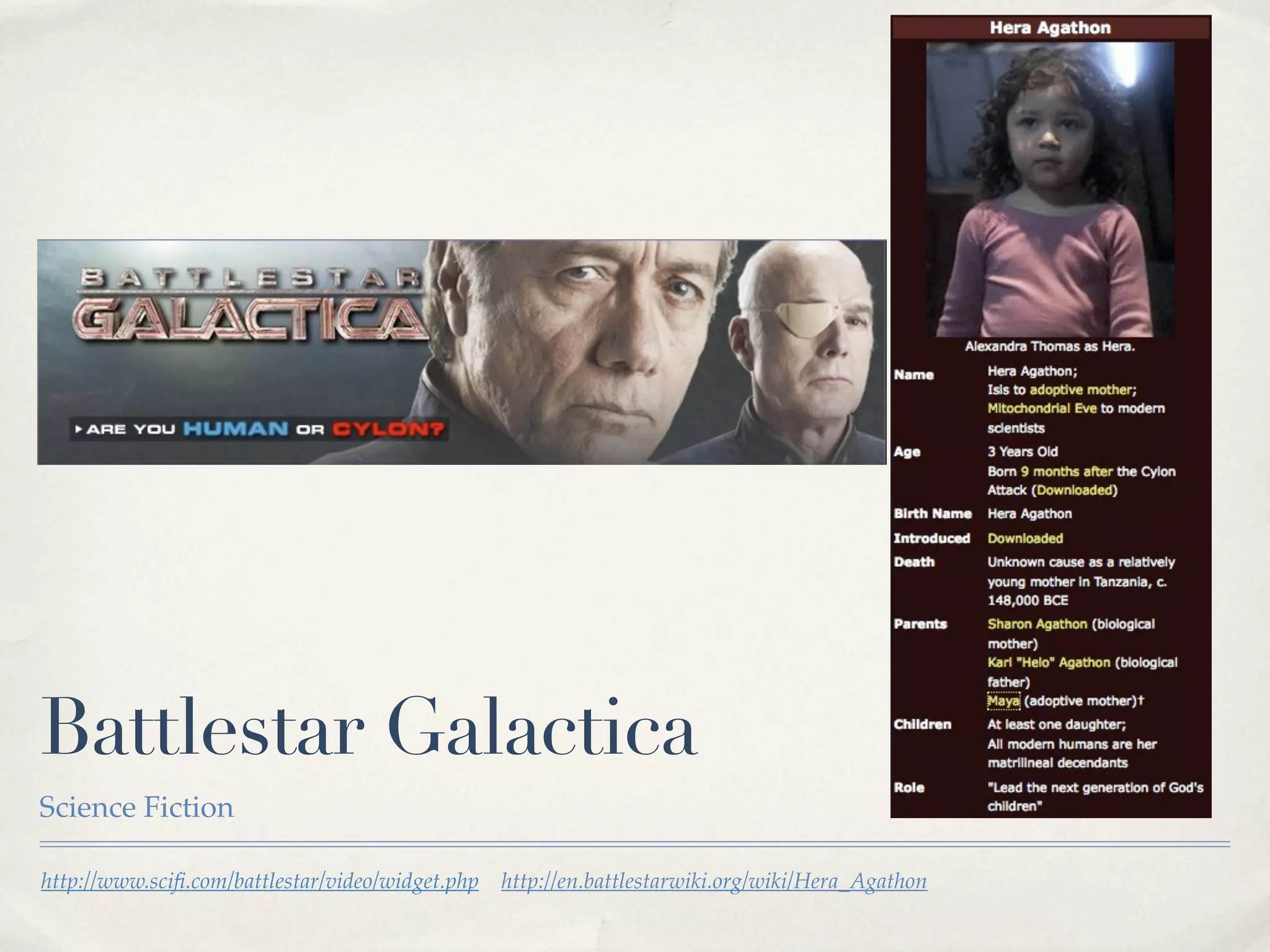
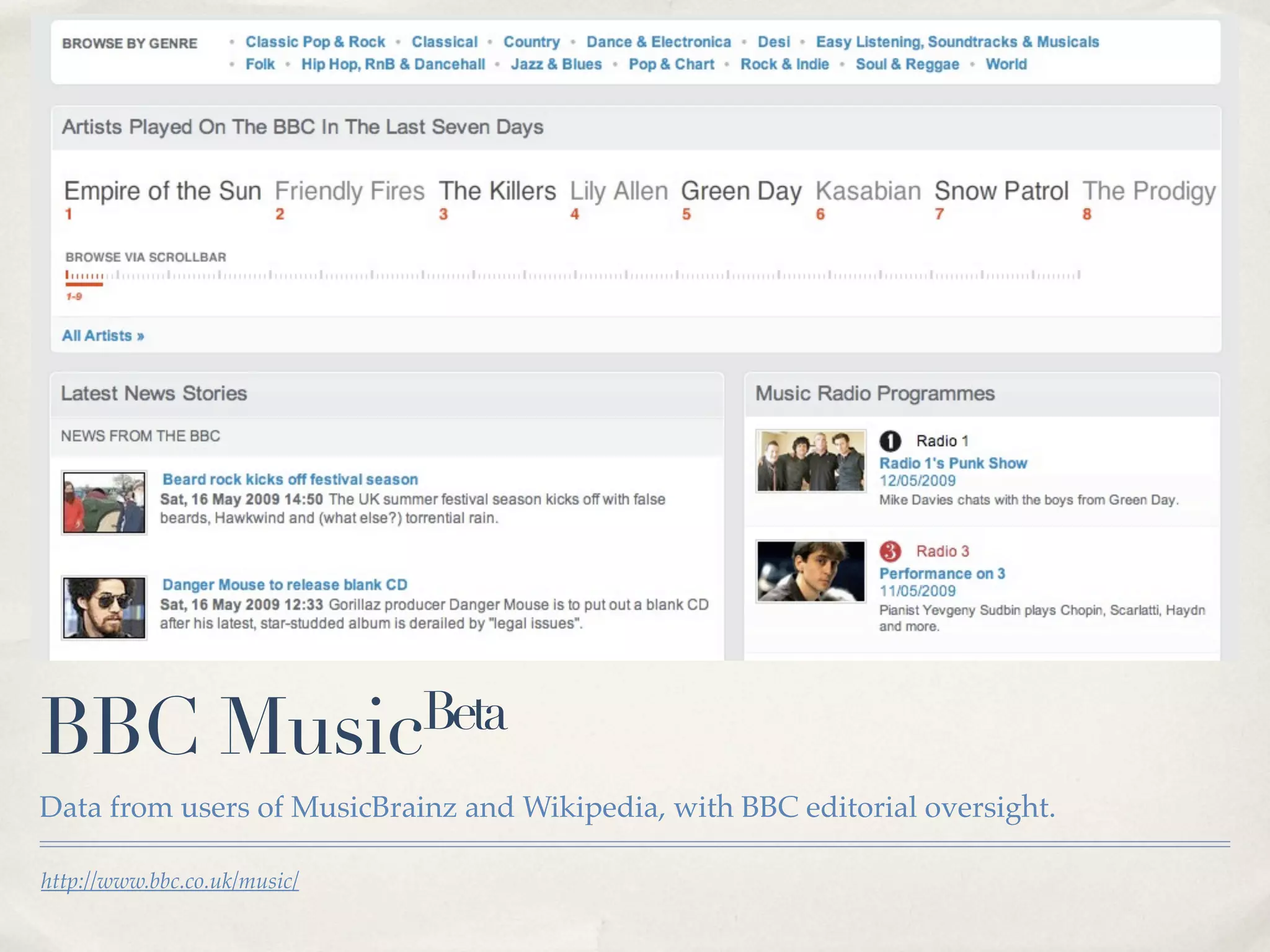
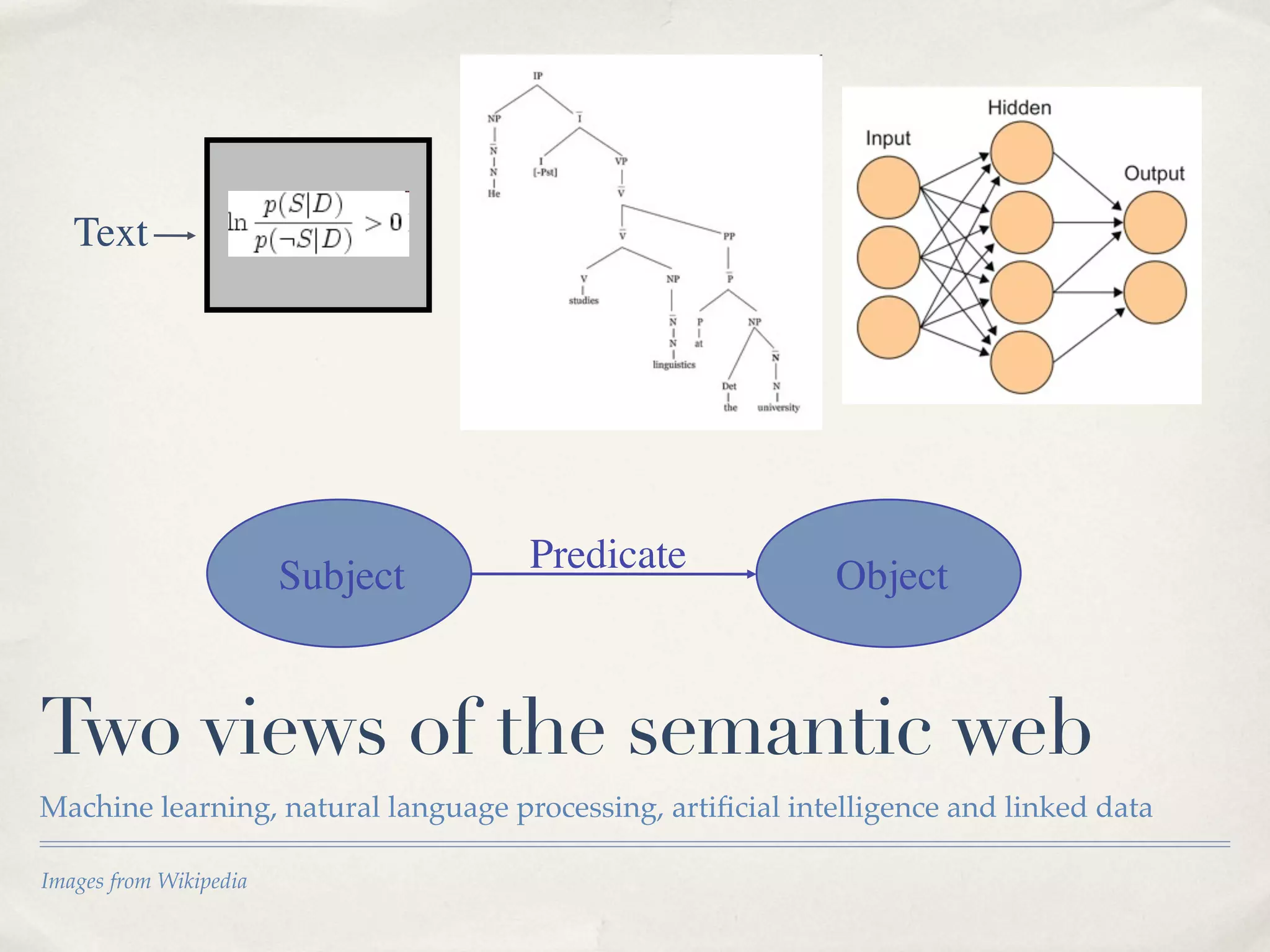
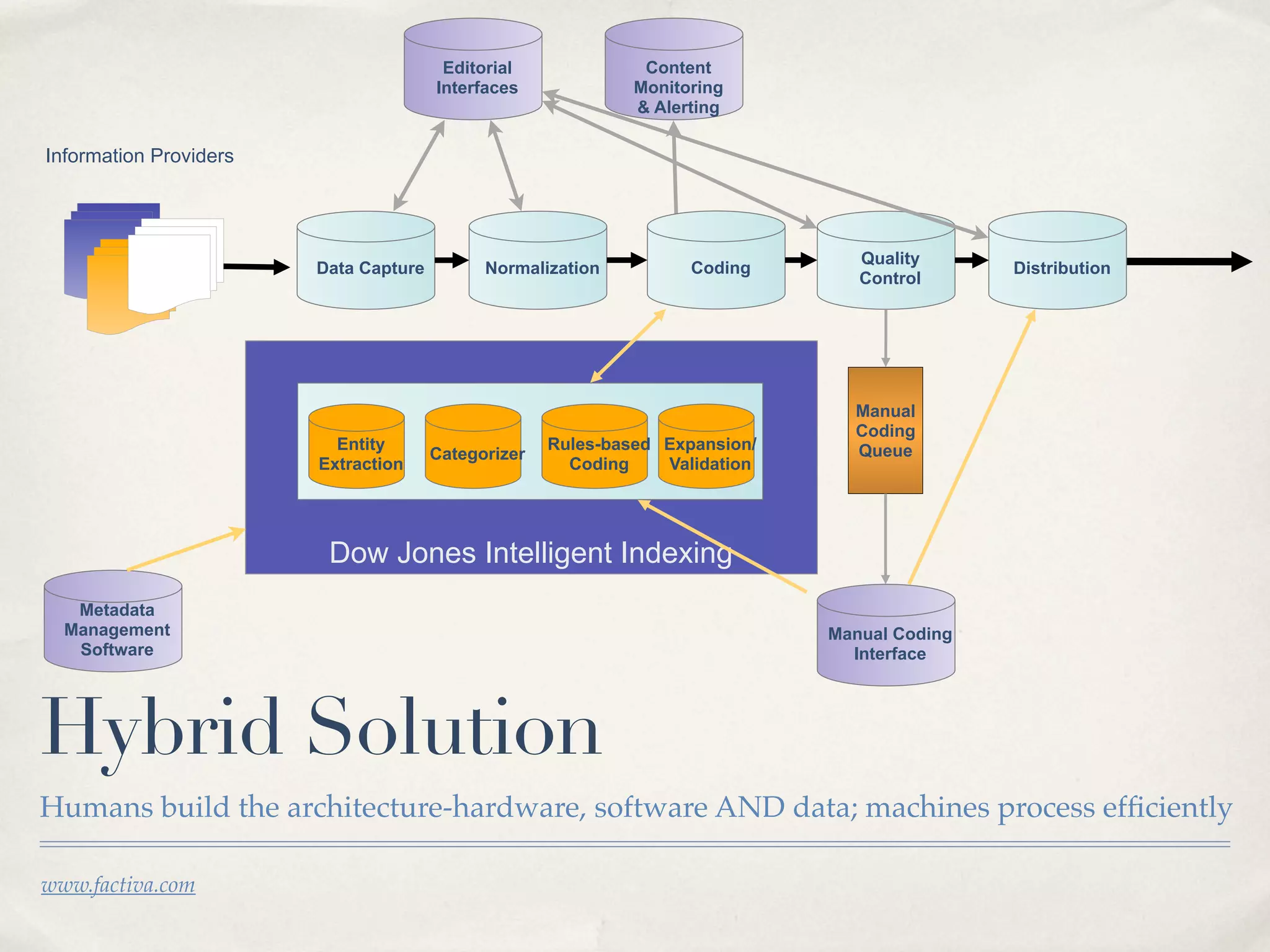
