Essay on Economy.pdf
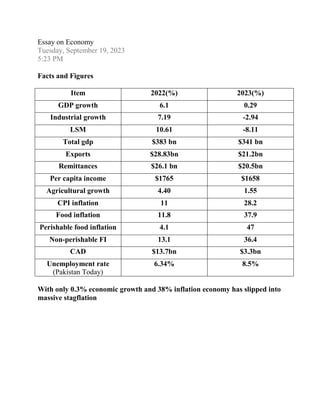
- 1. Essay on Economy Tuesday, September 19, 2023 5:23 PM Facts and Figures Item 2022(%) 2023(%) GDP growth 6.1 0.29 Industrial growth 7.19 -2.94 LSM 10.61 -8.11 Total gdp $383 bn $341 bn Exports $28.83bn $21.2bn Remittances $26.1 bn $20.5bn Per capita income $1765 $1658 Agricultural growth 4.40 1.55 CPI inflation 11 28.2 Food inflation 11.8 37.9 Perishable food inflation 4.1 47 Non-perishable FI 13.1 36.4 CAD $13.7bn $3.3bn Unemployment rate (Pakistan Today) 6.34% 8.5% With only 0.3% economic growth and 38% inflation economy has slipped into massive stagflation
- 2. 1-Strategies for poverty alleviation Introduction Pakistan, like many developing nations, has a significant informal economy that operates outside the purview of formal regulations and institutions. This informal sector plays a crucial role in providing livelihoods and economic support to a substantial portion of the population. However, it also poses challenges related to economic instability, lack of social protections, and reduced tax revenue. This essay, spanning 3000 words, explores Pakistan's informal economy, identifies the challenges it presents, examines the opportunities it offers, and discusses potential strategies for its formalization and improvement. I. Understanding Pakistan's Informal Economy A. Definition and Scope 1. Informal vs. Formal Sectors 2. Key Characteristics of the Informal Economy B. Size and Significance 1. Informal Employment Statistics(75%) 2. Contribution to GDP(40%)($507Billion) II. Drivers of the Informal Economy in Pakistan A. Economic Factors 1. Limited Access to Credit 2. Low Skill Levels
- 3. 3. Limited Employment Opportunities in the Formal Sector B. Socio-Cultural Factors 1. Social Networks and Trust 2. Traditional Labor Practices C. Legal and Regulatory Framework 1. Complex Bureaucracy 2. High Compliance Costs III. Challenges Posed by the Informal Economy A. Economic Challenges 1. Reduced Tax Revenues 2. Economic Instability 3. Lack of Access to Financial Services B. Social Challenges 1. Lack of Social Protections 2. Vulnerability to Exploitation 3. Income Inequality C. Legal and Regulatory Challenges 1. Limited Labor Rights 2. Informal Labor Market Practices 3. Ambiguities in Property Rights IV. Opportunities within the Informal Economy A. Job Creation and Livelihoods 1. Diverse Employment Opportunities 2. Entrepreneurship and Self-Employment B. Informal Skills and Traditions
- 4. 1. Traditional Artisanal Skills 2. Adaptation to Local Needs C. Resilience and Adaptability 1. Informal Safety Nets 2. Response to Economic Shocks V. Strategies for Formalization and Improvement A. Legal Reforms and Simplification 1. Streamlining Business Registration 2. Rationalizing Labor Laws 3. Enhancing Property Rights B. Access to Financial Services 1. Microfinance and Banking Inclusion 2. Mobile Banking and Digital Payments C. Skills Development and Education 1. Vocational Training Programs 2. Promoting Literacy and Basic Education D. Social Protections 1. Social Safety Nets 2. Access to Healthcare and Education E. Tax Reforms and Revenue Generation 1. Broadening the Tax Base 2. Progressive Taxation 3. Tax Incentives for Formalization F. Government Support for Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
- 5. 1. Access to Credit and Capital 2. Capacity Building and Market Linkages G. Promoting Cooperative Models 1. Farmer Cooperatives 2. Informal Workers' Associations VI. Case Studies and Success Stories A. The Benazir Income Support Program (BISP) 1. Providing Financial Support to Vulnerable Populations 2. Conditional Cash Transfers B. The Ehsaas Program 1. Expanding Social Safety Nets 2. Targeting Poverty Alleviation C. The Lahore Waste Management Company (LWMC) 1. Formalizing Waste Collection Services 2. Employment Opportunities for Informal Workers D. The Role of the Aga Khan Rural Support Program (AKRSP) 1. Rural Development and Livelihood Enhancement 2. Community-Based Initiatives VII. Challenges to Formalization A. Resistance to Change 1. Inertia within Informal Sectors 2. Cultural and Traditional Practices B. Enforcement and Compliance 1. Monitoring Informal Activities
