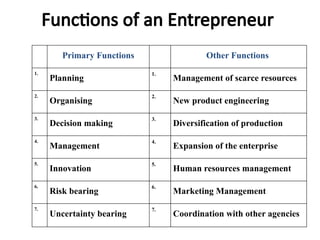
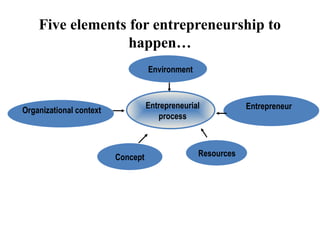
An entrepreneur is an individual who identifies opportunities, innovates, and assumes risks to achieve economic benefits and drive social change. They come in various types, including innovative, imitative, and drone entrepreneurs, and their functions include planning, organizing, decision-making, and risk management. Successful entrepreneurs like Dhirubhai Ambani exemplify the traits and skills necessary for business success, including resilience and adaptability in various industries.