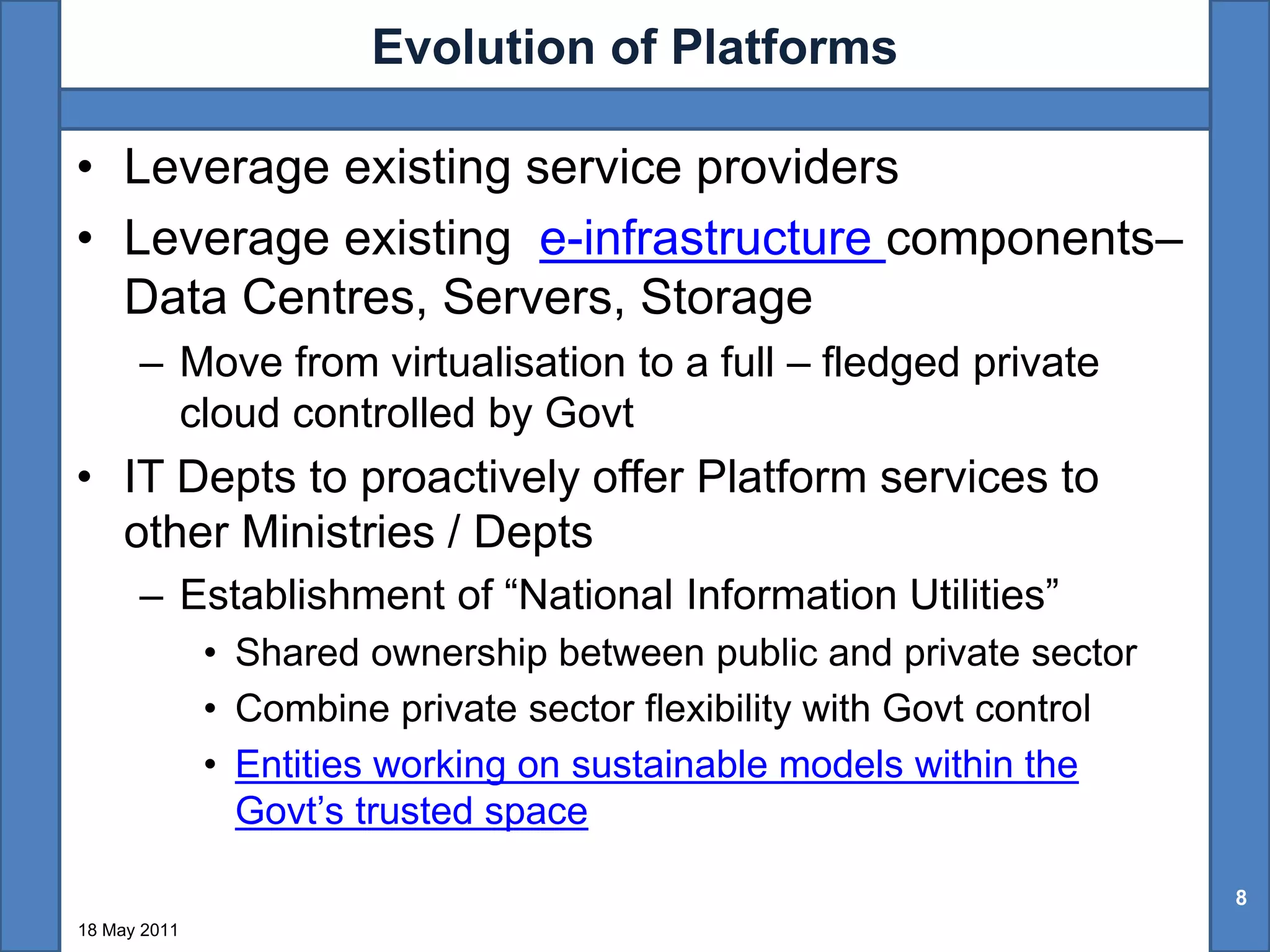
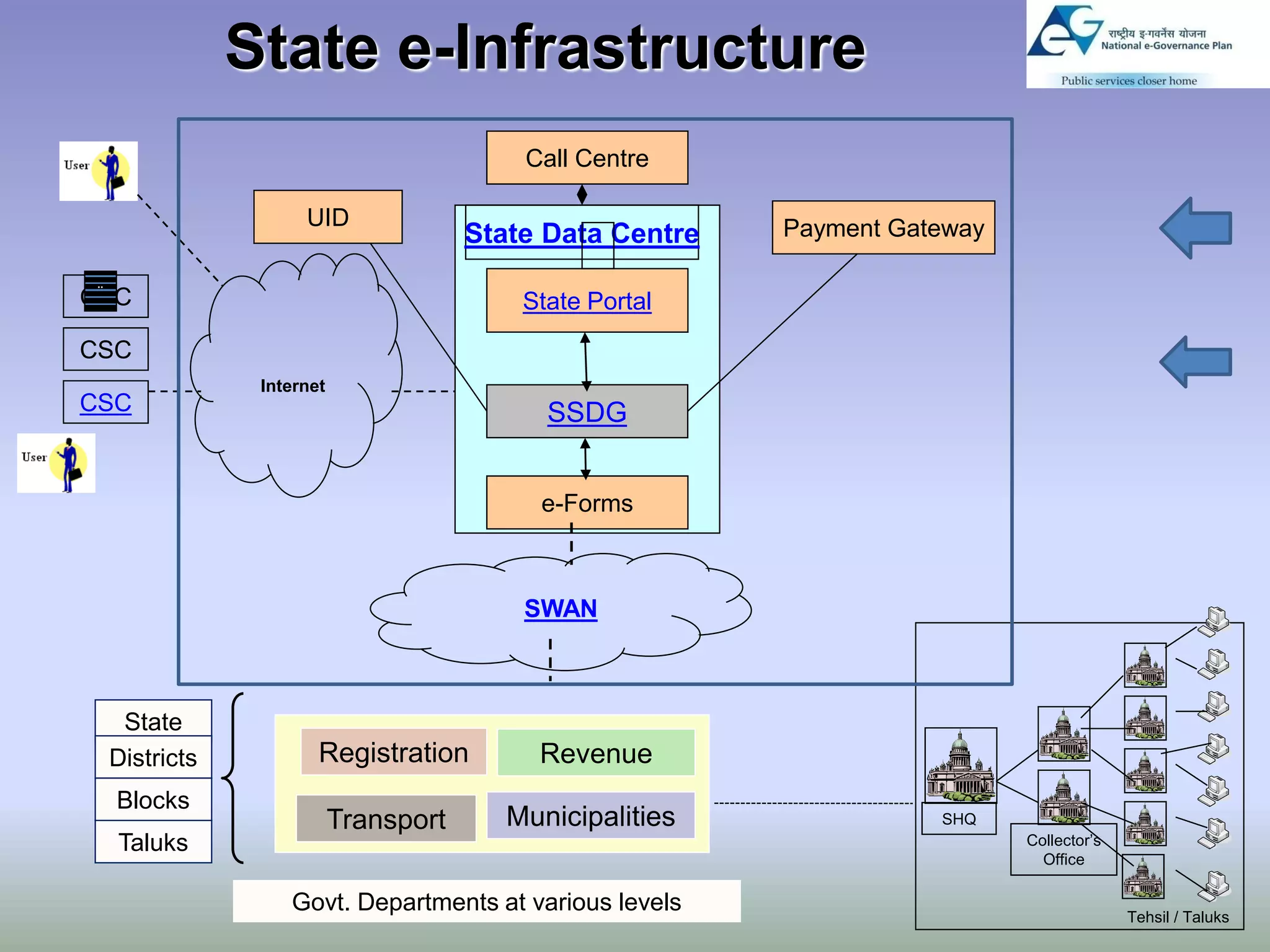
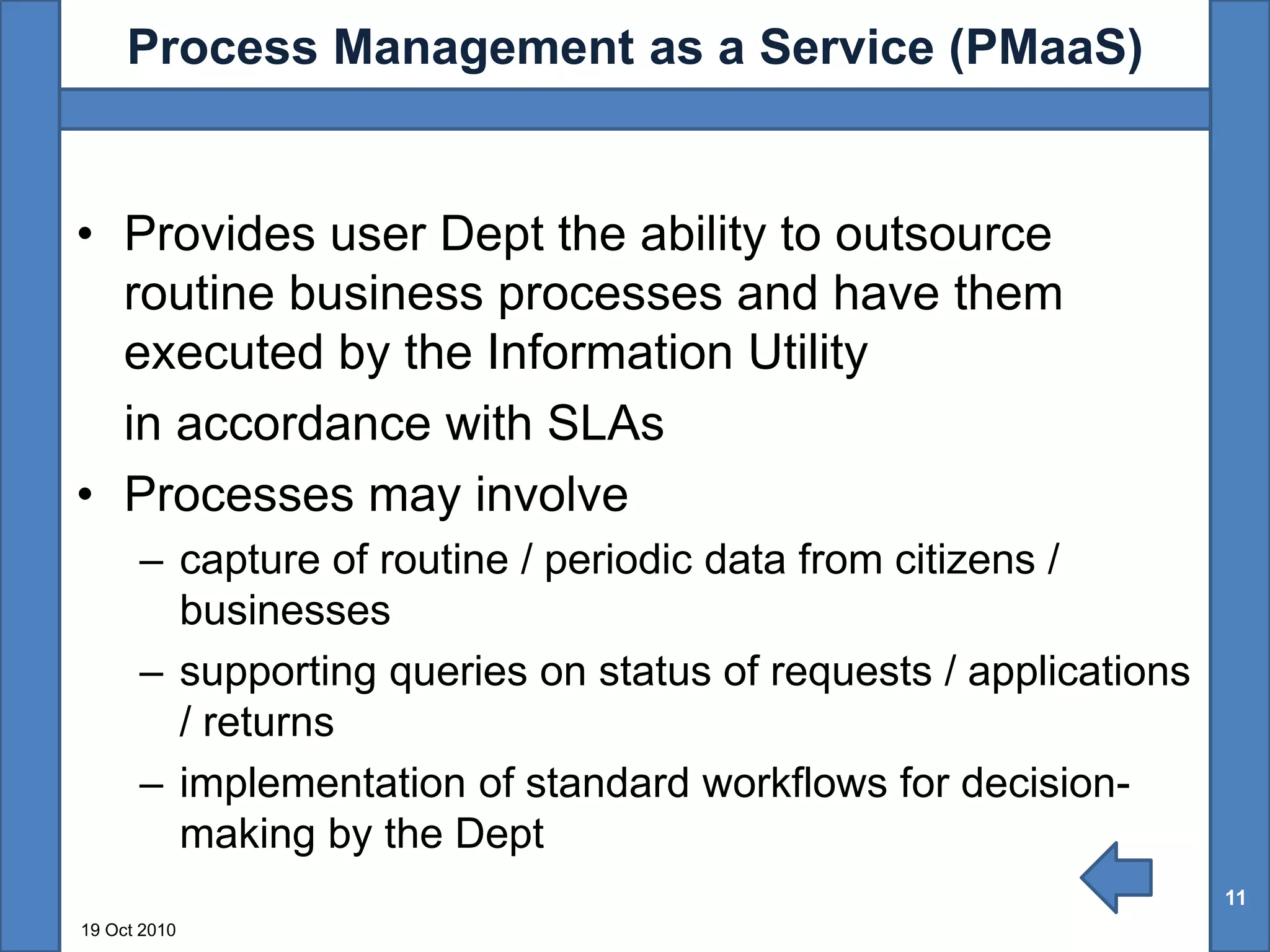
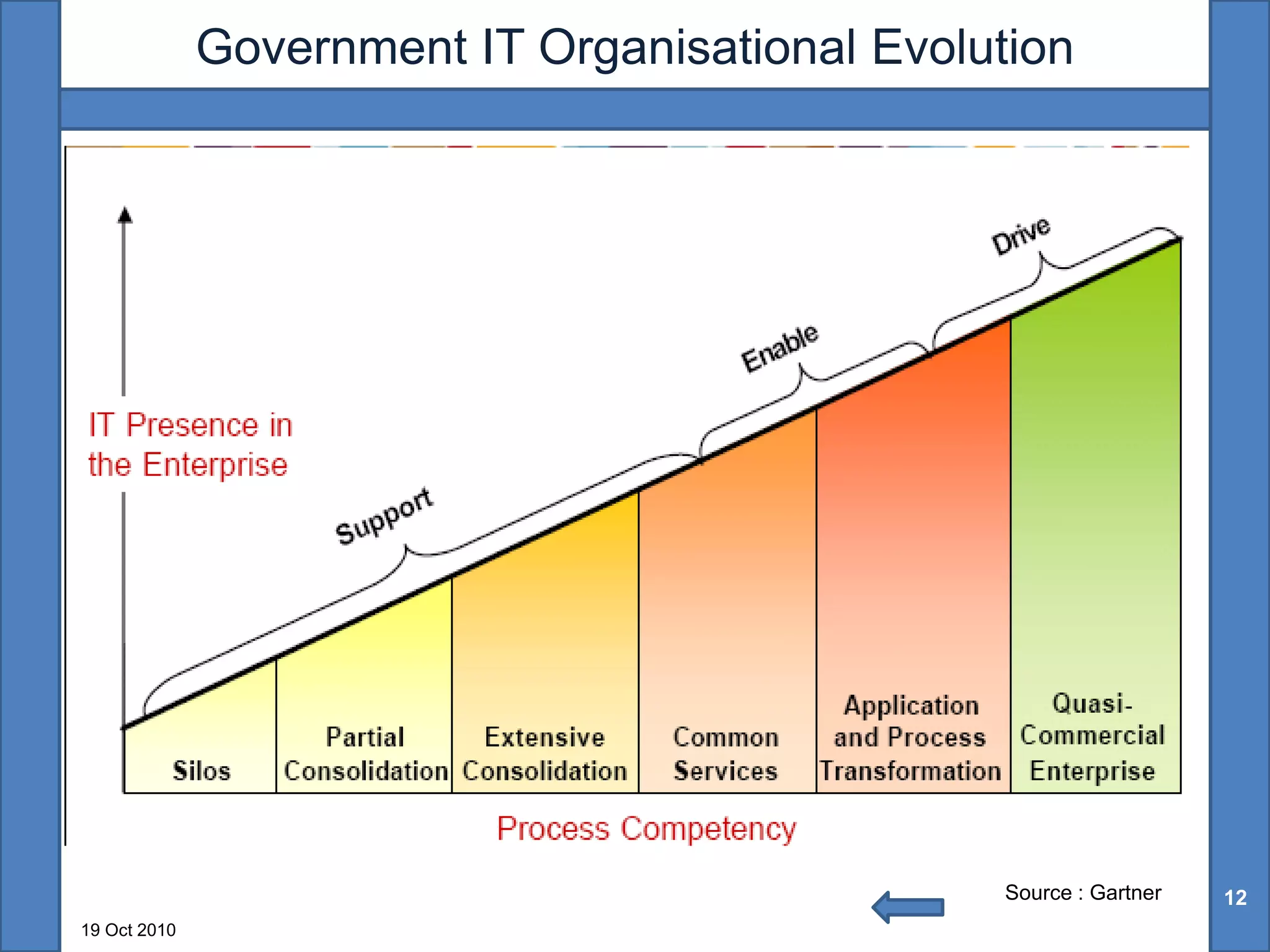
The document discusses the benefits of shared technology platforms in e-governance projects in India. It notes that individual government projects currently operate standalone systems, wasting resources through redundant infrastructure spending and "reinventing the wheel". Shared platforms allow for expedited procurement, pooled IT resources on demand, adherence to interoperability standards, and a shift from capital expenditure to operational expenditure models. The key elements of shared platforms include common infrastructure, software development environments, standardized processes, and call center/help desk support services. Information utilities would offer these platforms on a services basis including infrastructure as a service, platform as a service, and software/process management as a service. This enables agencies to leverage existing e-infrastructure and outsource routine