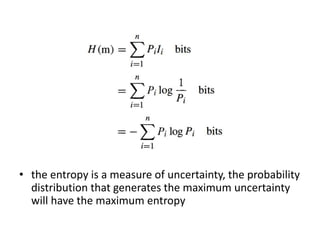
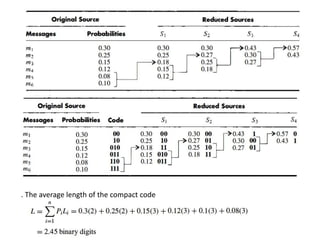
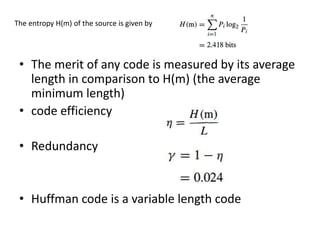
The document discusses the relationship between probability, information content, and entropy, stating that the amount of information in a message is related to its unexpectedness. It explains that a memoryless source has independent messages and defines entropy as a measure of uncertainty, with maximum entropy corresponding to maximum uncertainty. Additionally, it covers source encoding, emphasizing the efficiency and length of codes, particularly the Huffman code.