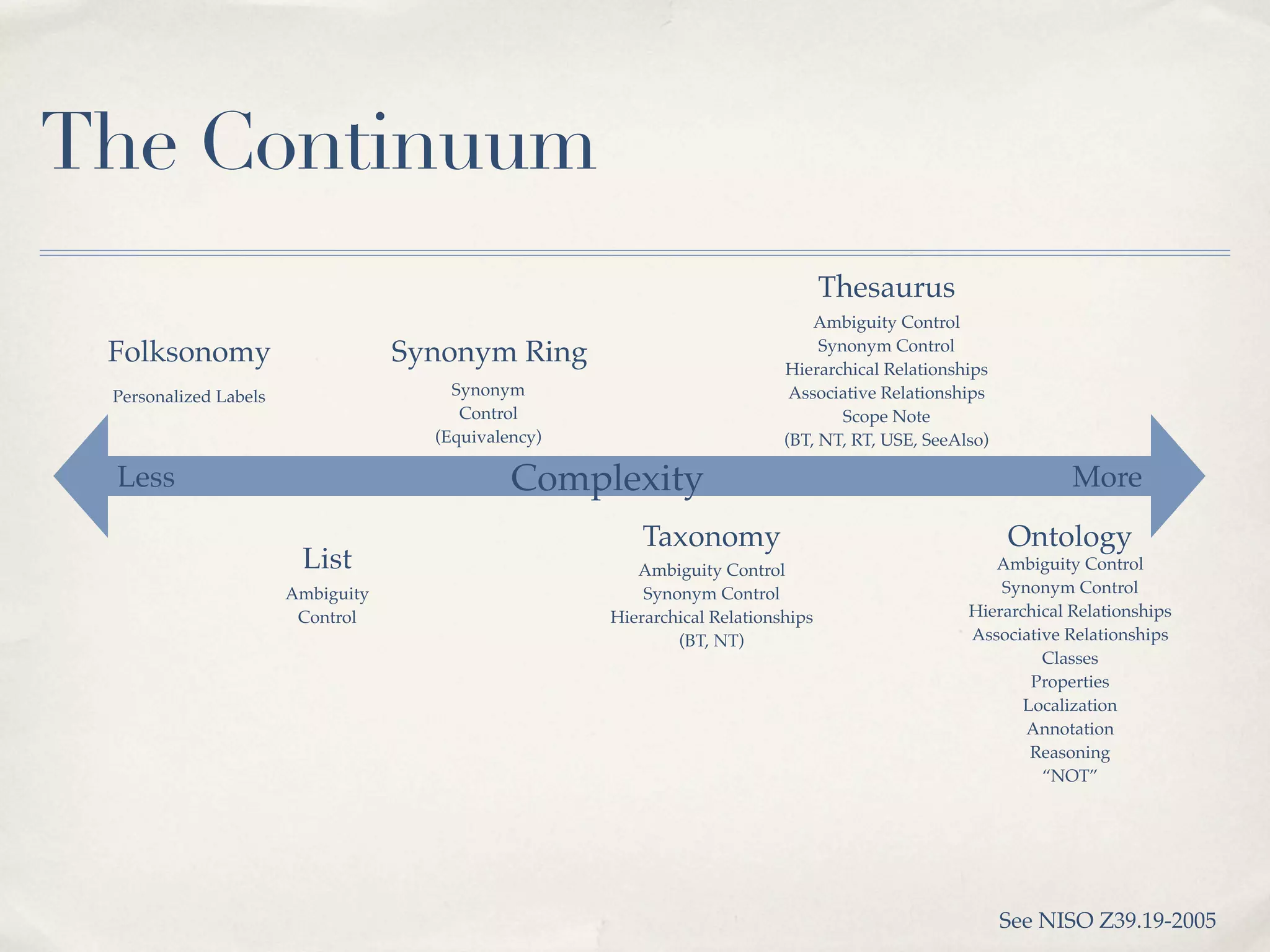
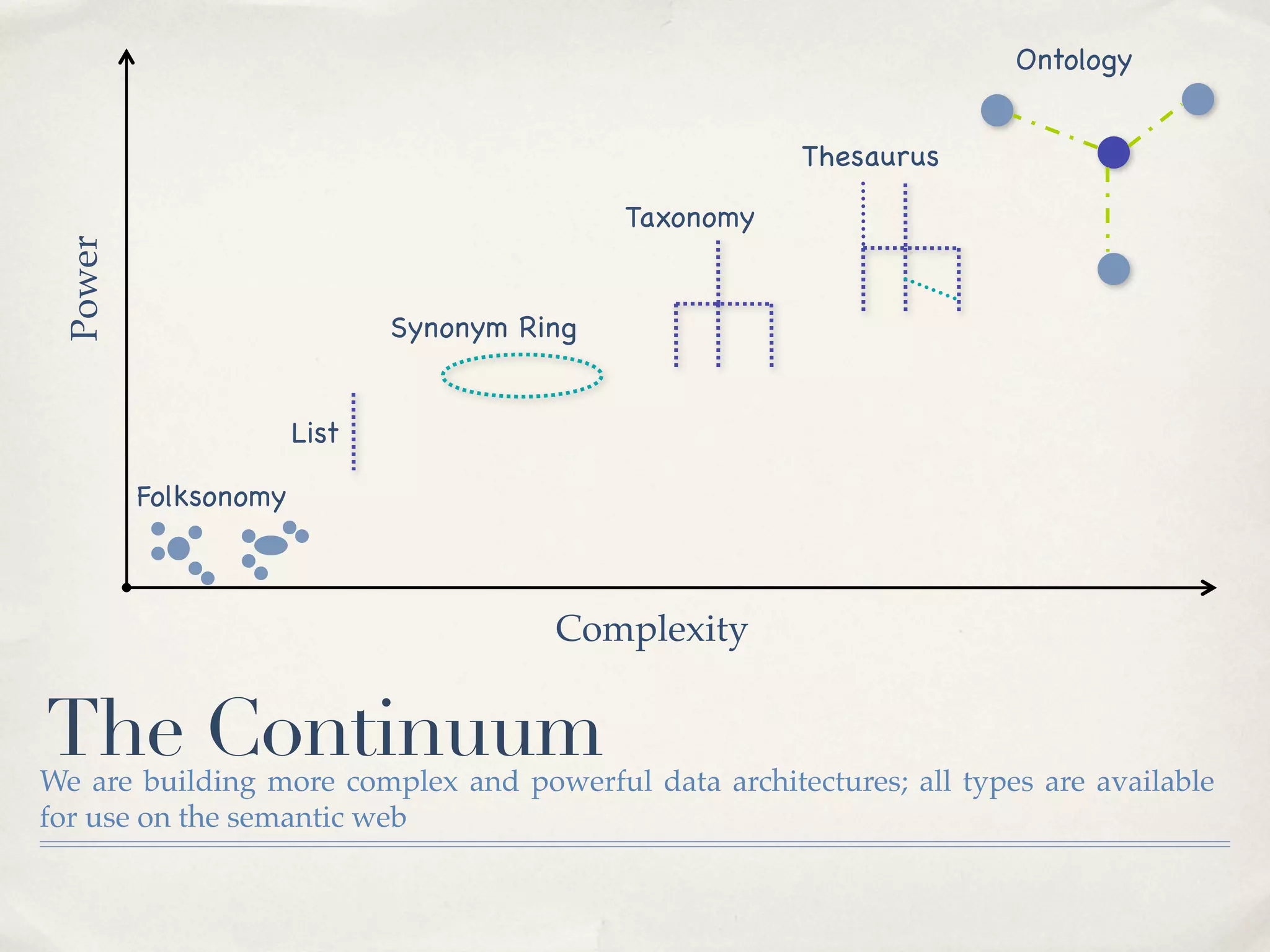
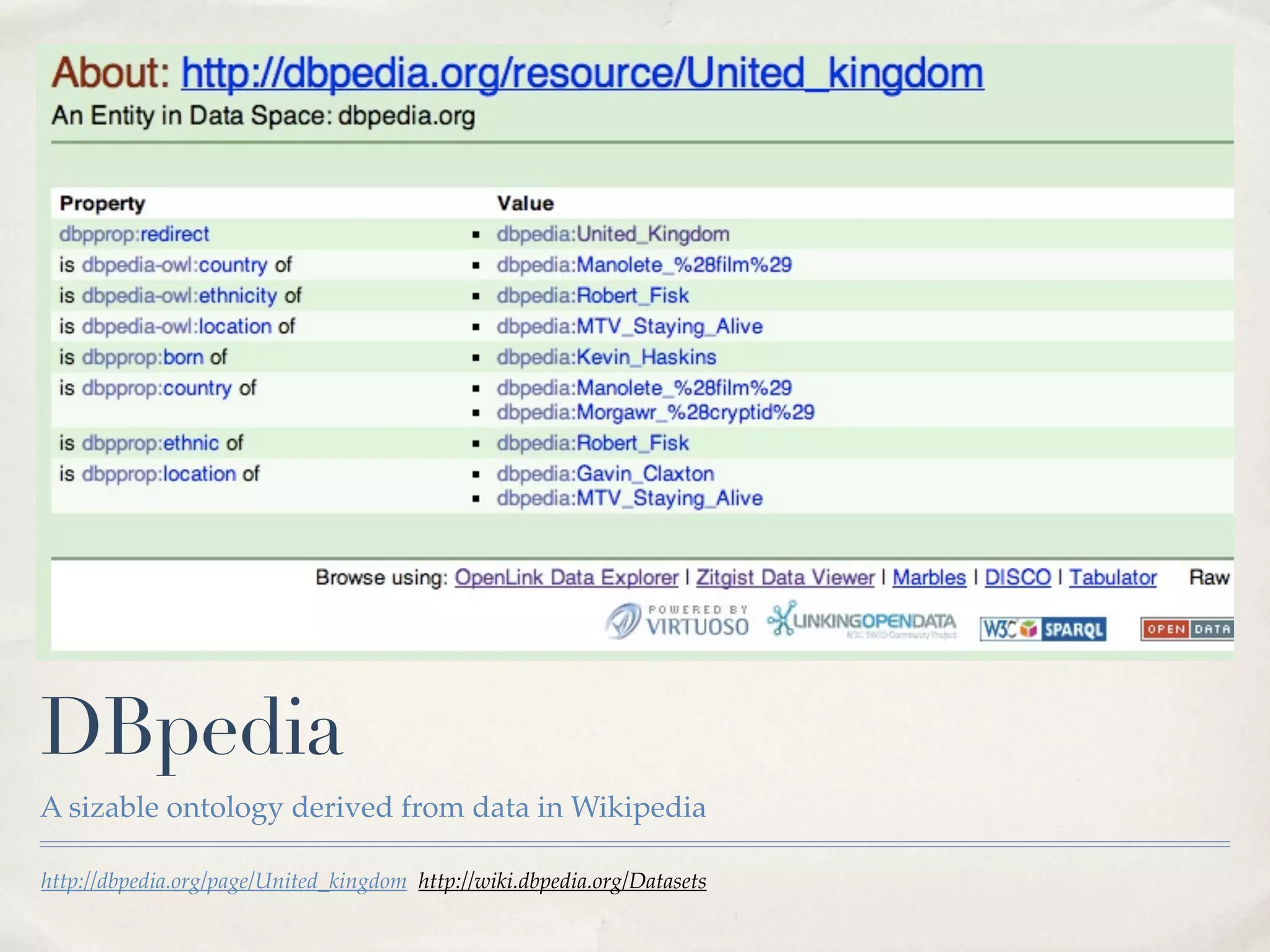
