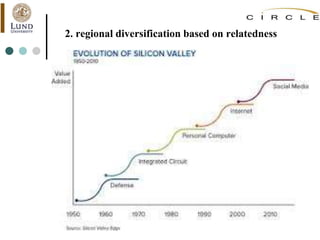
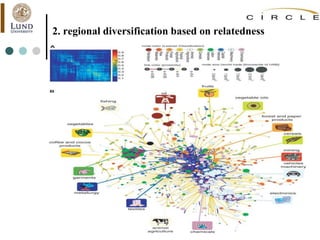
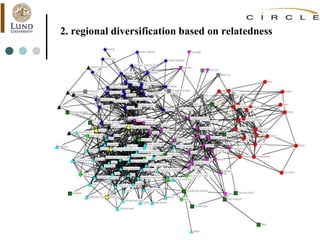
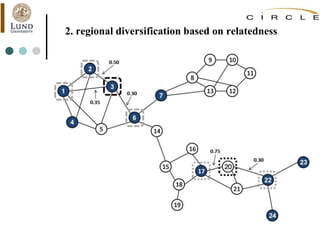
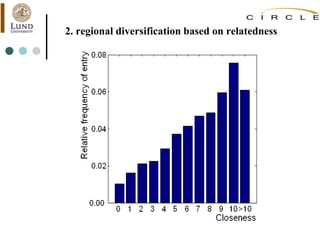
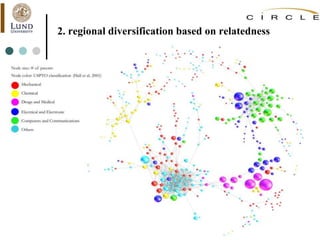
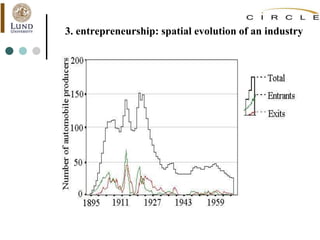
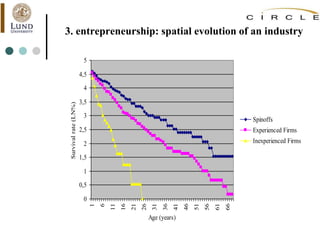
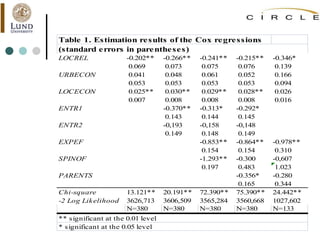
This document summarizes an academic lecture on evolutionary economic geography and regional diversification. It discusses three key topics: 1) How related variety between industries in a region promotes regional growth through knowledge spillovers. 2) How regions diversify into new industries that are related to existing regional capabilities. New industries often branch out from technologically-related industries. 3) How experienced entrepreneurs from related industries help new industries evolve spatially, as seen in the development of the British automobile industry. Their survival rates were higher, influencing which regions the industry developed in.