- 6. 2. Avoidance Strategies C. Resource Constraints 1. Financial and Human Resource Limitations 2. Political Will and Commitment VIII. Conclusion In conclusion, Pakistan's informal economy is a significant aspect of the country's socio-economic landscape, offering both challenges and opportunities. While it provides employment and livelihoods to millions, it also poses challenges related to taxation, social protections, and economic stability. The formalization and improvement of the informal economy require a multifaceted approach that involves legal reforms, financial inclusion, skills development, and social protections. Several successful initiatives and programs in Pakistan provide valuable insights into the potential for positive change within the informal sector. Addressing the challenges to formalization, including resistance to change and enforcement difficulties, is essential for creating a more inclusive and equitable economy. By recognizing the value of the informal economy and implementing strategies for its improvement, Pakistan can work toward a more sustainable and inclusive future for all its citizens. 2-IMF bailouts: roads to stability or recipes for disaster Introduction The International Monetary Fund (IMF) plays a pivotal role in the global financial system by providing financial assistance to countries facing economic crises. While IMF bailouts are intended to restore economic stability and prevent financial contagion, they have been a subject of debate for decades. Critics argue that these programs often come with stringent conditions and may exacerbate economic hardships in recipient nations. This essay, spanning 3000 words, delves into the complexities of IMF bailouts, examining their goals, the conditions attached, and their impact on recipient countries, with a focus on whether they ultimately lead to stability or disaster. I. Understanding the IMF and Its Role
- 7. A. Origins and Objectives 1. Founding Principles 2. Maintaining Global Economic Stability B. IMF Lending Programs 1. Emergency Financial Assistance 2. Structural Adjustment Programs (SAPs) 3. Poverty Reduction and Growth Facility (PRGF) II. Goals of IMF Bailouts A. Restoring Economic Stability 1. Currency Stabilization 2. Addressing Balance of Payments Crises B. Preventing Contagion 1. Containing Regional and Global Economic Spillovers 2. Maintaining Confidence in the International Financial System III. Conditions Attached to IMF Bailouts A. Fiscal and Monetary Policies 1. Austerity Measures 2. Exchange Rate Policies 3. Inflation Targets B. Structural Reforms 1. Privatization 2. Trade Liberalization 3. Public Sector Reforms C. Social Impact
- 8. 1. Impact on Vulnerable Populations 2. Income Inequality and Poverty D. Governance and Transparency 1. Anti-Corruption Measures 2. Enhancing Accountability IV. The Impact of IMF Bailouts A. Success Stories 1. South Korea's Recovery in 1997 2. Argentina's Turnaround in 2002 B. Criticisms and Challenges 1. Macroeconomic and Social Costs 2. Conditionalities and Sovereignty 3. Moral Hazard C. The Debate Over Economic Liberalization 1. Trade-Off Between Liberalization and Sovereignty 2. Debate Over Deregulation V. Case Studies: The Asian Financial Crisis A. Thailand 1. Currency Crisis and IMF Intervention 2. Economic Consequences and Recovery B. Indonesia 1. Social and Political Turmoil 2. Post-Crisis Governance and Economic Transformation C. South Korea
- 9. 1. The Chaebol Crisis 2. Restructuring and Recovery VI. Lessons Learned and Reforms A. The IMF's Evolving Approach 1. Shift from Austerity to Growth-Focused Policies 2. Enhanced Monitoring and Surveillance B. Calls for Reform 1. Quota and Governance Reforms 2. Assessing Conditionality C. Alternatives to IMF Bailouts 1. Regional Financial Arrangements 2. Debt Relief Initiatives VII. Ethical Considerations A. Social Responsibility and Equity 1. Impact on Vulnerable Populations 2. Ethical Principles in Policy Formulation B. Environmental Sustainability 1. Climate Considerations in Economic Policies 2. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) VIII. The Way Forward A. Strengthening Global Governance 1. IMF Reform 2. Multilateral Coordination B. Tailoring IMF Programs
