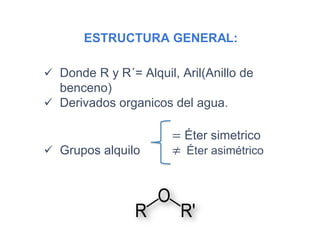
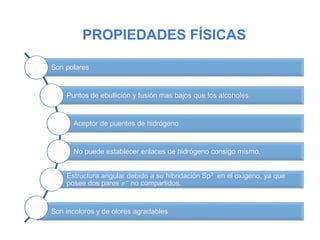
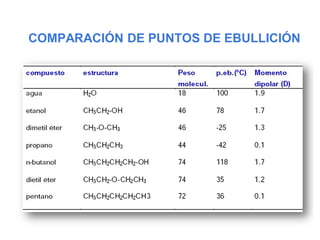
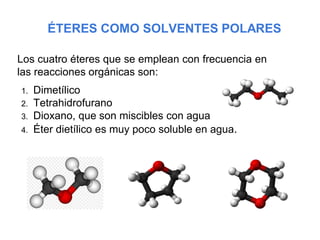
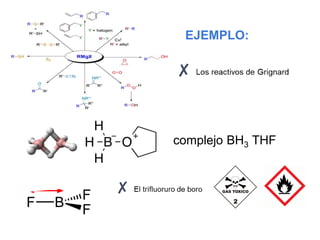
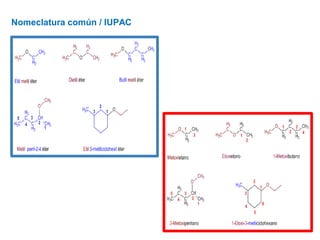
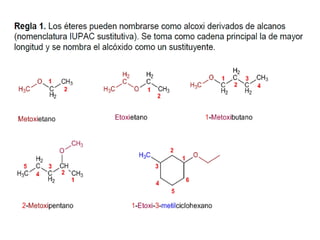
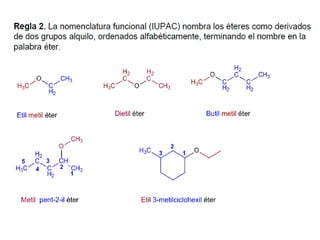
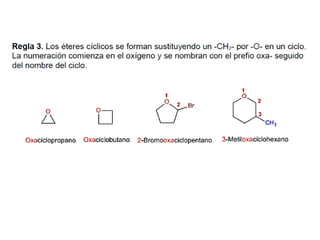
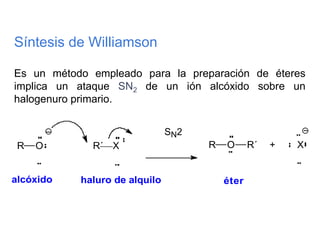
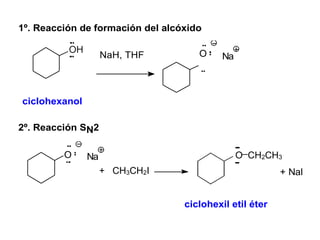
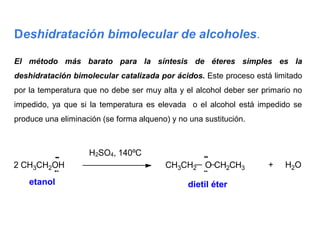
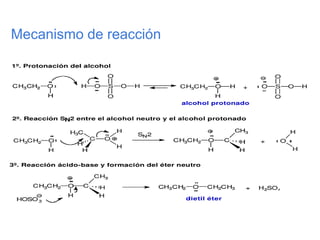
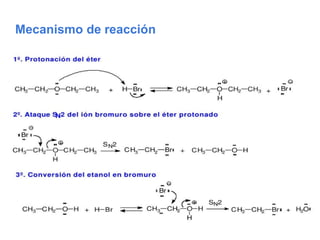
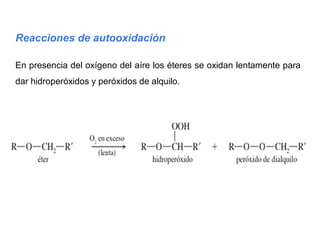
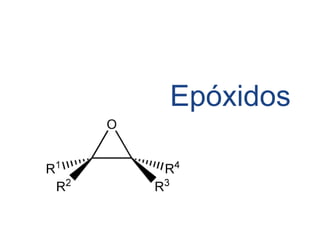
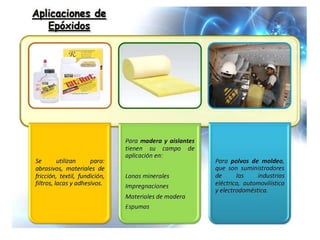
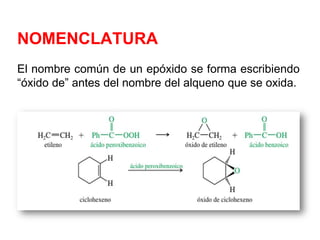
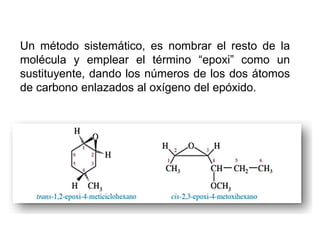
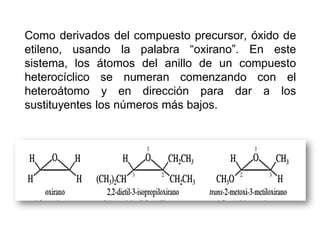
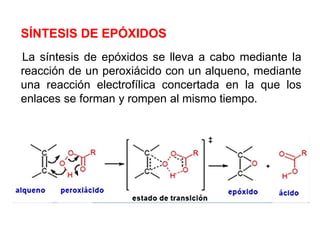
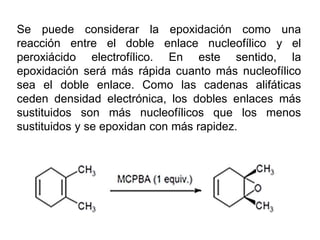
