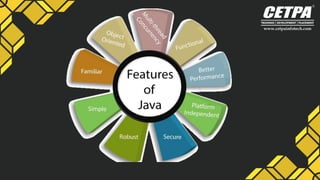
This document provides an overview of the Java programming language, including its history, applications, versions, features, components, and platforms. Java is an object-oriented language designed to be platform independent so that code can run on any device. It has a wide variety of uses including for mobile apps, web apps, enterprise software, and more. The language was created in 1991 and released publicly in 1995 with the goals of being fast, secure, and reliable.