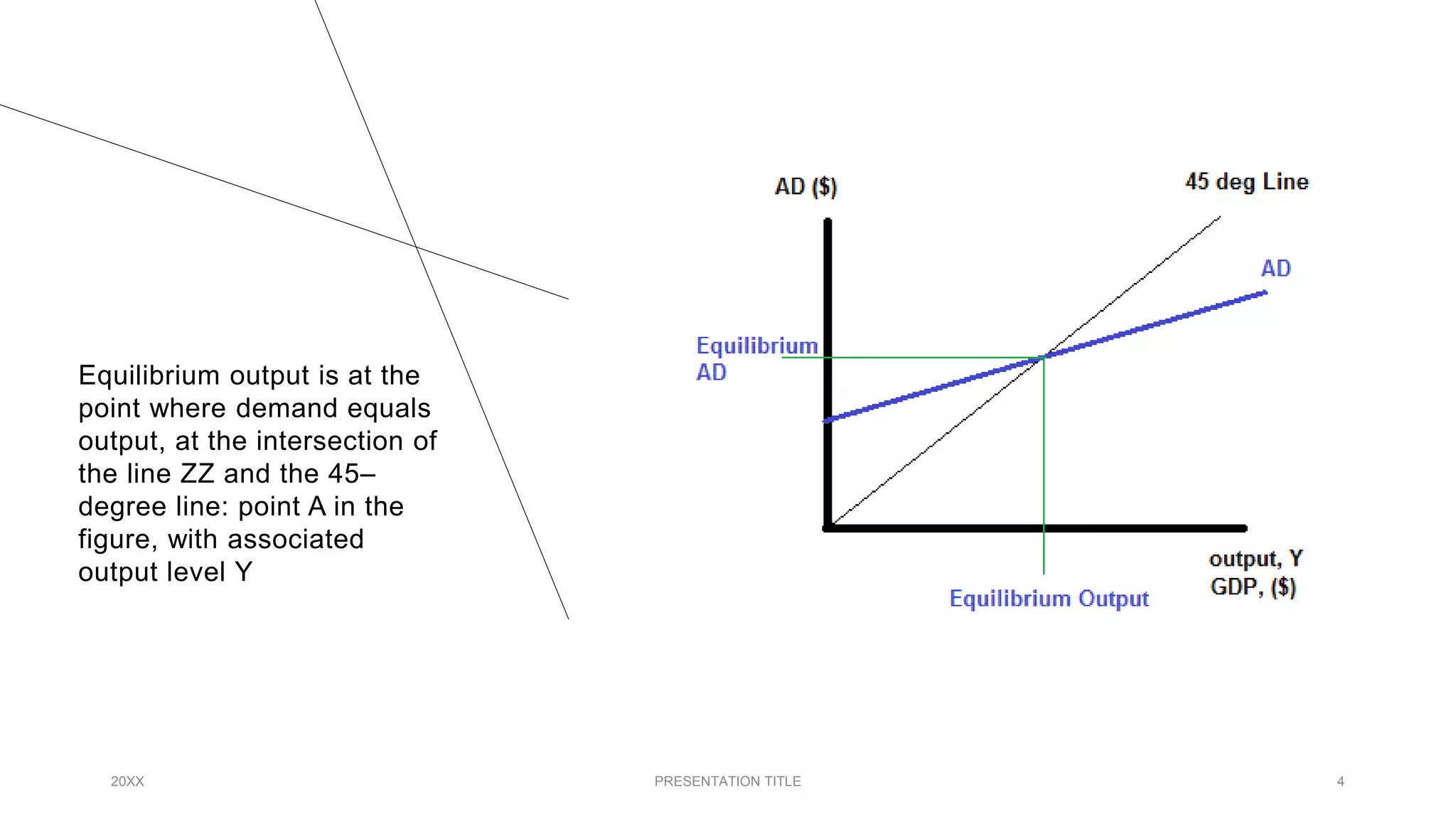
The document discusses equilibrium output and trade balance in the European Union over the last 5 years. It provides data showing that from 2017 to 2021, the EU experienced moderate average annual GDP growth of 1.5%, with a sharp decline in output in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Regarding trade balance, the EU maintained an average annual surplus of around €200 billion over this period mainly from strong exports in sectors like machinery and transport equipment, though this was partly offset by a deficit in energy trade. The pandemic also disrupted global trade and exports/imports. Overall, the EU's equilibrium output and positive trade balance were impacted by various external factors in recent years but have remained relatively stable.