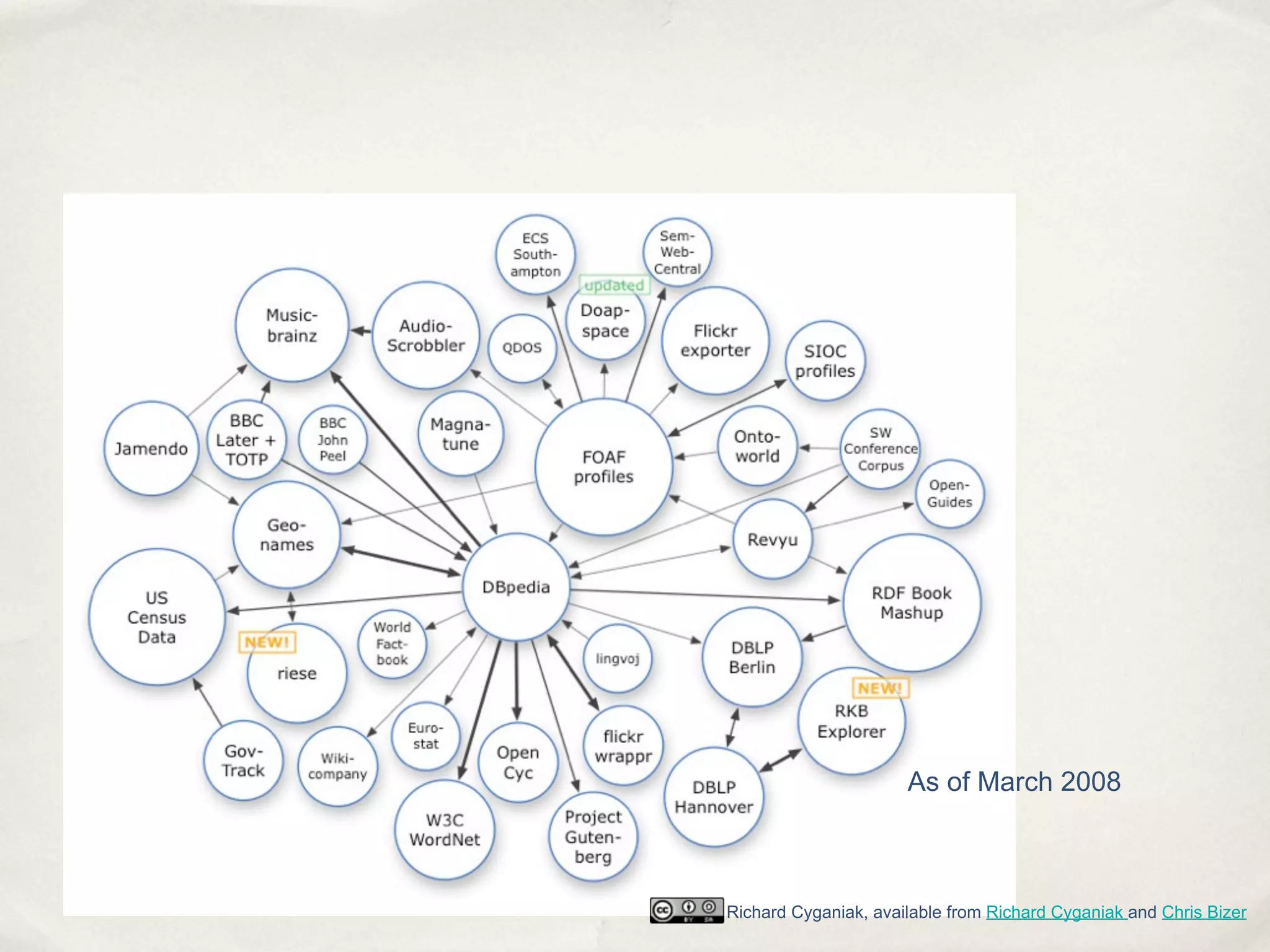
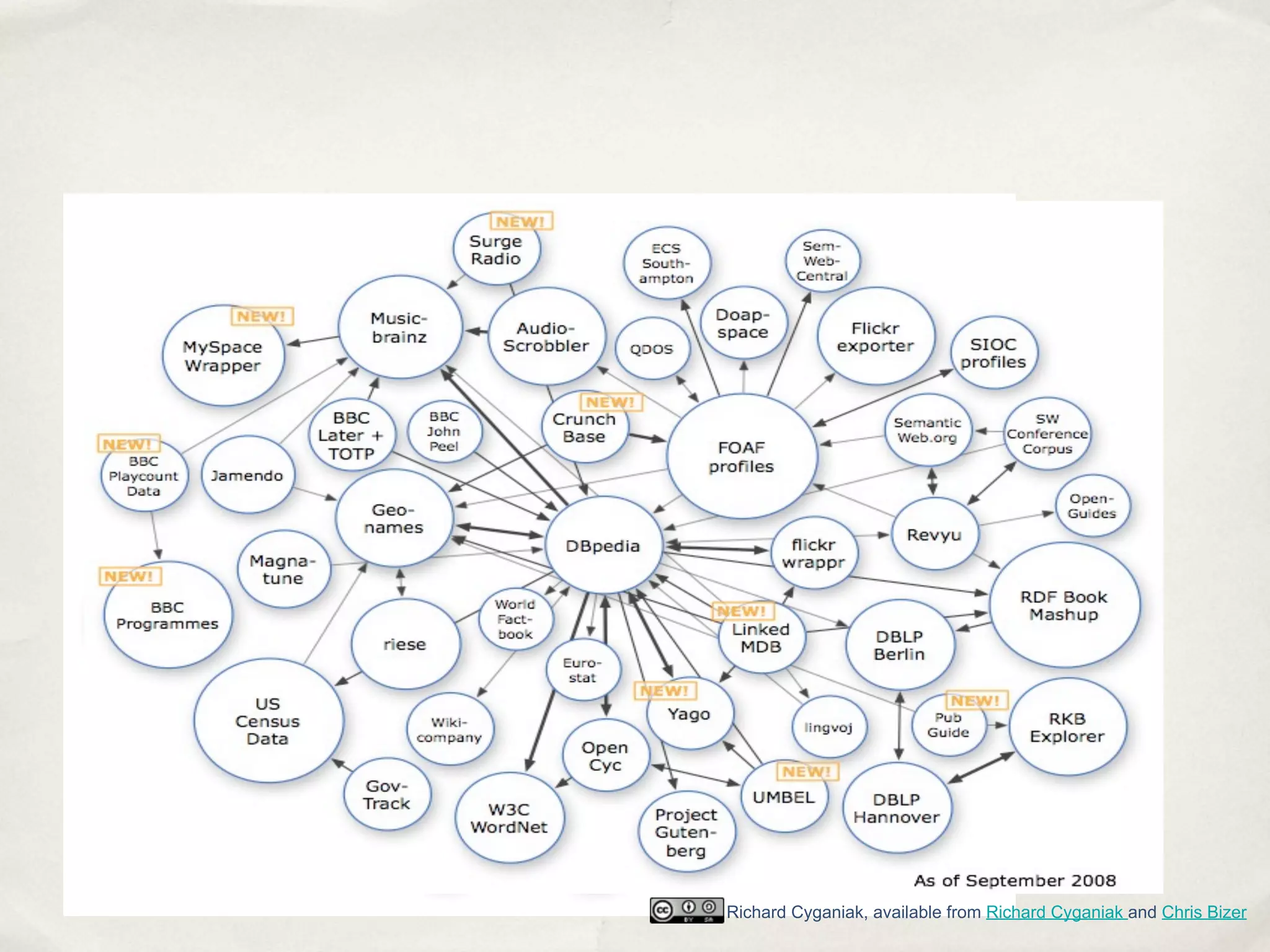
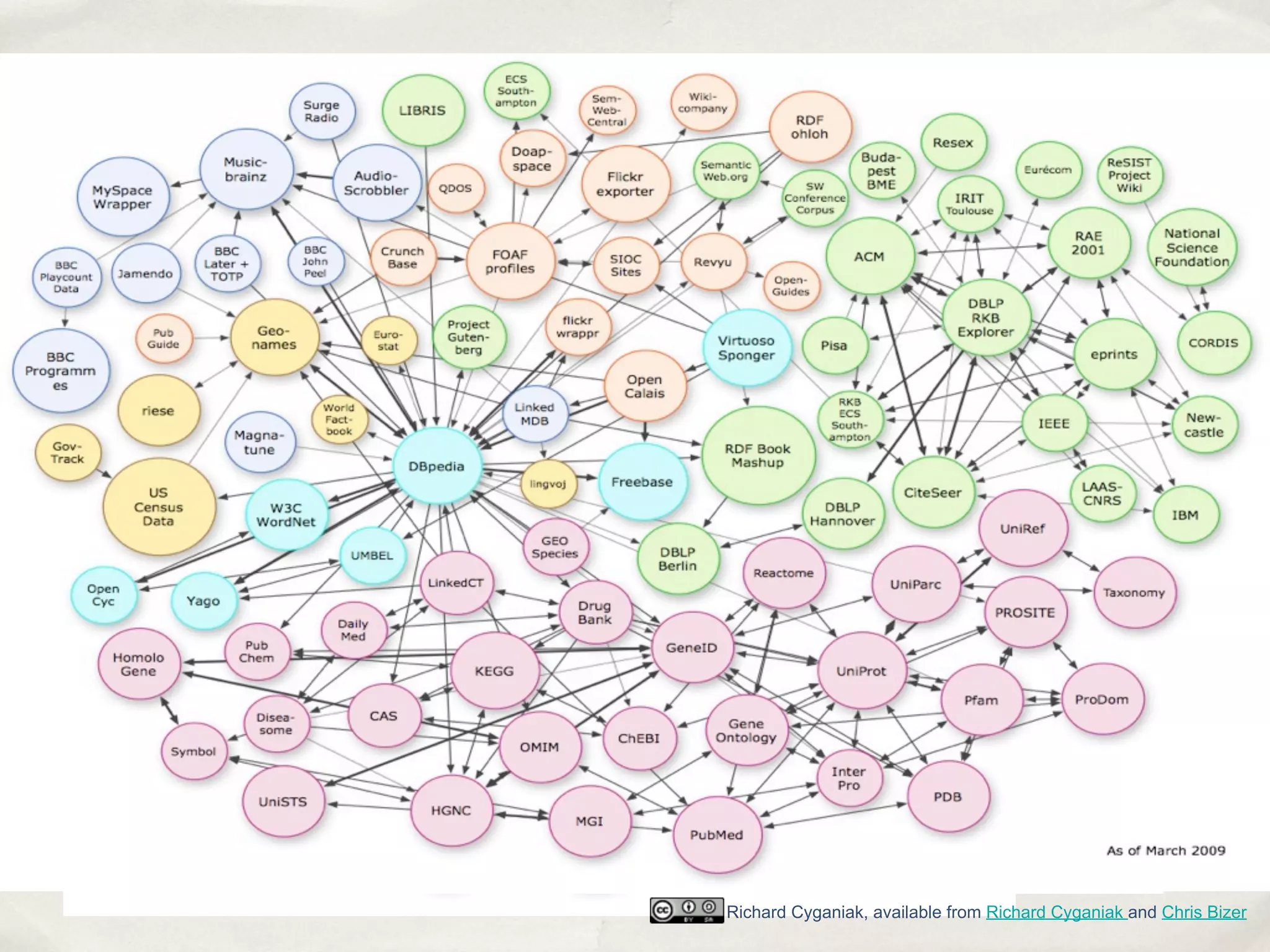
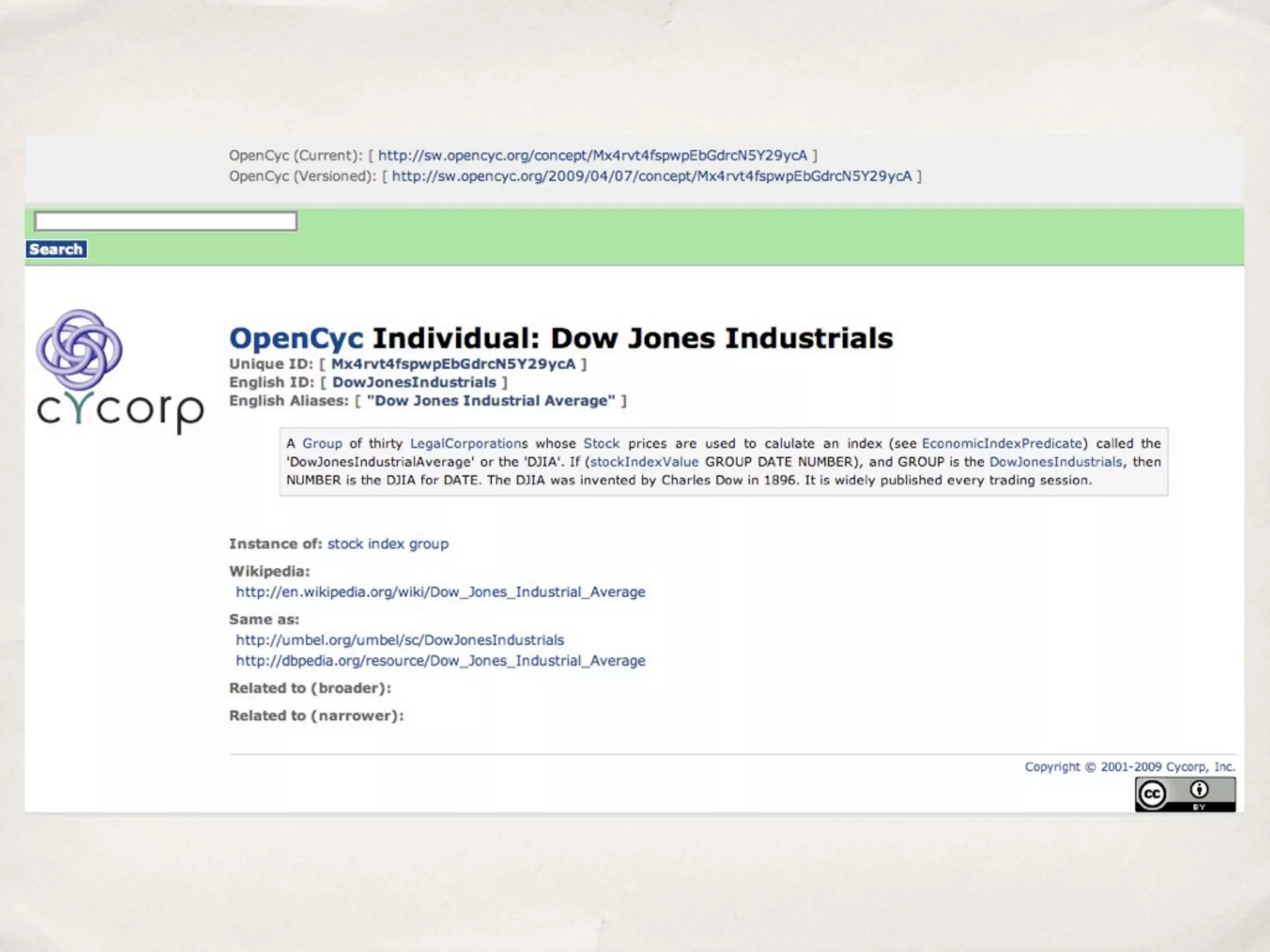