- 10. 1. Contextual Conditionality 2. Addressing Social Impact C. Promoting Sustainable Development 1. Integrating Economic and Environmental Objectives 2. Reducing Income Inequality IX. Conclusion In conclusion, IMF bailouts remain a controversial and multifaceted issue in the realm of international finance. While they are designed to restore economic stability and prevent financial contagion, they often come with stringent conditions and face criticism for their social and economic costs. The Asian Financial Crisis serves as a poignant example of the complex outcomes associated with IMF interventions. Reforming the IMF, enhancing global governance, and tailoring programs to individual country contexts are essential steps in ensuring that IMF bailouts contribute to stability rather than disaster. Ethical considerations, including social responsibility and environmental sustainability, should be integrated into economic policies to create a more inclusive and equitable global financial system. Ultimately, the debate over the role of IMF bailouts continues to evolve, reflecting the ever-changing dynamics of the global economy. 3-Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in Pakistan Introduction Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) plays a vital role in the economic development of nations, fostering growth, creating jobs, and facilitating the transfer of technology and expertise. In Pakistan, FDI has been a critical component of the country's economic strategy, but it faces various challenges and opportunities. This essay, spanning 3000 words, will delve into the dynamics of FDI in Pakistan, examining the challenges it encounters, the opportunities it presents, and the strategies for enhancing FDI inflows in the country. I. Understanding FDI in Pakistan
- 11. A. Definition and Forms of FDI 1. Equity Investments 2. Reinvestment of Earnings 3. Other Capital B. FDI Statistics in Pakistan 1. Historical Trends 2. Sectoral Distribution 3. Country Sources II. The Importance of FDI A. Economic Growth and Development 1. Contribution to GDP 2. Job Creation 3. Technology Transfer B. Balance of Payments 1. Export Promotion 2. Forex Reserves C. Global Integration 1. Trade Linkages 2. Attracting Multinational Corporations (MNCs) III. FDI Policies and Framework in Pakistan A. Legal Framework 1. Investment Policy 2020 2. Bilateral Investment Treaties (BITs) 3. Legal Protections and Guarantees B. Incentives and Concessions
- 12. 1. Tax Holidays and Exemptions 2. Duty-Free Imports 3. Investment Promotion Agencies C. Sector-Specific Policies 1. Energy 2. Infrastructure 3. Technology and Innovation IV. Challenges to FDI in Pakistan A. Security Concerns 1. Political Instability 2. Terrorism and Militancy B. Infrastructure Deficiencies 1. Energy Shortages 2. Transportation and Logistics C. Bureaucratic Hurdles 1. Regulatory Red Tape 2. Complex Taxation D. Corruption and Governance 1. Transparency and Accountability 2. Rule of Law E. Economic Stability 1. Inflation and Exchange Rate Volatility 2. Fiscal and Monetary Policies F. Social and Cultural Factors 1. Labor Market Issues
- 13. 2. Socio-Cultural Challenges V. Opportunities for FDI in Pakistan A. Infrastructure Development 1. Energy Projects 2. Transportation and Logistics 3. Telecommunications B. Manufacturing and Industrialization 1. Textiles and Garments 2. Automobiles and Engineering 3. Pharmaceuticals C. Agriculture and Food Processing 1. Agribusiness 2. Food Security Initiatives D. Technology and IT Services 1. Software Development 2. Outsourcing E. Renewable Energy 1. Solar and Wind Projects 2. Energy Sustainability VI. Case Studies: Successful FDI Initiatives A. China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) 1. Infrastructure Development 2. Energy Projects 3. Trade Expansion B. Telenor and Other Telecom Investments
- 14. 1. Expanding Mobile Services 2. Digital Inclusion C. Engro Fertilizers 1. Local Manufacturing and Production 2. Agricultural Enhancement D. Honda and Toyota Manufacturing 1. Automobile Production 2. Export Growth VII. Strategies to Enhance FDI in Pakistan A. Political and Security Stability 1. Political Reforms 2. Counterterrorism Efforts B. Infrastructure Development 1. Addressing Energy Shortages 2. Transportation Improvements C. Regulatory Reforms 1. Streamlining Bureaucracy 2. Tax Simplification D. Investment Promotion and Facilitation 1. Ease of Doing Business Reforms 2. One-Window Operations E. Corruption Control 1. Strengthening Anti-Corruption Measures 2. Promoting Transparency