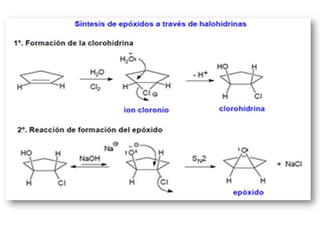
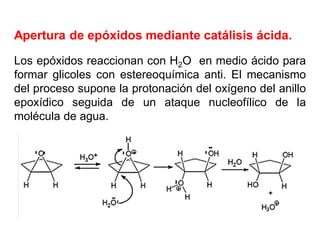
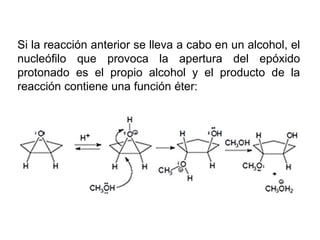
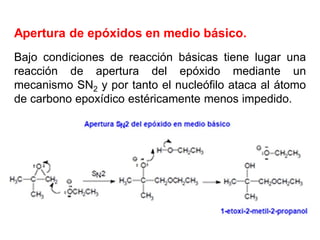
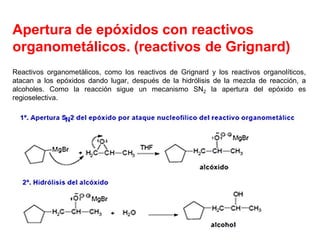
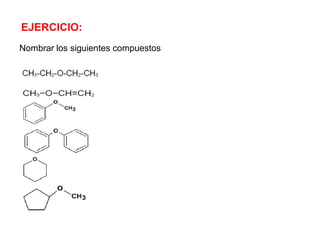
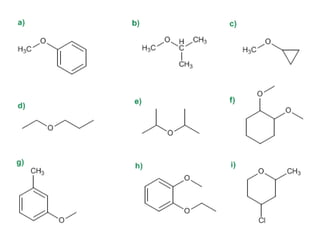
Éteres are organic compounds that contain an oxygen atom bonded to two alkyl or aryl groups. They are commonly used as solvents in organic chemistry due to their low reactivity. There are several methods for synthesizing ethers, such as the Williamson ether synthesis, which involves a nucleophilic substitution reaction between an alkoxide ion and an alkyl halide. Ethers can also be synthesized through the acid-catalyzed dehydration of two alcohol molecules. Ep oxides are cyclic ethers containing an oxygen atom in a three-membered ring. They are highly reactive and can undergo ring-opening reactions under acidic or basic conditions.