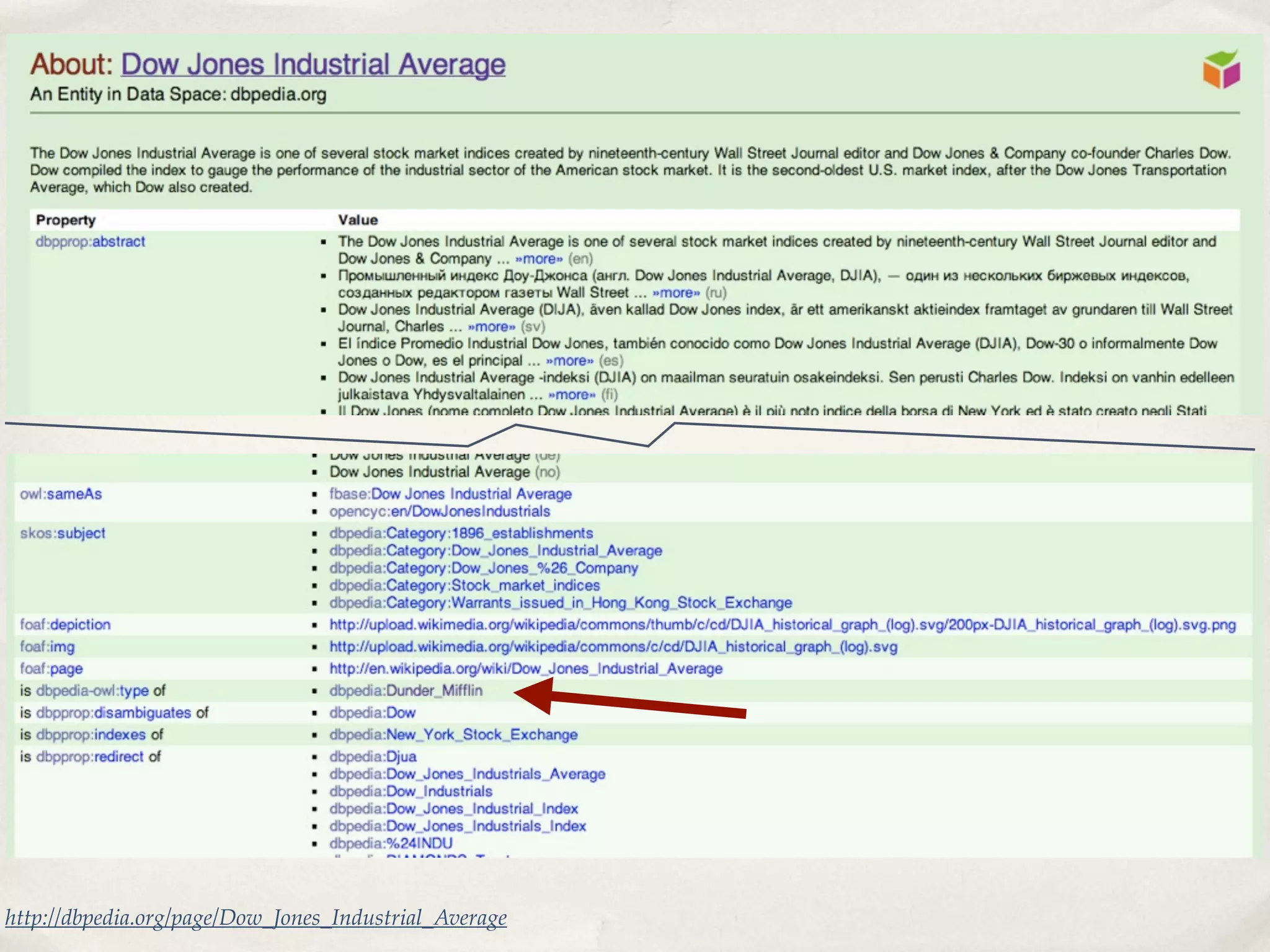
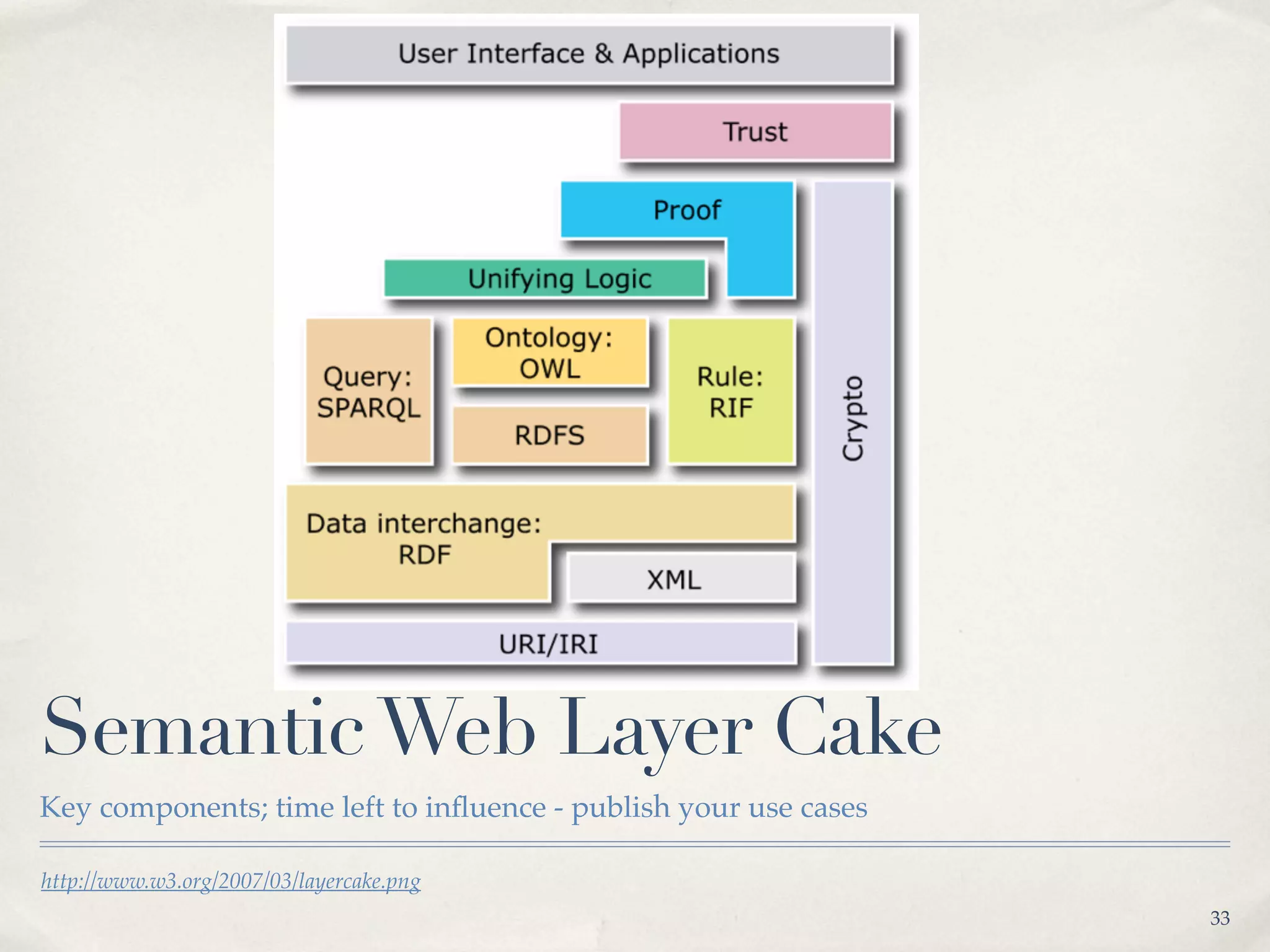
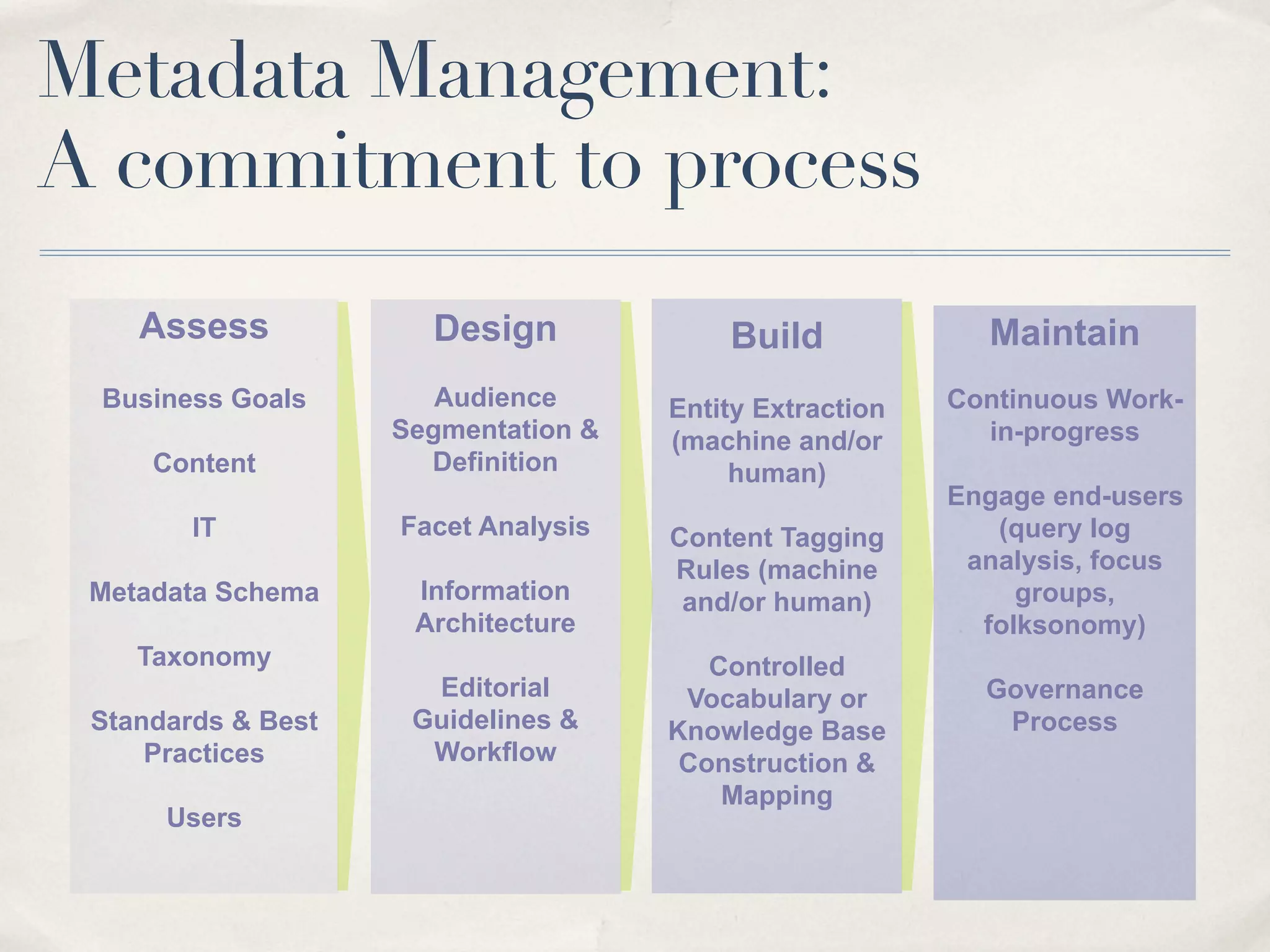
