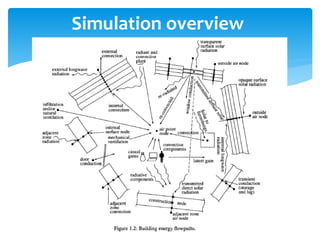
This document provides an overview of thermal energy systems analysis. It discusses key concepts like conservation laws and balances that engineers must understand to analyze or design thermal energy systems. Examples of thermal energy systems include heating/cooling systems and power/refrigeration cycles. The document also outlines software tools commonly used for analysis, like REFPROP and Engineering Equation Solver. It defines types of energy and the laws of energy, and notes that simulation allows testing design modifications to achieve more energy-efficient results.