- 15. F. Economic Diversification 1. Encouraging Technology and Knowledge-Based Industries 2. Promoting Renewable Energy VIII. The Role of International Cooperation A. Bilateral and Multilateral Agreements 1. Free Trade Agreements 2. BITs and Investment Treaties B. Collaboration with International Financial Institutions 1. World Bank and IMF Support 2. Technical Assistance Programs IX. Conclusion In conclusion, FDI is essential for Pakistan's economic growth and development. While the country offers various opportunities for foreign investors, it also faces numerous challenges related to security, infrastructure, governance, and bureaucracy. Strategies for enhancing FDI inflows must focus on political stability, regulatory reforms, infrastructure development, and corruption control. Case studies of successful FDI initiatives, such as CPEC and telecom investments, highlight the potential for transformative economic impact. International cooperation through bilateral agreements and collaboration with international organizations also plays a crucial role in attracting FDI. Realizing Pakistan's potential as an attractive investment destination requires concerted efforts from both the government and the private sector, with a strong emphasis on improving the investment climate, addressing challenges, and fostering an environment conducive to foreign investment. 4-Promotion of Tax Culture in Pakistan: Prospects and Challenges Introduction
- 16. Taxation is the lifeblood of any modern nation-state, providing the necessary funds for public services, infrastructure development, and economic growth. In Pakistan, however, there has been a long-standing issue with tax evasion and a lack of tax compliance. The promotion of a tax culture in Pakistan is essential to ensure fiscal sustainability, reduce the tax gap, and support the country's development goals. This essay, spanning 3000 words, will delve into the prospects and challenges of fostering a tax culture in Pakistan. I. Understanding the Tax Culture A. Definition and Scope B. Importance of a Tax Culture C. Link Between Tax Culture and Economic Development II. The Current State of Taxation in Pakistan A. Tax Revenue Collection 1. Tax-to-GDP Ratio 2. Composition of Tax Revenue B. Tax Evasion and Informal Economy 1. Tax Gap 2. Informal Sector's Contribution C. Tax Compliance Challenges 1. Complex Tax Laws 2. Lack of Transparency 3. Taxpayer Mistrust III. Prospects of Promoting a Tax Culture in Pakistan A. Economic Growth 1. Increased Revenue Collection 2. Infrastructure Development 3. Public Service Delivery
- 17. B. Social Equity 1. Reducing Income Inequality 2. Enhanced Social Safety Nets 3. Poverty Alleviation C. Fiscal Sustainability 1. Reducing Budget Deficits 2. Minimizing Reliance on Borrowing 3. Debt Servicing D. Improved Governance 1. Transparency and Accountability 2. Reduced Corruption 3. Strengthened Institutions IV. Challenges to Promoting a Tax Culture in Pakistan A. Tax Aversion 1. Negative Perceptions of Taxation 2. Historical Factors 3. Resistance to Compliance B. Complex Tax Laws and Procedures 1. Tax Code Complexity 2. Bureaucratic Hurdles 3. Need for Simplification C. Tax Evasion and Informal Economy 1. Informal Sector Challenges 2. Tax Evasion Strategies 3. Undeclared Wealth D. Weak Tax Administration
- 18. 1. Enforcement Capacity 2. Lack of Resources 3. Corruption E. Lack of Trust 1. Taxpayer Mistrust 2. Perceived Misuse of Funds 3. Accountability Deficits V. Strategies for Promoting a Tax Culture A. Taxpayer Education and Awareness 1. Outreach Campaigns 2. Financial Literacy Programs 3. Public Engagement B. Simplifying Tax Laws and Procedures 1. Tax Code Reforms 2. Digitalization and E-Governance 3. Transparent Auditing and Assessment C. Strengthening Tax Administration 1. Capacity Building 2. Modernization of Revenue Collection 3. Combating Corruption D. Progressive Taxation 1. Wealth Taxation 2. Revising Tax Brackets 3. Equitable Taxation Policies E. Enhanced Accountability and Transparency 1. Fiscal Reporting and Auditing 2. Independent Oversight
- 19. 3. Public Access to Tax Data VI. Case Studies and International Comparisons A. Successful Tax Culture Promotion in Other Countries 1. Nordic Countries 2. Singapore 3. Rwanda B. Lessons Learned and Applicability to Pakistan VII. Role of Technology and Innovation A. Digital Payments and E-Filing 1. Promoting Tax Transparency 2. Improving Tax Compliance B. Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence 1. Identifying Tax Evasion Patterns 2. Targeted Enforcement VIII. Building Trust and Accountability A. Transparent Use of Tax Revenue 1. Public Investment in Services 2. Infrastructure Development 3. Poverty Alleviation Programs B. Anti-Corruption Measures 1. Independent Oversight Bodies 2. Whistleblower Protections 3. Strict Enforcement of Anti-Corruption Laws IX. Conclusion