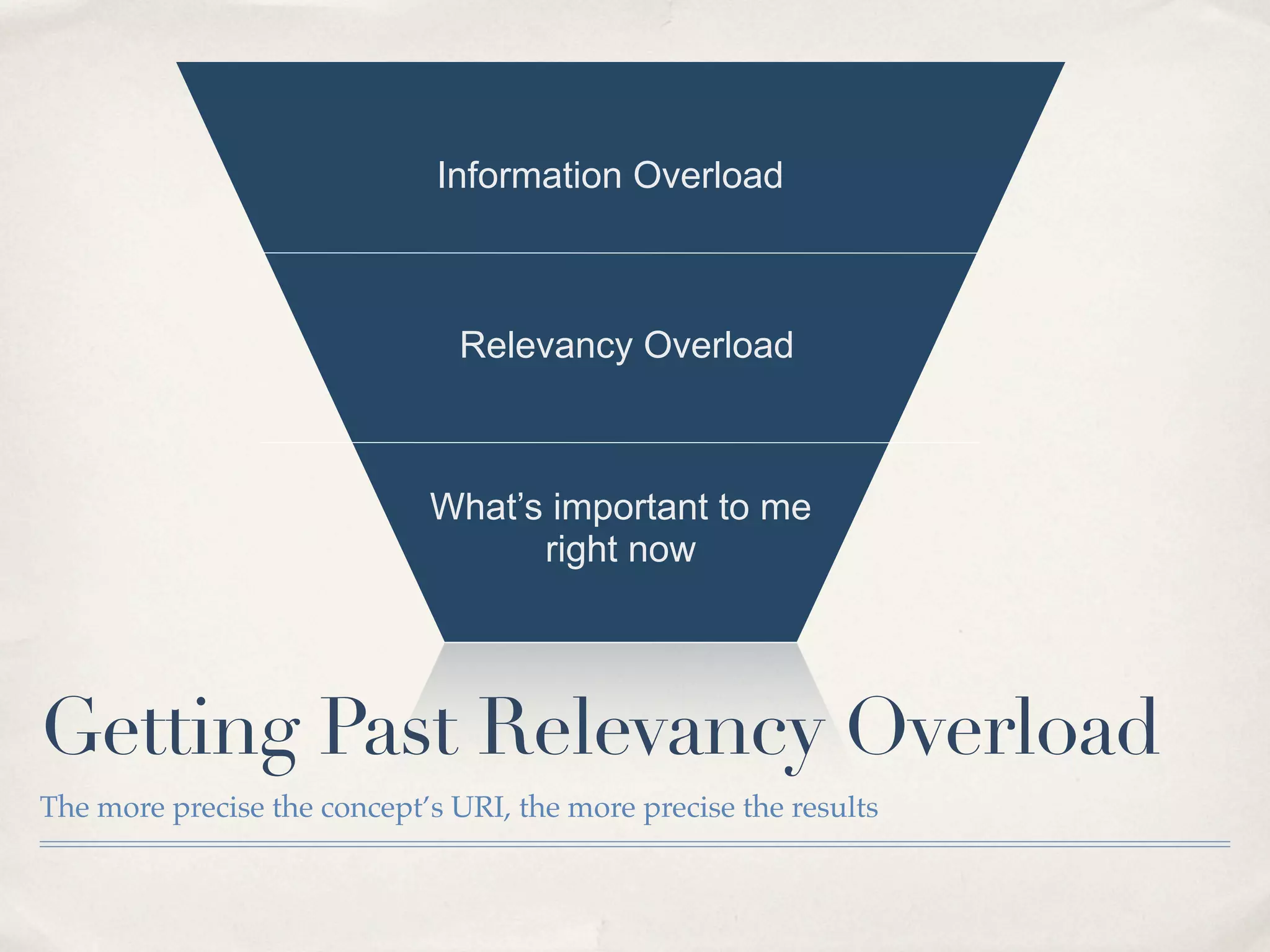
The document discusses the semantic web and metadata management. It defines the semantic web as a universal medium for exchanging information electronically that can be processed and still have meaning. It discusses challenges like overcoming prior integration issues and determining return on investment. It also discusses the importance of the semantic web for business needs like re-purposing data instead of re-creating it. Finally, it discusses getting past relevancy overload on the web by making concept URIs more precise to improve search results.