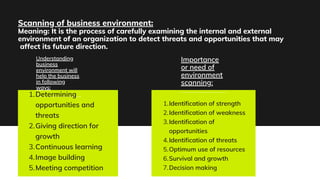
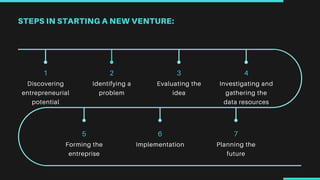
The document discusses the formation and identification of business opportunities within small-scale industries, emphasizing the importance of understanding both internal and external environments through methods like SWOT analysis. It outlines the steps necessary for starting a new venture, including project selection, feasibility studies, obtaining clearances, and arranging for funding and infrastructure. Additionally, it highlights the significance of market studies to validate business ideas and the associated financial, technical, and social feasibilities required for successful implementation.