- 20. In conclusion, the promotion of a tax culture in Pakistan is a critical imperative for the country's economic development, fiscal sustainability, and social equity. Despite numerous challenges, including tax aversion, complex tax laws, and weak tax administration, there are significant prospects for fostering a tax culture that encourages compliance and transparency. Effective strategies, including taxpayer education, simplification of tax laws, strengthening tax administration, progressive taxation, and enhanced accountability measures, must be implemented to address these challenges. Leveraging technology and learning from successful international models can further support Pakistan's efforts in building a robust tax culture that benefits both the government and the citizens. Ultimately, building trust, transparency, and accountability in tax collection and expenditure will be key to the success of these initiatives. 5-Foreign Aid and Economic Stability: An In-Depth Analysis Introduction Foreign aid, in the form of financial assistance, resources, and technical support provided by one country to another, has been a longstanding global practice. One of its primary objectives is to promote economic development and stability in recipient countries. However, the effectiveness of foreign aid in achieving economic stability has been a subject of ongoing debate. This essay, spanning 3000 words, aims to critically analyze the impact of foreign aid on economic stability, exploring its mechanisms, challenges, and potential benefits. I. Understanding Foreign Aid A. Types of Foreign Aid 1. Bilateral Aid 2. Multilateral Aid 3. Humanitarian Assistance 4. Technical Assistance B. The Evolution of Foreign Aid 1. Historical Context 2. Changing Aid Paradigms
- 21. II. Theoretical Perspectives on Foreign Aid A. Economic Growth Theories 1. Harrod-Domar Model 2. Solow-Swan Model 3. Endogenous Growth Theory B. Dependency Theory 1. Critiques of Aid Dependency C. Foreign Aid as a Tool of Geopolitics 1. Political and Strategic Interests 2. Conditionality and Influence III. The Mechanisms of Foreign Aid A. Infrastructure Development 1. Transportation and Communication 2. Energy and Utilities B. Human Capital Development 1. Education and Skills Training 2. Healthcare and Nutrition C. Poverty Alleviation 1. Microfinance and Livelihood Programs 2. Social Safety Nets D. Trade and Economic Diversification 1. Market Access and Trade Agreements 2. Promoting Export-Oriented Industries IV. The Impact of Foreign Aid on Economic Stability
- 22. A. Positive Contributions 1. Infrastructure Development and Productivity 2. Human Capital Accumulation 3. Poverty Reduction B. Challenges and Critiques 1. Aid Dependency and Corruption 2. Economic Distortions and Dutch Disease 3. Conditionality and Policy Imposition C. Case Studies and Empirical Evidence 1. The Marshall Plan 2. Aid Effectiveness in Sub-Saharan Africa 3. Chinese Aid in Africa V. The Role of Governance and Institutions A. Political Stability and Governance 1. Strengthening Rule of Law 2. Corruption Mitigation B. Aid Harmonization and Coordination 1. Reducing Donor Fragmentation 2. Alignment with National Strategies C. Ownership and Local Capacity Building 1. Strengthening Local Institutions 2. Empowering Local Communities VI. Foreign Aid and Economic Stability in Fragile States A. Conflict-affected Regions
- 23. 1. Humanitarian Aid vs. Development Aid 2. Post-Conflict Reconstruction B. Fragility and Resilience 1. Building Economic Resilience 2. Conflict Prevention VII. The Role of Multilateral Organizations A. United Nations Agencies 1. UNDP, UNICEF, and WHO 2. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) B. International Financial Institutions 1. World Bank and IMF 2. Structural Adjustment Programs (SAPs) and Critiques VIII. The Future of Foreign Aid A. New Aid Approaches 1. South-South Cooperation 2. Philanthropic Foundations B. Challenges and Critiques 1. Aid Fatigue and Declining Donor Commitment 2. Climate Change and Humanitarian Crises IX. Conclusion In conclusion, foreign aid's impact on economic stability is a complex and multifaceted issue. While foreign aid has the potential to promote economic growth, reduce poverty, and enhance infrastructure and human capital, it is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The effectiveness of foreign aid depends on numerous factors, including governance, local capacity, and the alignment of aid with recipient countries' priorities.
