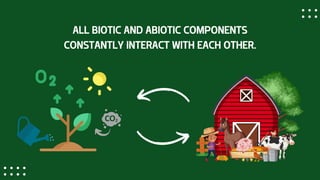
The document discusses the importance of environmental science, highlighting the components of the environment and human impacts such as pollution and resource depletion. It outlines practical actions for individuals to protect the environment, including reducing waste, conserving water, promoting renewable energy, and supporting sustainable practices. Additionally, it emphasizes the role of education and community outreach in fostering awareness and action towards environmental sustainability.