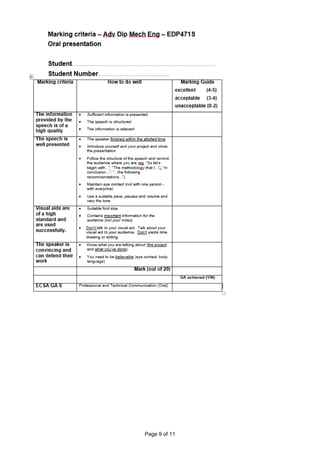
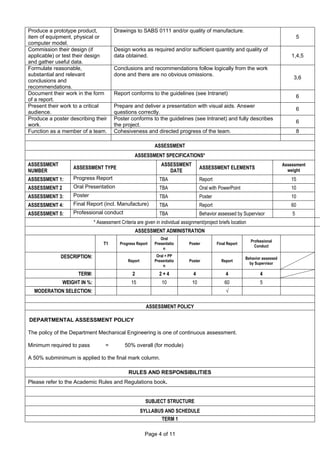
The document outlines the engineering design project course for an advanced diploma in mechanical engineering, including its objectives, qualification details, and assessment methods. Key components of the course include developing problem-solving skills, conducting research, and completing a mechanical engineering design project over one year. It emphasizes continuous assessment with a minimum passing mark of 50% and provides details on support available for students facing academic, social, or financial difficulties.
![Page 5 of 11
[1 Feb – 31 March]
WEEKS REFERENCE TOPIC DATE
1 Lecture (H Fawkes) Introduction to Engineering Design Project 4 TBA
1 Lecture (Librarian) Information Literacy TBA
1 Lecture (H Fawkes) Referencing and Plagiarism TBA
1 Lecture (H Fawkes) The Design Process TBA
1 Lecture (Guest) Engineering Professionalism TBA
TERMS 2 - 4
[13 April-15 Dec]
25 Ongoing supervision TBA
WORK INTEGRATED LEARNING
PROBLEM-BASED LEARNING No – Self-directed learning
PROJECT-BASED LEARNING Yes
WORKPLACE LEARNING It is a fourth year subject which does not require WPBL
GRADUATE ATTRIBUTES
1. Problem Solving
2. Application of Scientific and Engineering Knowledge
3. Engineering Design
4. Investigation
5. Engineering Methods, skills, Tools, including Information Technology
6. Professional and Technical Communication
7. Impact of Engineering Activity
8. Individual and Teamwork
9. Independent Learning
10. Engineering Professionalism
11. Engineering Management
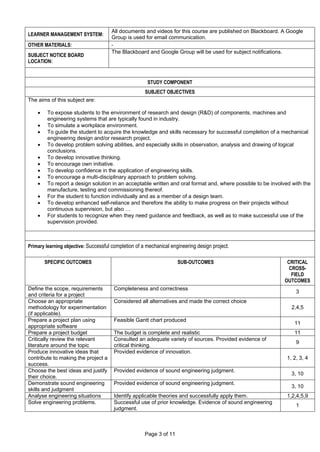
STUDENT SUPPORT
Academically, Students with difficulties are supported through Supervision.
Social difficulties: Students are encouraged to attend counselling sessions.
Financial difficulties: Students are encouraged to apply for financial assistance from the Financial aid unit.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engineeringdesignproject41-250205041140-2fe97426/85/Engineering-Project-Design-Project-4-1-pdf-5-320.jpg)