- 24. Challenges such as aid dependency, corruption, and policy imposition must be addressed to maximize aid's positive impact. In fragile states, foreign aid plays a critical role in post-conflict reconstruction and building resilience. The future of foreign aid calls for innovative approaches, increased coordination, and a renewed commitment to sustainable development. By learning from past experiences and adapting aid strategies to changing global challenges, foreign aid can continue to be a vital tool in achieving economic stability and fostering global development. 6- Real Development Transforms People's Lives, Not Just Economic Statistics Introduction The concept of development has evolved significantly over the years. While traditional measures of development often focus on economic indicators such as GDP growth, it is increasingly recognized that real development should go beyond mere economic statistics. True development must transform people's lives, improving their well-being, expanding opportunities, and promoting human dignity. This essay, spanning 3000 words, delves into the multifaceted nature of development, exploring the ways in which it can positively impact individuals and communities, transcending mere economic growth. I. Rethinking Development A. Beyond Economic Growth 1. GDP as a Limited Indicator 2. The Human Development Index (HDI) B. The Multidimensional Nature of Well-Being 1. Health and Longevity 2. Education and Knowledge 3. Income and Livelihood 4. Social Inclusion and Equity C. Sen's Capability Approach 1. Expanding Freedom and Opportunities
- 25. 2. Emphasis on Human Capabilities II. Health as a Measure of Development A. Access to Healthcare 1. Quality and Availability of Health Services 2. Preventive Healthcare B. Reducing Mortality Rates 1. Maternal and Child Mortality 2. Infectious Diseases and Vaccination Programs C. Improving Nutrition 1. Food Security 2. Addressing Malnutrition III. Education and Knowledge A. Universal Access to Education 1. Primary and Secondary Education 2. Higher Education and Vocational Training B. Quality of Education 1. Teachers and Infrastructure 2. Curriculum Relevance C. Lifelong Learning 1. Adult Education 2. Technical and Vocational Training IV. Economic Empowerment and Livelihood A. Employment Opportunities
- 26. 1. Formal vs. Informal Employment 2. Gender Disparities B. Entrepreneurship and Small Businesses 1. Microcredit and Small Enterprise Development 2. Economic Self-Sufficiency C. Income Inequality 1. Progressive Taxation 2. Wealth Redistribution V. Social Inclusion and Equity A. Reducing Discrimination 1. Gender Equality 2. Racial and Ethnic Inclusion 3. LGBTQ+ Rights B. Addressing Inequalities 1. Urban-Rural Disparities 2. Indigenous Communities C. Political Participation 1. Access to Decision-Making Processes 2. Strengthening Civil Society VI. Environmental Sustainability A. Sustainable Resource Management 1. Conservation of Ecosystems 2. Responsible Water and Energy Use B. Climate Change Mitigation
- 27. 1. Renewable Energy Transition 2. Adaptation Strategies C. Biodiversity Protection 1. Conservation Efforts 2. Ecosystem Services VII. Case Studies: Real Development in Action A. Kerala, India 1. Healthcare and Education Achievements 2. Social Inclusion and Equity Initiatives B. Bhutan's Gross National Happiness (GNH) 1. Prioritizing Well-Being over GDP 2. Environmental Sustainability C. Rwanda's Post-Genocide Recovery 1. Reconciliation and Social Inclusion 2. Economic Transformation D. The Nordic Model 1. Comprehensive Social Welfare Systems 2. Gender Equality and Economic Prosperity VIII. The Role of International Development Aid A. Foreign Aid and Assistance 1. Bilateral and Multilateral Aid 2. Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) B. International Organizations
- 28. 1. United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) 2. World Bank and International Monetary Fund (IMF) IX. Challenges and Critiques A. Measuring Development 1. Subjectivity and Cultural Variation 2. Ethical Considerations B. Environmental Trade-offs 1. Balancing Economic Growth and Sustainability 2. Extractive Industries and Resource Exploitation C. Political and Governance Challenges 1. Corruption and Lack of Accountability 2. Political Instability and Conflict D. Economic Disparities 1. Global North-South Divide 2. Inequities within Nations X. The Way Forward A. Multisectoral Approaches 1. Holistic Development Policies 2. Interdisciplinary Collaboration B. Empowering Communities 1. Participatory Development 2. Strengthening Local Institutions C. Fostering Innovation 1. Technological Advancements
- 29. 