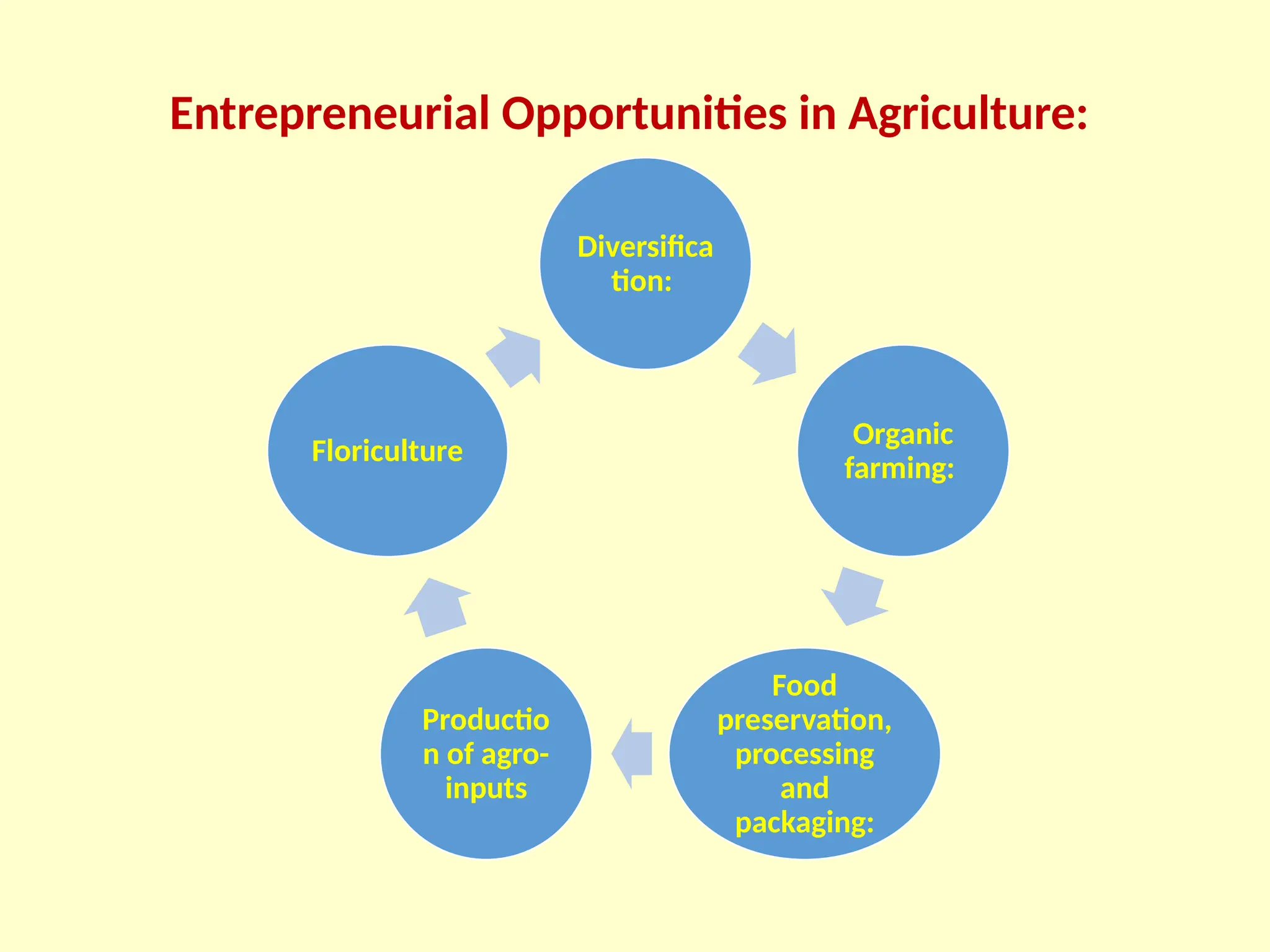
The document discusses entrepreneurship, defining it as the process of creating something new while taking risks for potential rewards. It highlights the role of entrepreneurs in economic development, categorizes different types of entrepreneurs, and outlines various competencies and government initiatives aimed at fostering entrepreneurship. Additionally, it addresses the challenges and opportunities in the agricultural sector for aspiring entrepreneurs.








![ 1961: David McClelland—A person with a
high need for achievement [N-Ach] who is
energetic and a moderate risk taker.
1964: Peter Drucker—One who searches for
change, responds to it and exploits
opportunities. Innovation is a specific tool
of an entrepreneur hence an effective
entrepreneur converts a source into a
resource.
2013: Ronald May—Someone who
commercializes his or her innovation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/entrepreneurshipdevelopment-240930191941-a7c0e3f9/75/Entrepreneurship-development-for-self-emloyment-pptx-9-2048.jpg)