2. Social Entrepreneurship D. Policy Reforms 1. Progressive Taxation and Wealth Redistribution 2. Strengthening Environmental Regulations E. Advocacy and Global Solidarity 1. Grassroots Movements 2. International Cooperation XI. Conclusion In conclusion, real development transcends economic statistics and delves into the well-being and capabilities of individuals and communities. It encompasses health, education, economic empowerment, social inclusion, and environmental sustainability. Successful case studies demonstrate that real development is achievable through a combination of policy reforms, community empowerment, and global solidarity. While challenges and critiques persist, the path forward lies in adopting multisectoral approaches, fostering innovation, and advocating for policies that prioritize human well-being and environmental stewardship. Real development is not an abstract concept; it is a tangible goal that, when achieved, transforms lives and creates a more equitable and sustainable world for all. 7-Human Development and Economic Sustainability Introduction Human development and economic sustainability are two interconnected and essential aspects of a nation's progress. While economic sustainability focuses on maintaining and improving economic well-being, human development emphasizes enhancing the quality of life for individuals within a society. This essay, spanning 3000 words, delves into the intricate relationship between human development and economic sustainability, exploring how these two dimensions interact, influence one another, and contribute to overall societal progress. I. Understanding Human Development
- 30. A. Definition and Dimensions 1. Amartya Sen's Capability Approach 2. The Human Development Index (HDI) B. Key Components 1. Health and Life Expectancy 2. Education and Knowledge 3. Standard of Living II. Economic Sustainability Defined A. The Three Pillars of Sustainability 1. Economic 2. Environmental 3. Social B. Beyond Economic Growth 1. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) vs. Genuine Progress Indicator (GPI) 2. Inclusive Wealth Index (IWI) III. The Nexus Between Human Development and Economic Sustainability A. Education and Skills Development 1. The Role of Education in Economic Productivity 2. Lifelong Learning and Adaptability B. Health and Well-being 1. Access to Healthcare and Economic Productivity 2. Preventive Healthcare and Reduced Economic Burden C. Poverty Eradication 1. Income Inequality and Social Cohesion
- 31. 2. Inclusive Economic Growth D. Gender Equality 1. Empowering Women and Economic Sustainability 2. The Economic Impact of Gender Discrimination E. Social Inclusion and Cohesion 1. Reducing Social Disparities and Economic Stability 2. The Cost of Social Unrest IV. Case Studies and Success Stories A. The Scandinavian Model 1. High HDI Scores and Economic Prosperity 2. Social Welfare Systems and Inclusive Policies B. Bhutan's Gross National Happiness (GNH) 1. Prioritizing Well-being over GDP 2. Sustainable Development and Cultural Preservation C. Kerala, India's Healthcare Success 1. Universal Healthcare Access and Economic Growth 2. The Health-Education-Economy Nexus V. Challenges and Barriers A. Economic Inequality 1. The Growing Wealth Gap 2. The Impact of Inequality on Human Development B. Environmental Sustainability 1. Economic Growth vs. Environmental Degradation 2. The Role of Natural Capital
- 32. C. Short-Term vs. Long-Term Goals 1. Economic Policies and Political Cycles 2. Balancing Immediate Economic Gains with Long-Term Sustainability VI. Strategies for Advancing Human Development and Economic Sustainability A. Inclusive Economic Growth 1. Employment Generation and Income Distribution 2. Poverty Alleviation Programs B. Sustainable Resource Management 1. Green Technologies and Renewable Energy 2. Circular Economy Principles C. Education and Skills Development 1. Access to Quality Education and Lifelong Learning 2. Vocational Training and Innovation D. Universal Healthcare Access 1. Strengthening Healthcare Systems 2. Preventive Care and Public Health Initiatives E. Gender Equality and Women's Empowerment 1. Gender-Inclusive Policies and Laws 2. Promoting Women in the Workforce VII. The Role of Technology and Innovation A. Technological Advancements 1. Digital Inclusion and Access to Information 2. Technological Solutions to Environmental Challenges
- 33. B. Innovation Ecosystems 1. Entrepreneurship and Start-ups 2. Research and Development Investments VIII. The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) A. The Global Agenda for Sustainable Development 1. Linking Human Development and Economic Sustainability 2. The 2030 Agenda for a Better World IX. Conclusion In conclusion, human development and economic sustainability are not isolated concepts but are deeply interconnected and mutually reinforcing. The enhancement of human capabilities, including education, health, gender equality, and social inclusion, positively influences economic sustainability, driving productivity and reducing social disparities. Conversely, economic sustainability, when approached holistically to consider environmental and social dimensions, contributes to improved human development by providing resources for social services, employment opportunities, and poverty reduction. The case studies of nations like the Scandinavian countries, Bhutan, and Kerala demonstrate the potential for achieving high levels of both human development and economic sustainability through inclusive policies and holistic approaches. Nevertheless, challenges such as economic inequality, environmental degradation, and short-term economic interests pose obstacles to achieving a harmonious balance between the two dimensions. Strategies for advancing human development and economic sustainability include inclusive economic growth, sustainable resource management, education and skills development, universal healthcare access, gender equality, and technological innovation. The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals serve as a global framework for integrating these strategies and guiding nations toward a future where human development and economic sustainability coexist, creating a better and more equitable world for all.
- 34. 8-Globalization of Markets Introduction The concept of globalization of markets has been a central theme in the world of business and economics for several decades. It represents the growing interconnectedness of economies, industries, and consumers on a global scale. As technology advances and trade barriers diminish, companies are increasingly operating in a global marketplace. This essay, spanning 3000 words, will delve into the concept of the globalization of markets, examining its historical context, driving forces, challenges, and the impact it has on businesses, consumers, and economies around the world. I. Historical Context of Globalization of Markets A. Early Trade Routes 1. Silk Road 2. Spice Trade B. Colonialism and Mercantilism 1. European Expansion 2. Exploration and Trade Dominance C. Post-World War II Globalization 1. Bretton Woods Institutions 2. Formation of the United Nations II. Forces Driving the Globalization of Markets A. Technological Advances 1. The Internet and E-commerce 2. Telecommunications and Connectivity B. Liberalization of Trade 1. GATT/WTO Agreements
- 35. 2. Regional Trade Blocs C. Transportation and Logistics 1. Containerization 2. Global Supply Chains D. Multinational Corporations 1. Market Expansion Strategies 2. Offshoring and Outsourcing E. Financial Integration 1. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) 2. Global Capital Markets III. Characteristics of Global Markets A. Homogenization of Consumer Preferences 1. Global Brands 2. Standardization vs. Adaptation B. Increased Competition 1. Entry of New Players 2. Market Saturation C. Market Expansion Opportunities 1. Emerging Markets 2. Niche Markets IV. Challenges and Critiques of Globalization of Markets A. Income Inequality 1. Winners and Losers 2. Wage Compression
- 36. B. Cultural Homogenization 1. Loss of Cultural Diversity 2. Westernization of Values C. Environmental Concerns 1. Resource Depletion 2. Pollution and Climate Change D. Dependency on Global Supply Chains 1. Vulnerability to Disruptions 2. Ethical and Human Rights Issues V. Globalization and Business Strategies A. Market Entry Strategies 1. Exporting 2. Joint Ventures and Alliances 3. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) B. Product and Service Customization 1. Adaptation to Local Markets 2. Global Product Strategies C. Global Marketing and Branding 1. Global vs. Local Campaigns 2. Cultural Sensitivity D. Supply Chain Management 1. Lean vs. Resilient Supply Chains 2. Risk Mitigation VI. Globalization and Consumer Behavior
- 37. A. Access to Global Products 1. Increased Consumer Choice 2. Consumer Expectations B. Cultural Influence on Consumption 1. Global Pop Culture 2. Local vs. Global Preferences VII. Government Policies and Globalization A. Trade Agreements 1. Regional Trade Blocs (e.g., NAFTA, EU) 2. Bilateral and Multilateral Agreements B. Protectionism vs. Liberalization 1. Tariffs and Trade Barriers 2. Free Trade Agreements C. Regulatory Frameworks 1. Consumer Protection 2. Intellectual Property Rights VIII. The Future of Globalization of Markets A. Emerging Technologies 1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) 2. Blockchain 3. 5G and IoT B. Geopolitical Shifts 1. Rise of Asia 2. New Economic Powers
- 38. C. Sustainability and Ethical Concerns 1. ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) Standards 2. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) D. Global Crises and Shocks 1. Pandemics 2. Climate Catastrophes IX. Conclusion In conclusion, the globalization of markets is a multifaceted phenomenon that has reshaped economies, industries, and consumer behaviors worldwide. It has been driven by technological advances, trade liberalization, the rise of multinational corporations, and financial integration. While it has brought about numerous benefits, such as increased consumer choice and market opportunities, it has also presented challenges, including income inequality, cultural homogenization, and environmental concerns. The future of globalization will be shaped by emerging technologies, geopolitical shifts, sustainability imperatives, and responses to global crises. Governments, businesses, and consumers must navigate this evolving landscape with an awareness of both the opportunities and challenges it presents. Effective global market strategies should be underpinned by adaptability, ethical considerations, and a commitment to sustainable and responsible globalization.